Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is associated with high morbidity and mortality. Current standard tools to monitor LN are suboptimal compared to the invasive renal biopsy. The Renal Activity Index In Lupus (RAIL) considers the urine concentrations of 6 biomarkers (neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, ceruloplasmin, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, adiponectin, hemopexin, kidney injury molecule-1) and has been shown to reflect histologic activity with 92% accuracy. Biomarkers part of his score have also demonstrated changes that predicted response to LN therapy at least 3 months earlier. We aimed to study the changes in the RAIL score in relation to induction treatment in LN.
Methods: Urine samples were collected from active LN patients prior to induction treatment for LN and serially afterwards, coinciding with clinical visits. Luminex Bead Multiplex Assay was used for the analyses of urine biomarkers included in the RAIL. RAIL scores were calculated per the defined algorithm for each urine sample1. Serial data collected between 0 and 6 months post LN diagnosis included LN histologic class as per the International Society of Nephrology (ISN)/Renal Pathology Society (RPS), renal SLE disease activity index (rSLEDAI) score, and type of therapy.
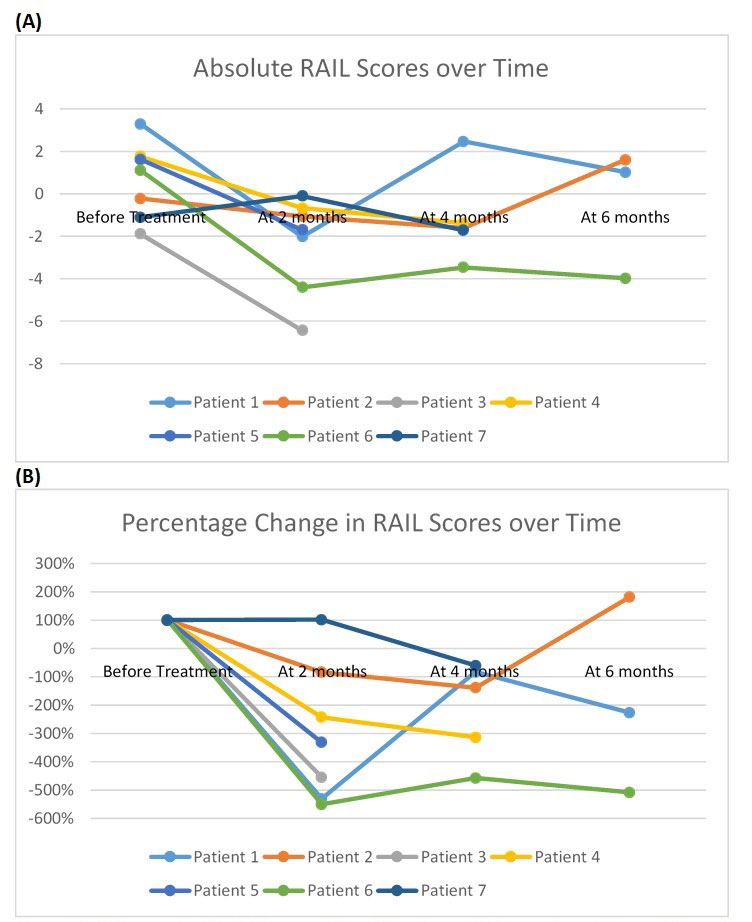
Results: At the time of the analysis, data from 6 active LN patients were collected longitudinally. Patients were all females and all had class IV LN per the ISN/RPS. All patients were started on intravenous (IV) methylprednisolone and cyclophosphamide (CYC) therapy. All but one patient completed 6 doses of monthly CYC before switching to oral mycophenolate mofetil therapy. The RAIL scores for the 6 patients ranged between -1.8 and 3.3. All patients had reductions in their RAIL score at 4 months period (mean absolute decline of 4.3 points; Figure 1A, mean % decline of 211%; Figure 1B). Among 3 with longer follow-up information, all but 2 patients maintained a decline of RAIL scores below the baseline. Patient 1 is known to have medication non-adherence. At 4 months Patient 1 had a prominent rise in RAIL score after which repeat renal biopsy showed persistently high activity of LN leading to commencement of Rituximab therapy. Patient 2 had only 3 monthly doses of CYC. All rSLEDAI scores decreased between baseline and the 6 months interval, except for Patient 2.
Conclusion: RAIL scores show overall improvement from baseline with LN induction therapy. Lack of improvement was associated with flare of disease. Additional data points and a larger study sample are required to study the ability of the RAIL score to reflect clinical improvement of LN. As with other biomarkers, biologic variability creates a variable distribution across patients, therefore it is important to analyze the relative change in the score over time.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aljaberi N, Ma Q, Hennard T, Mathur A, Brunner H. The Performance of a Renal Activity Index in Lupus Nephritis in Induction Therapy [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-performance-of-a-renal-activity-index-in-lupus-nephritis-in-induction-therapy/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-performance-of-a-renal-activity-index-in-lupus-nephritis-in-induction-therapy/