Session Information
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-4:00PM
Background/Purpose: Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA) is characterized by vasculitis in lungs, kidneys and the ear, nose and throat region. Regular monitoring and treatment adjustments are needed, as disease activity tends to fluctuate over time. Unfortunately, good markers for disease activity are lacking, leading to over- and undertreatment. Immunoglobulin G4 positive (IgG4+) B-cells and plasma cells are implicated in the pathogenesis of GPA. Recently, we developed a test that indirectly measures the presence of IgG4+ B-cells/plasma cells in blood by measuring the IgG4:IgG RNA ratio1. We hypothesized that this test could serve as a disease activity marker in GPA. Here we test the IgG4:IgG RNA ratio in peripheral blood as a disease activity marker in GPA.
Methods: 29 PR3-ANCA positive GPA patients were included. Mean age was 53 years, 55% were female, and 41% had active disease. For each patient ESR, CRP, BVAS, and PR3-ANCA-titre was measured. Active disease was defined as BVAS ≥3. We also included 10 healthy controls (HC) and 63 patients with other immune mediated inflammatory diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) (n = 24), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) (n = 19), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) (n = 20)). The IgG4:IgG RNA ratio in peripheral blood samples was measured using a validated qPCR test1.
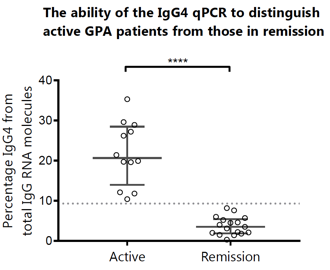
Results: The median IgG4:IgG RNA ratio was significantly higher in the GPA cohort (6.0; IQR 2.7-19.8) compared to all controls: 1.2 in SLE (0.7-3.3; p<0.0001), 2.5 in RA (IQR 0.7-4.1; p<0.05), 1.6 in PSC (IQR 1.0-2.8; p<0.01) and 1.3 in HC (IQR 0.6-1.8, p<0.001). In addition, the median IgG4:IgG RNA ratio was significantly higher in active disease (20.7; IQR 14-28.5) compared to remission (3.5; IQR 1.9–5.5) (p<0.0001). An IgG4:IgG RNA ratio of 9.3 differentiated perfectly between active disease and remission (AUC 1.000). The IgG4:IgG RNA ratio (p<0.0001) outperformed other disease activity parameters such as ESR (p<0.05), CRP (p<0.01) and PR3-ANCA titre (ns) in detecting active disease. The height of the IgG4:IgG RNA ratio significantly correlated with height of the BVAS (Spearman r=0.78, p<0.0001).
Conclusion: The IgG4:IgG RNA ratio distinguishes active GPA from GPA in remission with excellent specificity and sensitivity. Moreover, the ratio shows a significant correlation with disease severity and outperforms other disease activity parameters. Retesting in a prospective study is indicated to validate the IgG4:IgG ratio as a novel marker of disease activity in GPA.
1 Doorenspleet ME et al. Hepatology 2016;64(2):501-7.
Figure 1. Scatter dot plot portraying the qPCR results on a linear scale (Y-axis) in active disease (X axis left) and remission (X axis right). Active disease is based on a BVAS ≥3. **** = p < 0.0001
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Al-Soudi A, Doorenspleet ME, Esveldt R, Burgemeister L, Hak L, Tas SW, van Vollenhoven RF, Klarenbeek PL, de Vries N. The IgG4:IgG RNA Ratio in Peripheral Blood Perfectly Differentiates Active Disease from Remission in Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. a New Disease Activity Marker? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-igg4igg-rna-ratio-in-peripheral-blood-perfectly-differentiates-active-disease-from-remission-in-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-a-new-disease-activity-marker/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-igg4igg-rna-ratio-in-peripheral-blood-perfectly-differentiates-active-disease-from-remission-in-granulomatosis-with-polyangiitis-a-new-disease-activity-marker/