Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2257–2325) SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The Lupus Foundation of America Rapid Evaluation of Activity in Lupus (LFA-REAL) clinican-reported outcome (ClinRO) correlates well with other disease activity indices such us the SLEDAI-2K and the PGA; however, its predictive value remains to be evaluated. The aim of this study was to evaluate the predictive value of the LFA-REAL and damage accrual in SLE patients.
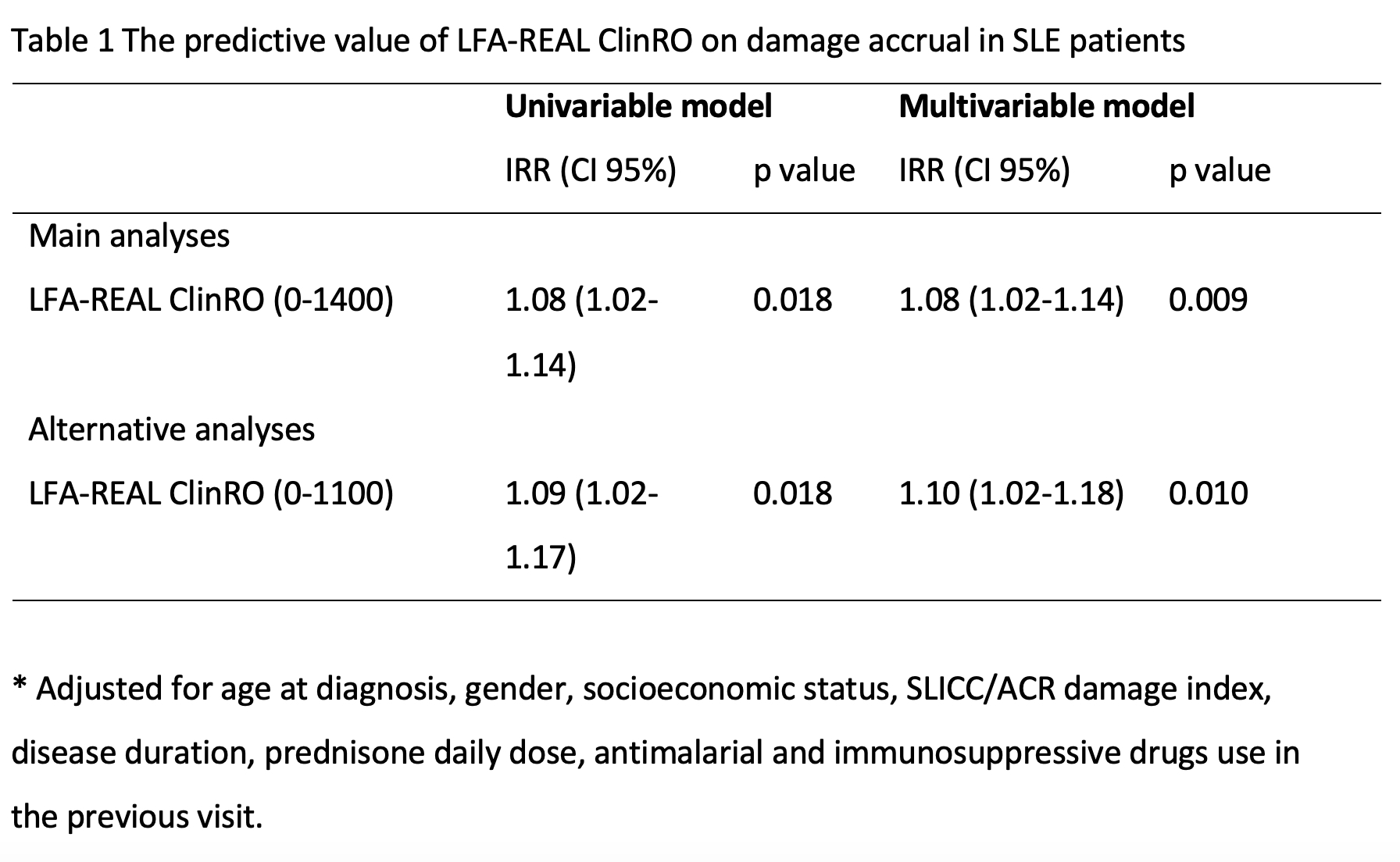
Methods: We evaluated SLEs patients from the Almenara Lupus Cohort, Lima, Peru. The LFA-REAL ClinRO includes nine domains: mucocutaneous, musculoskeletal, cardiorespiratory, neuropsychiatric, renal, hematological, constitutional, vasculitis and other. Mucocutaneous includes one global scale and three subdomains (rash, alopecia and mucosal ulcers), and musculoskeletal includes one global scale and two subdomains (arthralgia/arthritis and myalgia/myositis). For each manifestation, a Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) from 0 to 100 mm is used, with anchors separating mild, moderate and severe disease. Additionally, two possible summary results can be reported. The first one includes only individual manifestations and does not include the global measurement of mucocutaneous and musculoskeletal involvement; it ranges from 0 to 1400 (the sum of 14 VAS). The alternative option is to include only the global domains and not the individual manifestations; it ranges from 0 to 1100 (the sum of 11 VAS). Damage was assessed with the SLICC/ACR damage index (SDI). Generalized estimating equations were performed, using as the outcome any increase in the SDI and the LFA-REAL ClinRO in the previous visit; multivariable models were adjusted for possible confounders measured at the same visit as the self-efficacy instrument. Incidence Rate Ratio (IRR) was reported per 10 units increase in the LFA-REAL ClinRO. The main model was done using the first global LFA-REAL ClinRO; the alternative model was done using the alternative method to calculate the LFA-REAL ClinRO.
Results: A total of 456 patients and 1536 visits were included. The mean LFA-REAL ClinRO (0-1400) was 18.2 (SD 30.7); the mean alternative LFA-REAL ClinRO (0-1100) was 16.9 (SD 27.4) and the mean SLEDAI-2K was 2.5 (4.2). During the follow-up visits, 63 (13.8%) patients accrued damage once and four (0.9%) accrued damage twice. In the univariable and multivariable models, both LFA-REAL ClinRO predicted damage accrual (Table 1).
Conclusion: The LFA-REAL ClinRO is predictive of damage accrual, even after adjusting for possible confounders. Larger studies are needed to determine the relevance of this index for SLE patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ugarte-Gil M, Gamboa-Cárdenas R, Pimentel-Quiroz V, Reategui-Sokolova C, Elera-Fitzcarrald C, Noriega E, Pastor-Asurza C, Rodriguez-Bellido Z, Perich-Campos R, Alarcón G. The LFA-REAL Clinician Reported Outcome Predicts Damage in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Data from a Prevalent Latin American Lupus Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-lfa-real-clinician-reported-outcome-predicts-damage-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-data-from-a-prevalent-latin-american-lupus-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-lfa-real-clinician-reported-outcome-predicts-damage-in-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle-data-from-a-prevalent-latin-american-lupus-cohort/