Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Treatments Poster III: Biosimilars and New Compounds
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its treatment have significant impacts on health-related quality of life (HRQoL), work productivity (WP) and activity participation. Data are limited comparing the magnitude of impacts observed in routine clinical practice and randomized controlled trials (RCTs). This study evaluated the impact of RA on HRQoL, WP and activity participation among adult RA patients in the US general population compared with patients from two sarilumab pivotal phase 3 RCTs. Sarilumab is a human anti-IL-6Rα monoclonal antibody for treatment of moderate-to-severely active RA.
Methods: “Real world” data were from adult participants of the cross-sectional 2015 US National Health and Wellness Survey (NHWS) with a patient-reported diagnosis of RA, moderate/severe disease activity and administered disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) at the point of survey. RCT data were from MOBILITY – Part B and TARGET trials comparing the efficacy and safety of sarilumab subcutaneous (SC) 150 mg and 200 mg every 2 weeks (q2w) plus methotrexate in MOBILITY or conventional DMARDs in TARGET versus placebo in patients with moderate-to-severely active RA and inadequate responses to methotrexate (MTX-IR, MOBILITY) or tumor necrosis factors inhibitors (TNF-IR, TARGET). HRQoL was measured using the Short Form-36v2 (SF-36v2) in the NHWS, and both RCTs at baseline and Week 24; WP impairment (WPI) and activity impairment (AI) were measured via the WPAI scale in the NHWS and MOBILITY. Bivariate analyses evaluated between-group differences in SF-36v2 physical (PCS) and mental (MCS) component summary and domain scores and WPAI absenteeism, presenteeism (% work time missed), overall WPI and AI.
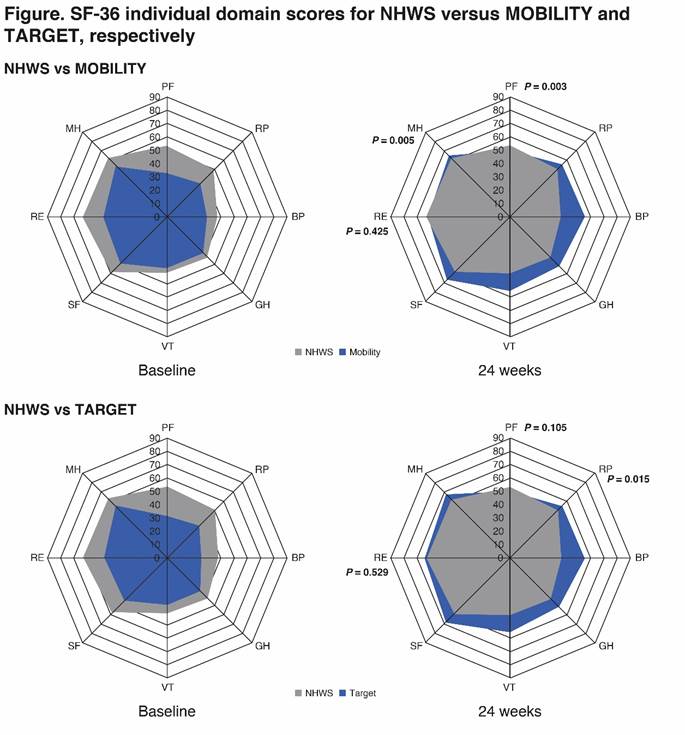
Results: Mean ages of the analyzed cohorts were 54, 51 and 53 years; 61%, 82%, and 80% were female, respectively in NHWS (n=2016), MOBILITY (n=799) and TARGET (n=365). At baseline, versus NHWS patients, those enrolled in MOBILITY reported greater presenteeism (47.25 vs 37.50; P < 0.001), overall WPI (51.29 vs 43.11; P = 0.001) and AI (62.42 vs 50.96; P < 0.001). Patients in MOBILITY and TARGET reported significantly lower baseline scores versus NHWS in SF-36v2 PCS (31.27, 29.42 vs 38.54) MCS (38.86, 38.73 vs 43.97), and all domain scores (P < 0.001; Figure) indicating greater HRQoL impairment. At Week 24 both trial cohorts reported improved HRQOL (Figure) and AI in MOBILITY (34.08 vs 39.76, respectively; P < 0.05) following treatment with sarilumab than the NHWS cohort scores.
Conclusion: Patients in both sarilumab RCTs reported worse baseline HRQoL, and in MOBILITY greater WPI and AI than NHWS RA patients. After 24 weeks treatment with sarilumab, both RCT cohorts reported improvements exceeding NHWS scores, with few exceptions. These data offer perspective on the benefits of sarilumab treatment on HRQOL, WP and AI.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis, sarilumab, anti-IL-6Rα, health-related quality of life
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Strand V, Carpinella CM, Lee LK, Boklage S, Reaney M. The Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Patient-Reported Outcomes: Comparison between Sarilumab Clinical Trials and Real-World Patient Data [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-patient-reported-outcomes-comparison-between-sarilumab-clinical-trials-and-real-world-patient-data/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-on-patient-reported-outcomes-comparison-between-sarilumab-clinical-trials-and-real-world-patient-data/