Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: The European League Against Rheumatism recommends tight control of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, tight control of RA may depend on several factors, including patient characteristics and disease activity, social and medico-economic parameters.
The purpose of our study is to determine which factors influence the time-to-introduction of first biologic agent in RA patients in the French ESPOIR (study and following of undifferentiated early stage arthritis) cohort.
Methods: Among the 813 ESPOIR patients, 641 RA patients satisfying the ACR/EULAR 2010 RA diagnostic criteria were followed over 5 years. Among them, we excluded patients participating in therapeutic trials, such that 619 RA patients were analysed.
The outcome variable was the delay between the first stable symptoms and the introduction of the first biologic agent. The potential explanatory variables tested were patients and disease characteristics as well as health care system characteristics (medical center of follow-up, time to first rheumatologist consultation, population of city of residence).
Survival rates were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. Cox proportional hazards models were used to determine independent predictors of introduction of the first biologic agent.
Results: Among the 619 RA patients (mean age 50.3 years, 50.6% Rheumatoid Factor positive and 43.3% ACPA positive, 27.1% with erosion on baseline X-rays), 121 (19.5%) had received a biologic agent at 5 years (TNF-blockers for most of them, rituximab and abatacept for 14 of them).
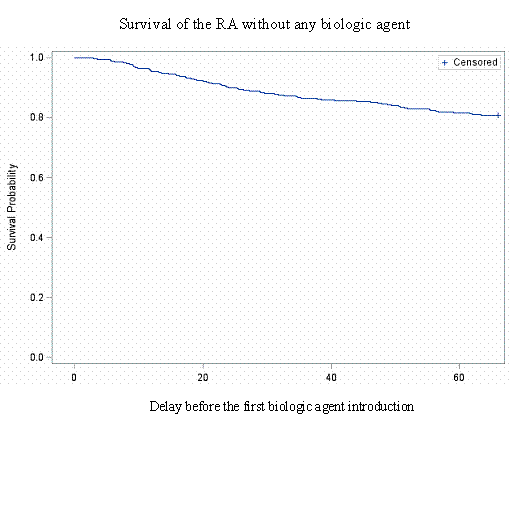
The mean time between the first stable symptoms to the introduction of the first biologic agent was 27.9 months (± 17.2), the median was 23.7 months (Q1 13.2, Q3 43.8).
The results of the Cox model are shown in figure 1.
The time-to-introduction of first biologic was significantly decreased by the presence of ACPA (Risk ratio [RR]: 3.4; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.1-5.5), younger patient age (RR: 0.97; CI 0.95: 0.95-0.99) and by the use of a DMARD during the first year of evolution of the disease (RR: 2.2, CI 0.95: 1.4- 4.4). There was no protective effect of corticosteroids (RR: 2.5, CI 0.95: 1.5-4.1). The medical center of follow up was related to the time-to-introduction of first biologic (RR: 0.4, CI 0.95: 0.2-06). However, no influence of other socio-economics parameters such as professional activity, employment status, population of city of residence, or time to first rheumatologist consult was noted.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that there was no peak period in the distribution of a biologic agent’s introduction in the first five years of follow-up of the ESPOIR cohort. However, the medical center of follow-up shown to have a large impact on the time-to-introduction of the first biologic agent. By contrast, the time to first rheumatologist consult or social parameters do not have any influence on the first biologic agent’s start.
Disclosure:
S. Emilie,
None;
C. Gaujoux-Viala,
None;
B. Granger,
None;
A. C. Rat,
None;
B. Combe,
None;
B. Fautrel,
None.
« Back to 2012 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-progression-of-the-rate-of-biologic-initiation-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-is-constant-over-the-first-5-years-in-the-espoir-cohort/