Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The ACR’s COVID-19 Vaccine Guidance recommends all patients with rheumatic diagnoses be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2. The predominant SARS-CoV-2 vaccines used in the United States are based on mRNA technology. Little is known about the immunogenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines in patients with SLE, many of whom are on immune suppressing medications. This study sought to determine the humoral immunogenicity of two doses of the SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines made by Moderna and Pfizer/BioNTech in SLE patients, stratified by immunosuppression.
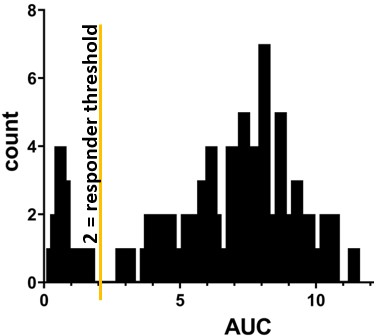
Methods: We obtained biobanked serum from SLE patients and healthy control patients whose blood was drawn 14-180 days following dose #2 of a SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine. ELISA was performed using anti-wild-type spike protein ectodomain S1+S2. Area under the curve (AUC) was calculated for each individual. An AUC threshold of 2.0 was established to distinguish between responders and non-responders (Figure 1).
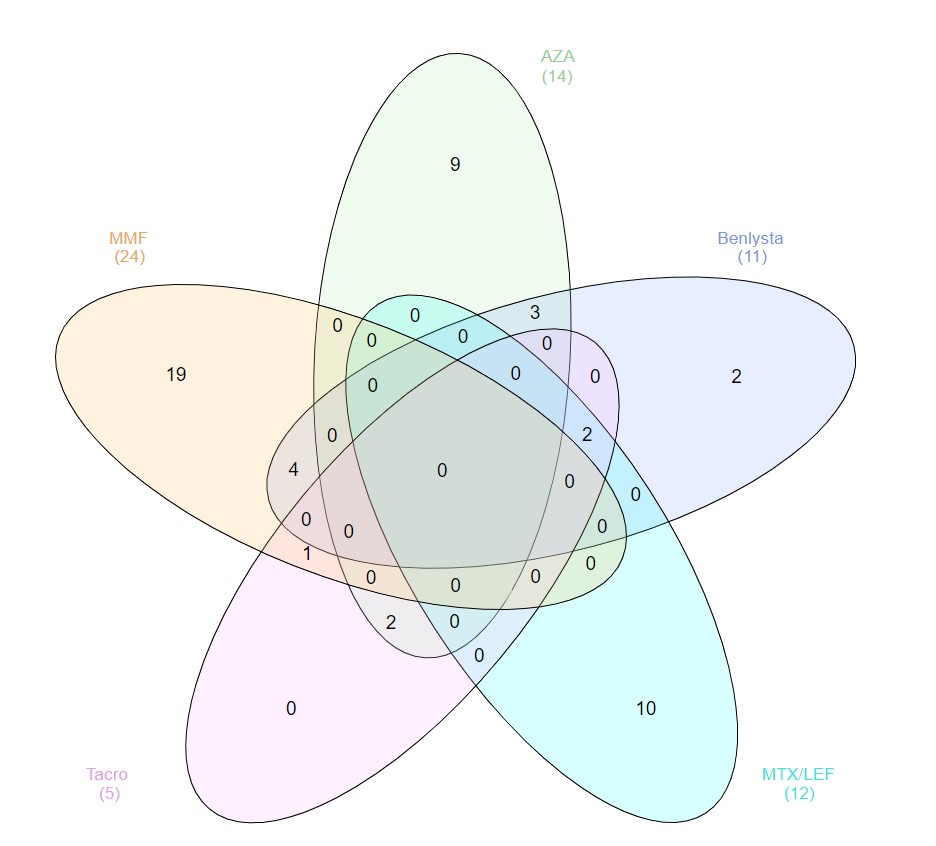
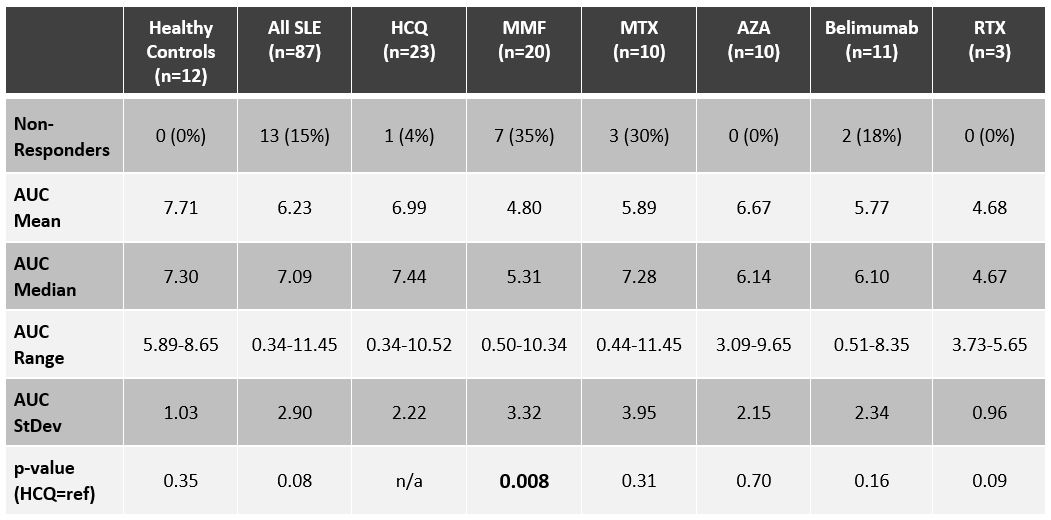
Results: Of the SLE patients (n=87), 23 (26%) were on no SLE therapy or HCQ monotherapy, 44 (51%) were on a DMARD and ≤7.5mg of prednisone, and 20 (23%) patients were on a biologic (rituximab=3, belimumab=11) and/or high-dose prednisone. Figure 2 depicts concomitant use of DMARDs and belimumab. As summarized in Table 1, the AUC for SLE patients was not significantly lower than for healthy controls (n=12): median AUC of 7.09 (range 0.34-11.45) versus 7.30 (range 5.89-8.65). The median AUC for SLE patients on no lupus medications or hydroxychloroquine monotherapy was 7.44 (range 0.34-10.52), with only one patient (4%) being classified as a non-responder. Ten (23%) of the SLE patients on DMARDs were non-responders, with mycophenolate and methotrexate having the biggest impact on AUC: seven (35%) of the patients on mycophenolate were non-responders (AUC median = 5.31; p=0.008), and 30% of the patients on methotrexate were non-responders (AUC median = 7.28; p=0.31). Three (15%) of the SLE patients on biologics and/or high-dose prednisone were non-responders, including two of the 11 belimumab patients (18%), one of whom was on concomitant mycophenolate, and the other on high-dose prednisone (20 mg daily). All three rituximab patients were classified as responders, although the median AUC (4.67) and mean AUC (4.68) were the lowest of any medication (range 3.73-5.65). The number of days between dose #2 and serum sample collection did not correlate with AUCs: the 13 non-responders were on average 66 days out from dose #2, whereas responders were on average 80 days out from dose #2.
Conclusion: SLE patients on certain immune suppressing medications, most notably mycophenolate, produce less SARS-CoV-2 anti-spike antibodies after receiving two doses of an mRNA vaccine. Neutralization assays and cell-based studies are necessary to understand the full picture of vaccine immunogenicity in SLE; nevertheless, decreased serologic response in SLE patients on certain medications should prompt studies exploring whether holding medications like mycophenolate will enhance the immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 and other vaccines.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sadun R, Crair D, Walter E, Rogers J, Clowse M, Eudy A, Sun K, Doss J, Criscione-Schreiber L, Valencia S, Moody M. The Impact of Immunosuppression on the Humoral Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines in SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-immunosuppression-on-the-humoral-immunogenicity-of-sars-cov-2-mrna-vaccines-in-sle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-immunosuppression-on-the-humoral-immunogenicity-of-sars-cov-2-mrna-vaccines-in-sle/