Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: This study aimed to analyze the immune cell profiles, especially B cells and B-cell receptor (BCR) of systematic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients with or without Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, and to identify the differences between the two groups.
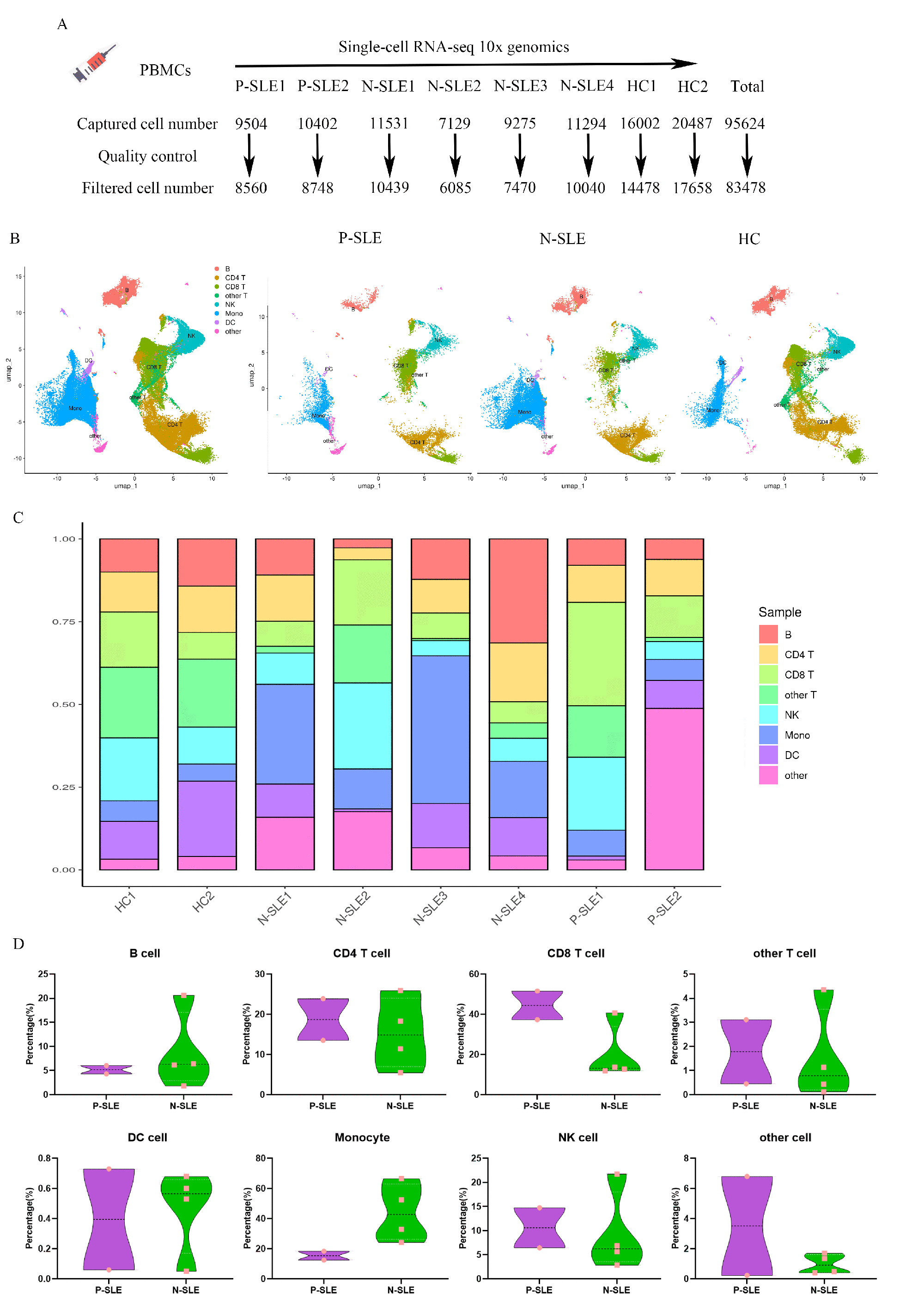
Methods: We included 2 cases of SLE patients with EBV infection (P-SLE), 4 cases of SLE patients without EBV infection (N-SLE), and 2 cases of healthy controls (HC). Using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) to interrogate the heterogeneity of cell populations by combining the transcriptomic profile and BCR repertoire.
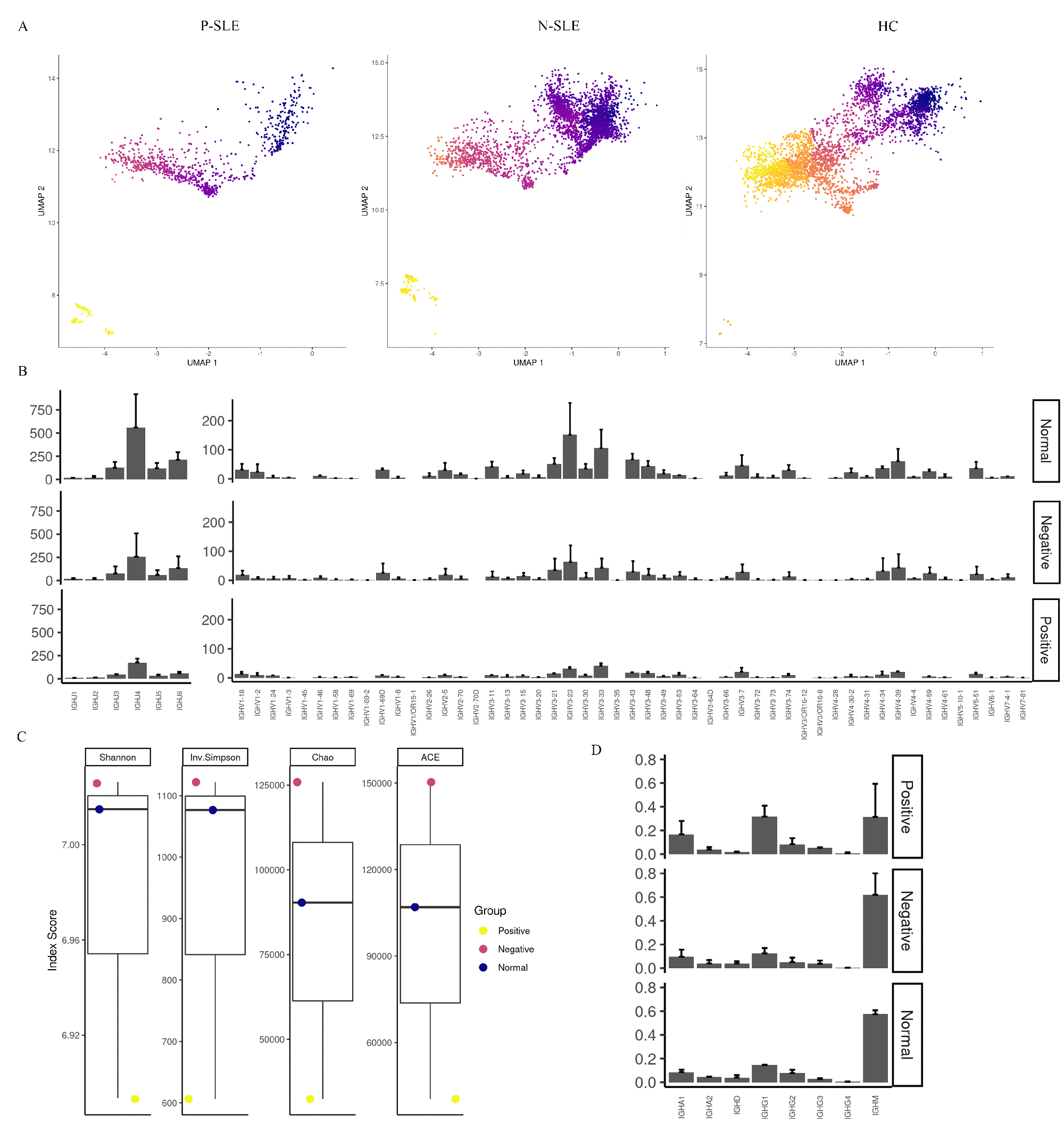
Results: 83478 cells were obtained in our study and were divided into 8 major cell types or subtypes, including B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, other T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, monocytes, dendritic cells (DCs) and other cells. There is no significant difference in the proportion of cell clusters between P-SLE and N-SLE. Interferon-alpha/beta pathways were upregulated in T cells, monocytes, and B cells in P-SLE compared with N-SLE. B cells were further divided into four different clusters, including naive B cells, intermediate B cells, memory B cells, and plasmablast. For V gene segments in the heavy chain, IGHV3, IGHV4, and IGHV2 gene families were frequently used in both patients and HC, especially IGHV3 and IGHV4 families. However, the frequencies of gene segments in each IGHV family were significantly different between the three groups. We also found that the BCR diversity was significantly reduced in P-SLE compared with N-SLE and HC. Moreover, IgM presents the largest proportion in all BCR repertoire, but its proportion was significantly decreased in P-SLE patients. We also observed that the proportions of IgG1, IgG3, and IgA1 were significantly increased in P-SLE than that in HC or N-SLE.
Conclusion: Our study provides a comprehensive characterization of the immune cell profiles and BCR repertoire in SLE patients with or without EBV infection, which contributes to the understanding of the mechanism for the immune response to EBV infection in SLE patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hu L, Tu J, Gui J, Fang M, Chen X, Sun L. The Landscape of Immune Cells in Systematic Lupus Erythematosus Patients with Epstein-Barr Virus Infection by Single-cell Sequencing [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-landscape-of-immune-cells-in-systematic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-with-epstein-barr-virus-infection-by-single-cell-sequencing/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-landscape-of-immune-cells-in-systematic-lupus-erythematosus-patients-with-epstein-barr-virus-infection-by-single-cell-sequencing/