Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Previous study using cluster analysis technique analyzed the association between comorbidities and various outcome measures in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). Due to the cross-sectional nature of the study, however, prognostic information about each group were not provided. Using the data retrieved from Korean College of Rheumatology Biologics (KOBIO) registry, which includes longitudinal data of axSpA patients using anti-TNF agents, this study aims to perform cluster analysis to differentiate axSpA patients in terms of comorbidities and to examine the differential treatment outcomes of these groups.
Methods: Clinical characteristics and demographic data of axSpA patients in KOBIO registry were analyzed using an agglomerative hierarchical cluster analysis. The optimum number of clusters was determined by the pseudo-F statistic. After clustering, baseline clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes were compared between isolated axSpA and classified comorbidity groups using multivariable linear models and mixed linear models, respectively.
Results: 1,207 patients were included in the study. At least one comorbidity was seen in 464 (38%) axSpA patients. Compared with those with isolated axSpA, patients with comorbidity were older, longer disease duration, and reported higher patient global assessment of disease activity (PtGA, p = 0.019), and BASFI (p < 0.001), but did not have significantly different BASDAI, ESR, and CRP levels (Table 1). The most common comorbidities were hypertension (14.4%), hyperlipidemia (13.0%), and obesity (4.5%). The hierarchical cluster analysis classified patients in 21 groups. We combined clusters 17-21 for further evaluation due to the small size of clusters (< 5 patients). In multivariable linear models for baseline clinical characteristics, we found that patients in the hypothyroidism, asthma, and headache clusters reported poorer PtGA, BASDAI, or BASFI, and the weight loss cluster had higher level of CRP, compared with patients with isolated axSpA even after adjustment of patient demographic data (Table 2). After 1-year treatment of anti-TNF agents, the patients in the hypothyroidism and weight loss clusters decreased greater amounts of BASDAI and BASFI scores and ESR/CRP levels, respectively, compared with patients with isolated axSpA (Table 3). However, the degree of improvement in asthma and headache clusters, which had higher disease activities at baseline, was similar with isolated axSpA. Therefore, they still had higher disease activity scores at the 1-year follow-up.
Conclusion: Comorbidity could affect the treatment outcomes in patients with axSpA in certain subgroups. Thus, we should also pay attention to the comorbidities when treating axSpA.
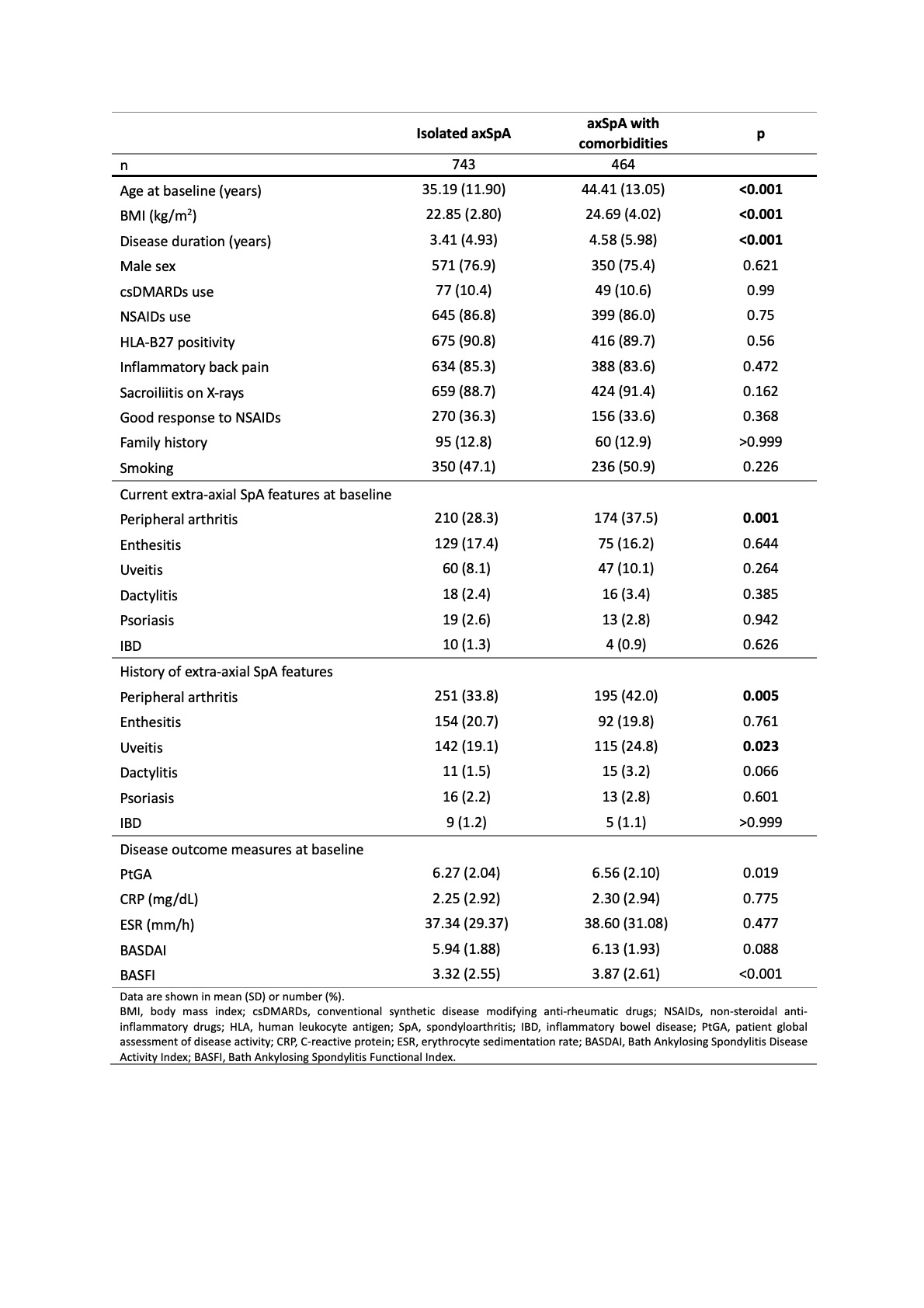 Table 1. Patient and disease characteristics according to the presence or absence of comorbidities.
Table 1. Patient and disease characteristics according to the presence or absence of comorbidities.
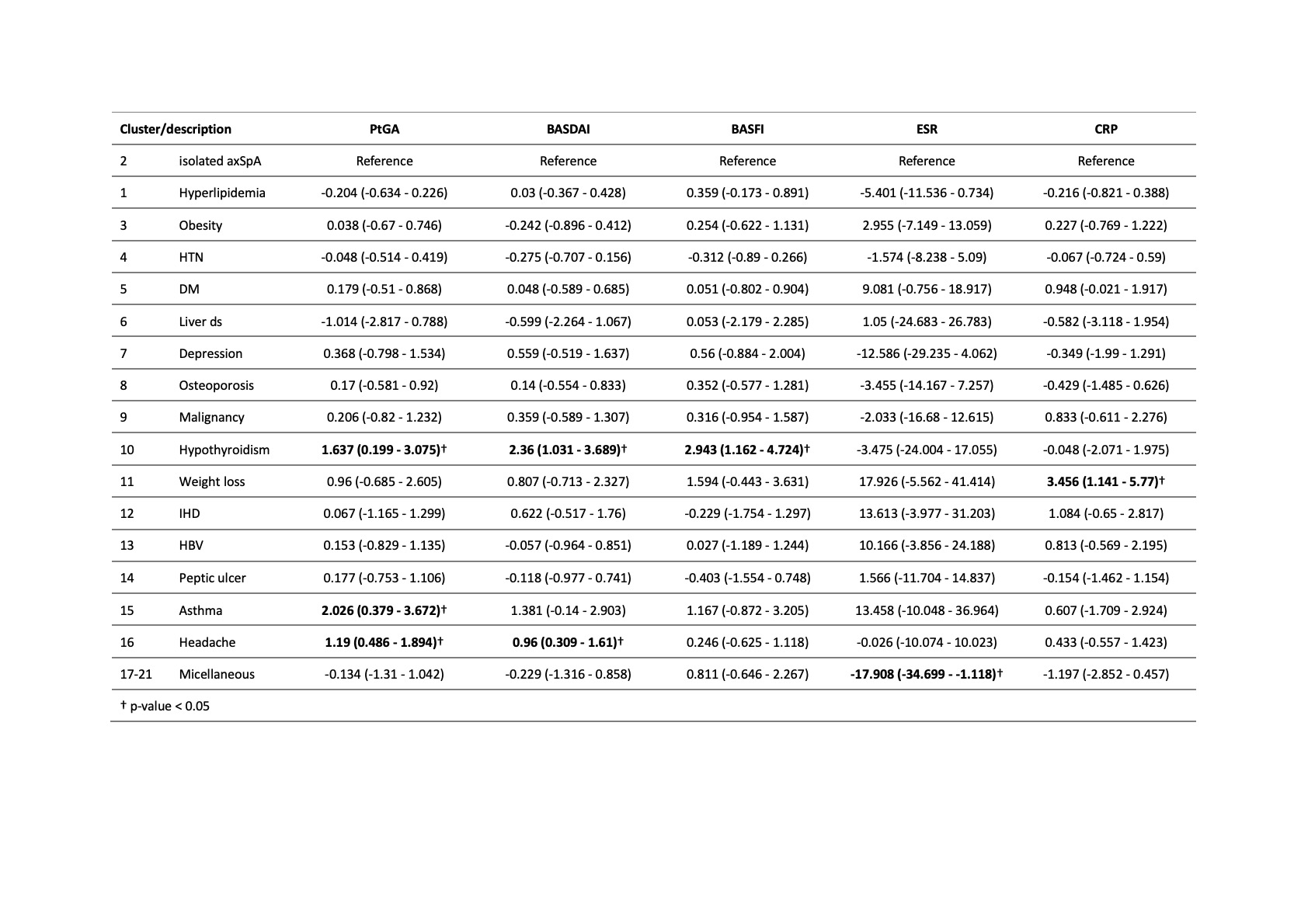 Table 2. Comparing each cluster to patients with isolated axSpA (i.e. no comorbidity) using multivariable linear models for each baseline clinical outcome measure as the dependent variable, and cluster as a dummy independent variable.
Table 2. Comparing each cluster to patients with isolated axSpA (i.e. no comorbidity) using multivariable linear models for each baseline clinical outcome measure as the dependent variable, and cluster as a dummy independent variable.
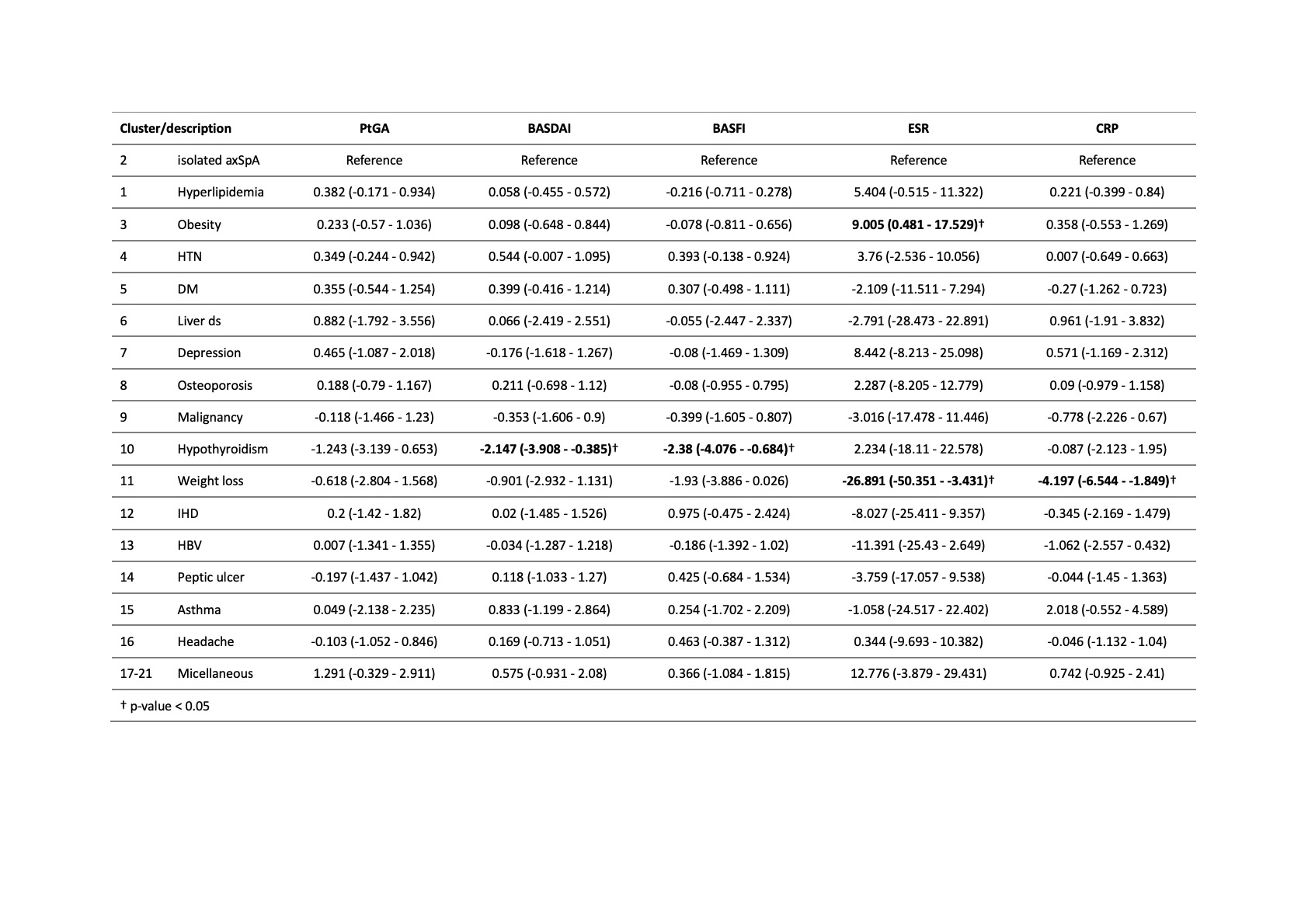 Table 3. Comparing each cluster to patients with isolated axSpA (i.e. no comorbidity) using multivariable linear mixed models for each treatment outcome measure at 1-year follow-up as the dependent variable.
Table 3. Comparing each cluster to patients with isolated axSpA (i.e. no comorbidity) using multivariable linear mixed models for each treatment outcome measure at 1-year follow-up as the dependent variable.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee S, Kang S, Eun Y, Kim H, Cha H, Koh E, Lee J. The Impact of Comorbidities on Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis: A Cluster Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-comorbidities-on-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-cluster-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-comorbidities-on-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-a-cluster-analysis/
