Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1100–1123) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In 2015, the 20-item Tophus Impact Questionnaire (TIQ-20) was developed as a tophus-specific patient reported outcome measure (Aati et al., 2015). Initial analysis of the TIQ-20 showed good psychometric properties, with high internal, face and construct validity, reproducibility, and feasibility. To date, responsiveness over time has not been reported. The aim of this study was to determine whether the TIQ-20 changes during urate-lowering therapy.
Methods: We analysed data from a two-year randomized controlled trial of allopurinol dose escalation (Stamp et al, 2017). Briefly, participants with gout on allopurinol with serum urate ≥0.36mmol/L (6mg/dL) were randomised to immediate allopurinol dose escalation to achieve a serum urate of < 0.36mmol/L, or a control group with no change in allopurinol dose. After one year, participants in the control group also had allopurinol dose escalation to achieve a serum urate of < 6mg/dL.
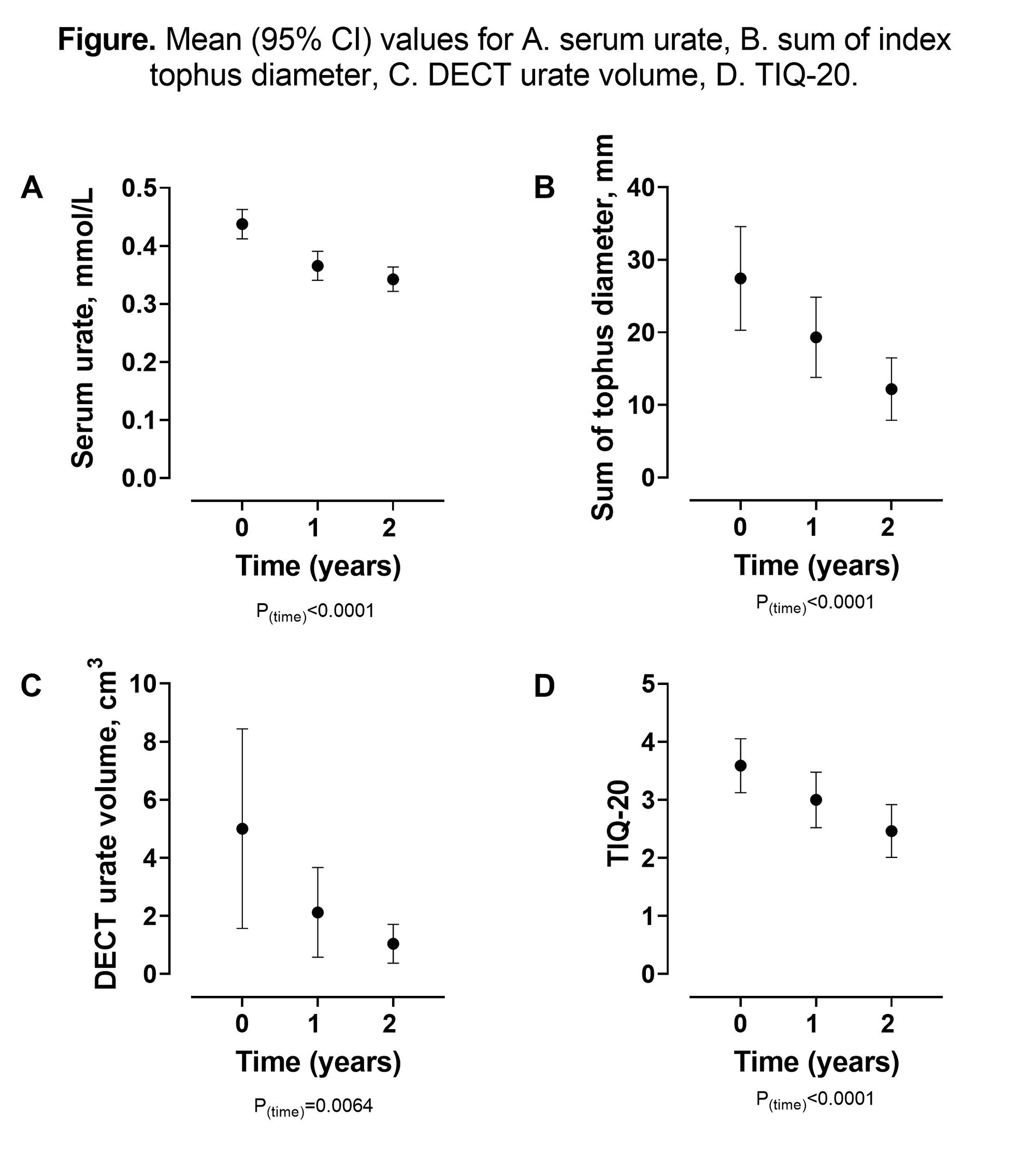
For participants with tophaceous gout, the longest diameter of up to three index tophi was measured using Vernier calipers and the TIQ-20 was recorded at study visits. Participants at the one site were invited into an imaging sub-study with dual energy CT (DECT) of the feet at baseline, Year 1, and Year 2.
Participants were included in this analysis if they had tophaceous gout and TIQ-20 scores available at baseline, Year 1, and Year 2 (n=58, 39 with DECT data). Data from these visits were analysed using mixed model analysis. Cohen’s d was calculated as a standardized effect size for assessing the difference between the baseline and Year 2 tophus mean values. Rasch modelled TIQ-20 scores were used throughout the analysis.
Results: The mean (SD) serum urate reduced over the two-year period from 0.44 (0.10) to 0.34 (0.08) mmol/L, P< 0.001 (Figure). Improvements were observed in all tophus measures including the TIQ-20 over the two-year period, with no difference between the two treatment groups (P >0.34 for treatment allocation). For the entire group, the mean (SD) sum of the index tophi diameter reduced from 27.4 (27.2) to 12.2 (16.4) mm, P< 0.0001, and the DECT urate volume reduced from 5.01 (9.85) to 1.04 (2.03) cm3, P=0.006 (Figure). The TIQ-20 scores also reduced over two years from 3.59 (1.77) to 2.46 (1.73), P< 0.0001 (Figure), and the mean (95% CI) TIQ-20 change over the two years was -1.13 (-1.54, -0.71). Cohen’s d for the sum of the index tophi diameter was 0.68, for DECT urate volume was 0.5, and for the TIQ-20 was 0.71.
Conclusion: For people with tophaceous gout treated with allopurinol using a treat to target serum urate approach, improvements in TIQ-20 occur, as well as improvements in physical and imaging tophus measures. These findings demonstrate that the TIQ-20 is a responsive instrument of tophus burden.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cao C, Gamble G, Horne A, Aati O, Doyle A, Drake J, Stamp L, Dalbeth N. The Tophus Impact Questionnaire (TIQ-20): Responsiveness to Change During Urate-Lowering Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-tophus-impact-questionnaire-tiq-20-responsiveness-to-change-during-urate-lowering-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-tophus-impact-questionnaire-tiq-20-responsiveness-to-change-during-urate-lowering-therapy/