Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0510–0542) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: AxSpA Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients (pts) with AS, higher BMI has been linked to higher disease activity1. However, given that BMI can be a poor indicator of body composition, using BMI alongside digital devices that can measure physical activity (PA) may be a more comprehensive measure of fitness. To better understand the impact of BMI and PA on treatment response, we evaluated outcomes in pts with AS treated with upadacitinib (UPA) 15 mg once daily through 52 weeks (wks) of the Phase 3 SELECT-AXIS 2 trial (NCT04169373), stratified by baseline (BL) BMI and level of PA2.
Methods: Pts with active AS and inadequate response to biologic DMARDs in SELECT-AXIS 2 were required to wear a wrist-worn actigraphy device that remotely monitored PA during the 14-wk, placebo-controlled portion of the study. In this post hoc analysis, we evaluated Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with CRP (ASDAS-CRP) and BASDAI scores at wk 52 among pts who received continuous UPA for 52 wks stratified by BL PA (inactive [< 5000 steps/day] or active [≥5000 steps/day])3 and BMI (overweight/obese [BMI ≥25 kg/m2] or healthy weight/underweight [BMI < 25 kg/m2]). BL step count was calculated by mean daily step counts for wk 1 in pts with at least 3 days of wearable device adherence, and at least 16 hours/day of wear time. One-way analysis of variance was used to investigate the association of ASDAS-CRP and BASDAI scores at each time point through wk 52 with each BL category; significant variables (p< 0.05) were then analyzed using a mixed model for repeated measures. A Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction was used to assess ASDAS-CRP or BASDAI scores in each combination of BL BMI and PA.
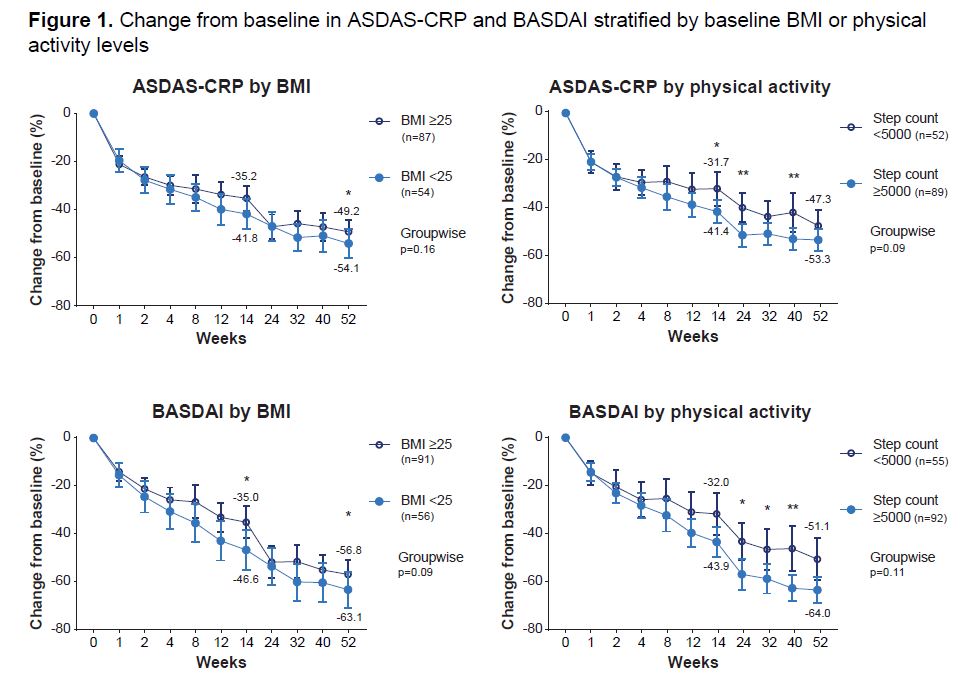
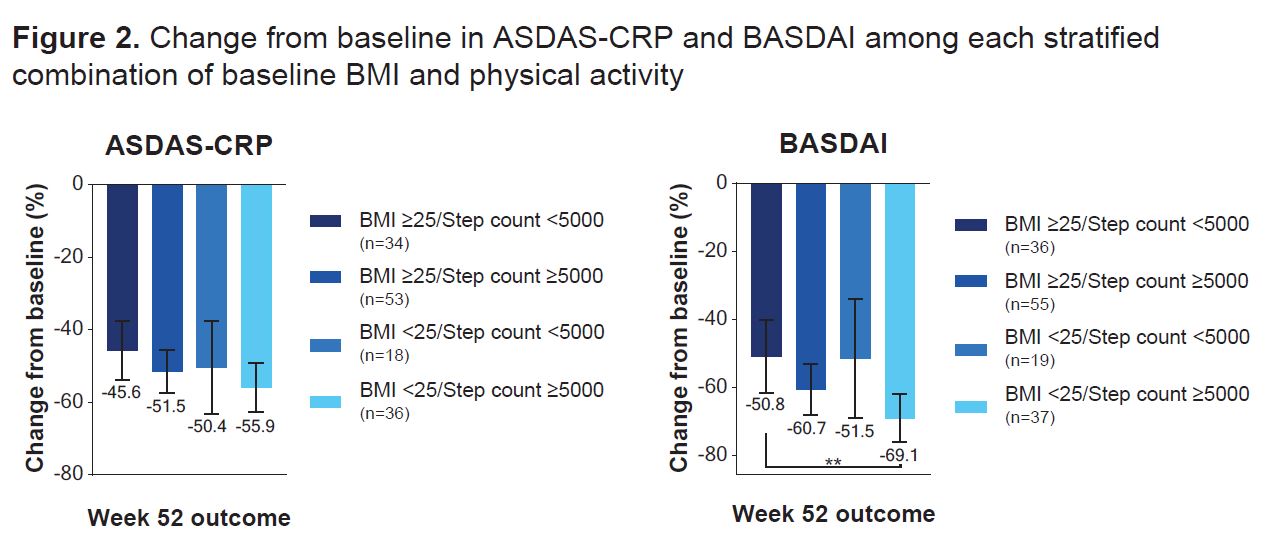
Results: Data were available from 141 pts for ASDAS-CRP and 147 pts for BASDAI who wore the actigraphy device. While no statistical differences in change from BL in ASDAS-CRP or BASDAI were observed between subgroups at wk 52, pts who were healthy weight/underweight or active at BL demonstrated a trend toward greater reduction in ASDAS-CRP and BASDAI scores at most time points from wk 8 onwards vs pts who were overweight/obese or inactive (Figure 1). When BL subgroups were considered concurrently, pts who were healthy weight/underweight and active at BL achieved significantly greater reduction in BASDAI scores over 52 wks vs pts who were overweight/obese and inactive (nominal p< 0.01; Figure 2). No significant differences were reported between pts with any other combination of BL BMI and PA for ASDAS-CRP or BASDAI.
Conclusion: Pts with active AS receiving UPA for 52 wks who were active or healthy weight/underweight at BL generally experienced greater decreases from BL in ASDAS-CRP and BASDAI vs pts who were inactive or overweight/obese. Pts with active AS receiving UPA who were active tended to have numerically greater improvements in disease activity vs pts who were inactive, regardless of BMI. BMI and PA together may offer a more clinically relevant way to determine outcomes than either measure alone.
References:
- Liew JW, et al. RMD Open 2020;6:e001225
- Van der Heijde D, et al. Lancet 2022;400:369–79
- Tudor-Locke C, et al. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 2013;38:100–14
As observed data, excluding missing data due to COVID_19. Error bars denote 95% confidence intervals.
ASDAS-CRP, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with CRP; BASDAI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BMI, body mass index.
As observed data, excluding missing data due to COVID_19. Error bars denote 95% confidence intervals.
ASDAS-CRP, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score with CRP; BASDAI, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index; BMI, body mass index.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Crowley A, Siegel L, Wickersham P, Jones H, Webster D, Shmagel A, Biljan A, Kiltz U, Helliwell P. The Impact of Baseline BMI and Physical Activity on Upadacitinib Treatment Response: A Post Hoc Analysis of Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis from the SELECT-AXIS 2 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-baseline-bmi-and-physical-activity-on-upadacitinib-treatment-response-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-from-the-select-axis-2-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-impact-of-baseline-bmi-and-physical-activity-on-upadacitinib-treatment-response-a-post-hoc-analysis-of-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-from-the-select-axis-2-study/