Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
In the last years the role played by the mtDNA haplogroups in the pathogenesis of OA attracted much attention. The aim of this study is to perform a meta-analysis to investigate the association between mtDNA haplogroups and the risk of radiographic OA progression
Methods:
For this work we collected previously published and personal data involving the study of the mtDNA haplogroups on the radiographic progression of OA in terms of KL grade. Meta-analysis was performed using R 2.15.0 software with the package meta added. Combined effect was estimated using a random-effects model using hazard ratios (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) as the outcome variable.
Results:
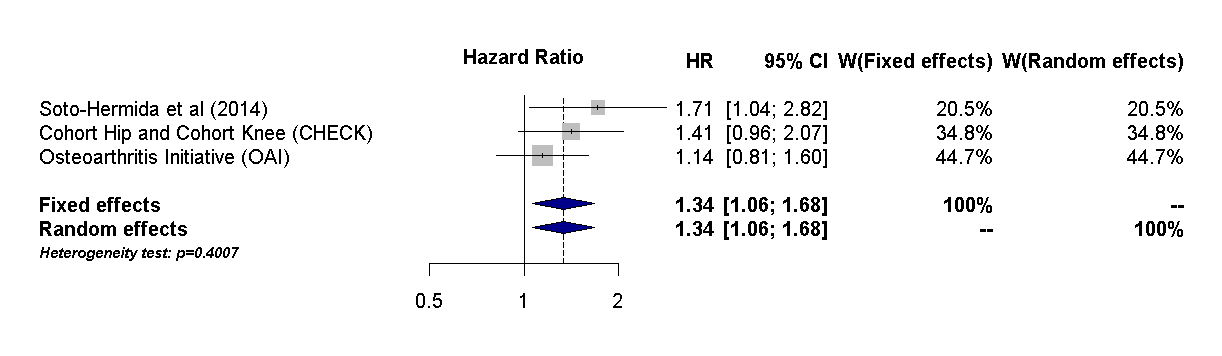
A total of 3 studies, involving 1603 OA patients (progressors and non-progressors) were involved. All the studies were based on the analysis of the mtDNA clusters TJ and the risk of radiographic progression. A significant association with a lower risk of radiographic OA progression was found for the mtDNA cluster TJ when compared with both HV (HR=1,3063; 95% CI=1,0673-1,5989; p-value=0.0096) and KU (HR=1,3359; 95% CI=1,065-1,6757; p-value=0.00123) considering the three cohorts combined (Figures 1 and 2)
Conclusion:
The current meta-analysis suggest that the mtDNA cluster TJ correlates with a lower risk of radiographic OA progression in terms of KL grade. The assignment of the polymorphims characteristic of the mtDNA cluster TJ could be potential complementary genetic biomarkers to predict the risk of OA progression.
Figure 1. Forest plot showing the comparison between the mtDNA cluster HV and TJ on the risk of radiographic OA progression
Figure 2. Forest plot showing the comparison between the mtDNA cluster KU and TJ on the risk of radiographic OA progression
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Soto-Hermida A, Rego-Pérez I, Fernandez-Tajes J, Fernandez Moreno M, Vazquez Mosquera ME, Cortés-Pereira E, Relaño-Fernandez S, Pertega S, Oreiro N, Fernandez-Lopez C, Blanco FJ. The Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Haplogroups Influence the Risk of Radiographic OA Progression. a Meta-Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-mitochondrial-dna-mtdna-haplogroups-influence-the-risk-of-radiographic-oa-progression-a-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-mitochondrial-dna-mtdna-haplogroups-influence-the-risk-of-radiographic-oa-progression-a-meta-analysis/