Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Muscle enzymes are a core set measure (CSM) in clinical trials. The 2016 ACR/EULAR myositis response criteria and the IMACS definition of improvement recommend using the most abnormal muscle enzyme at trial entry among the following five, creatine kinase (CK), aldolase, AST, ALT, and LDH. However, there is limited data on their relationship when assessed at the same time and which muscle enzyme should be followed as the CSM in adult myositis clinical trials. We aimed to evaluate the relationship of the aforementioned muscle enzymes in the Rituximab in Myositis (RIM) trial.
Methods: All five muscle enzymes and their summary statistics were analyzed at baseline and longitudinally in 75 adult polymyositis (PM) and 72 adult dermatomyositis (DM) subjects enrolled in the RIM Trial. Their respective values were incorporated into the published Total Improvement Score (TIS) of the 2016 ACR/EULAR Myositis Response Criteria at weeks 24 and 44. All muscle enzymes were reported as the times of upper limit of normal (xULN).
Results: At baseline, the CK was the most abnormal enzyme in adult PM and DM (81.3%, 55.6 %) followed by LDH (10.7%, 25%), aldolase (5.3%, 6.9%), AST (0%, 8.3 %) and ALT (2.7%, 4.2%). The CK was elevated in 86.7% of PM and 63.9 % of DM patients respectively, followed by LDH (89.3%, 62.5%), aldolase (68%, 51.4%), AST (65.3%, 45.8%) and ALT (65.3%, 47.2%). Similar results were seen across gender, race, age groups as well as different autoantibody subsets . Even when CK was not the most abnormal muscle enzyme in PM and DM (18.7%, 44.4%), the frequency of abnormal enzymes was: CK (5.3% PM, 9.7% DM), Aldolase (6.7% PM, 11.11%DM), LDH (12%PM, 16.7%DM), AST (4%PM, 6.9%), ALT (6.7%PM, 9.7%) and the CK levels were only marginally lower than the levels of the most abnormal enzyme. The median difference between the CK and most abnormal enzyme was only 0.03% at 24 weeks. Thus, when the CK was substituted as the most abnormal muscle enzyme in calculating the TIS, most (85.7%) adult myositis subjects (88% PM, 83.3% DM) had no change in the TIS at week 24. In the approximately 15% of subjects demonstrating a change in the TIS score, the mean (SD) change was quite small at 4.05 (1.8) for all subjects [3.89 (1.24) for PM and 4.17 (2.12) for DM (Figure 1)]. Only 1 adult PM patient had a change in the TIS score that translated to a shift from a ‘minimal’ clinical response to ‘no’ response. Similar results were observed at week 44.
The ratios between the different enzymes (expressed as xULN) across all the time points throughout the RIM Trial were relatively well preserved with median (IQR) ratios of CK with aldolase, LDH, AST, ALT of 0.41(0.12), 0.57 (0.35), 0.28 (0.15) and 0.32 (0.14) respectively (Figure 2).
Conclusion: The serum CK is most frequently elevated in adult PM and DM, followed by the LDH especially in DM, and can be used as the single muscle enzyme for published myositis response criteria without significant change in the outcome analysis. This is particularly important when other muscle enzyme levels may not be feasible for the determination of outcome given the adverse effect of many drugs. Muscle enzyme ratios are well-preserved over time, such that AST and ALT elevations outside of these ratios should prompt evaluation for other causes.
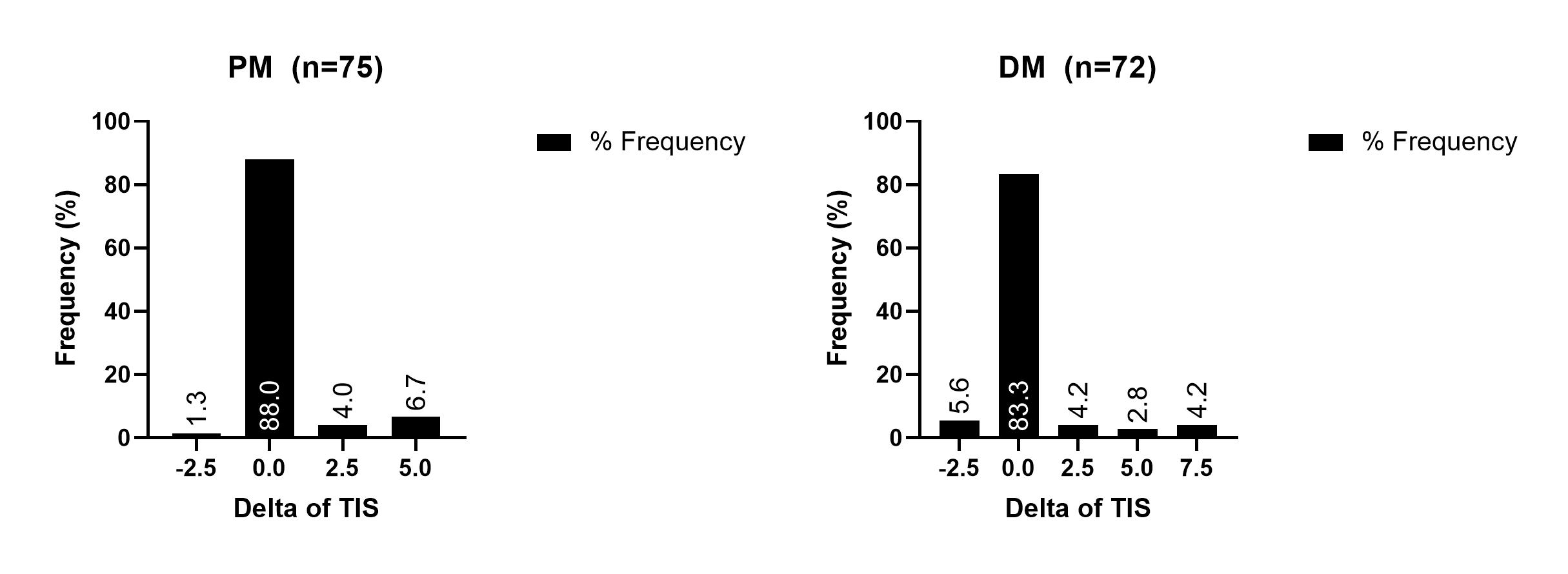 Figure 1: TIS change when CK is substituted for the most abnormal muscle enzyme in PM and DM subjects
Figure 1: TIS change when CK is substituted for the most abnormal muscle enzyme in PM and DM subjects
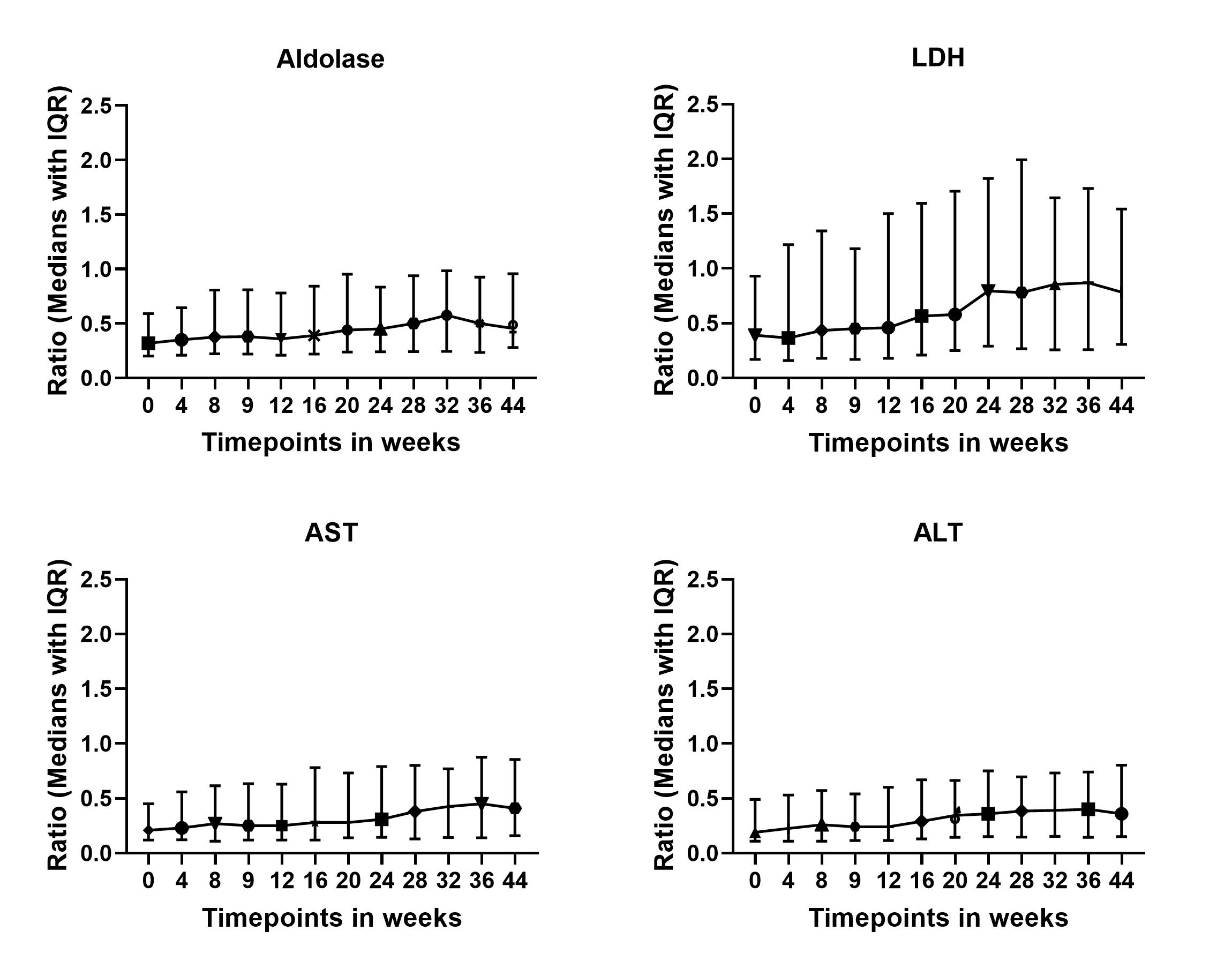 Figure 2: Ratios of the different muscle enzymes related to serum CK (all expressed as xULN)
Figure 2: Ratios of the different muscle enzymes related to serum CK (all expressed as xULN)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aggarwal R, Chandra T. The Relationship of Different Muscle Enzymes in Adult Myositis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-relationship-of-different-muscle-enzymes-in-adult-myositis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-relationship-of-different-muscle-enzymes-in-adult-myositis-patients/
