Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Since the spread of different SARS-CoV2 vaccines over the world, there was an uncertainty of the efficacy and safety of these vaccines in autoimmune rheumatic disease (ARD) patients receiving immunomodulators. Patients with ARD were not included in the vaccines phase 3 trials. Qatar national COVD19 vaccine campaign started in Jan 2021. BNT162b2 vaccine was the first to be introduced followed by mRNA-1273 vaccine.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the humoral immunity response of mRNA-based vaccines in ARD patients receiving immunomodulators.
Methods: SARS-CoV2 infection naïve ARD patients who underwent serological testing for anti-SARS-Cov2 S (Elecsys, Roche) were identified and their electronic medical records were reviewed retrospectively to capture demographic data, underlying ARD and the used immunomodulator agents. We included patients who completed two doses of the vaccine in Qatar and underwent anti-SARS-Cov2 S at least fourteen days post the 2nd dose of the vaccine. The test was considered non-reactive when the titer was zero and poorly reactive when the titer was < 132 U/ml which is the cut off used by American Association of Blood Bank to qualify COVID19 convalescent plasma donor. We ran a descriptive analysis comparing the immunogenic response on each immune modulator used in the cohort.
Results: 96 subjects were included in the analysis, 60 (60.2%) were females and median age was 46.7 years (std 12.0). 65.6% were Arab, 22.9% were Asian and 11.5% were from other ethnicities. ARDs distribution was as the following: rheumatoid arthritis 54 (56.3%), axial spondyloarthropathy18 (18.8%), psoriatic arthritis 10 (10.4%), systemic lupus erythematosus 5 (5.2%), vasculitis 3 (3.1%) Sjogren’s disease 2 (2.1%) and other ARD 4 (4.1%). In our cohort, the test was non-reactive in 6 patients and poorly reactive in 18 patients. Rituximab, glucocorticoid and mycophenolate were associated significantly with no reaction (p value 0.000, 0.001 and 0.003) and poor reaction (p value 0.015, 0.011 and 0.034), respectively. Methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, anti-TNF alfa, JAK inhibitors and tocilizumab were associated with normal humoral response to mRNA-based SARS-COV 2 vaccines.
Conclusion: The majority of patients on CsDMARDs, anti TNF-alfa, JAK inhibitors and tocilizumab had adequate serologic response to m-RNA based vaccines. Poor vaccine reactivity was mainly associated with Rituximab, glucocorticoid and mycophenolate use. Further analysis in larger matched cohorts is needed to identify the factors associated with poor immune response in this category of patients.
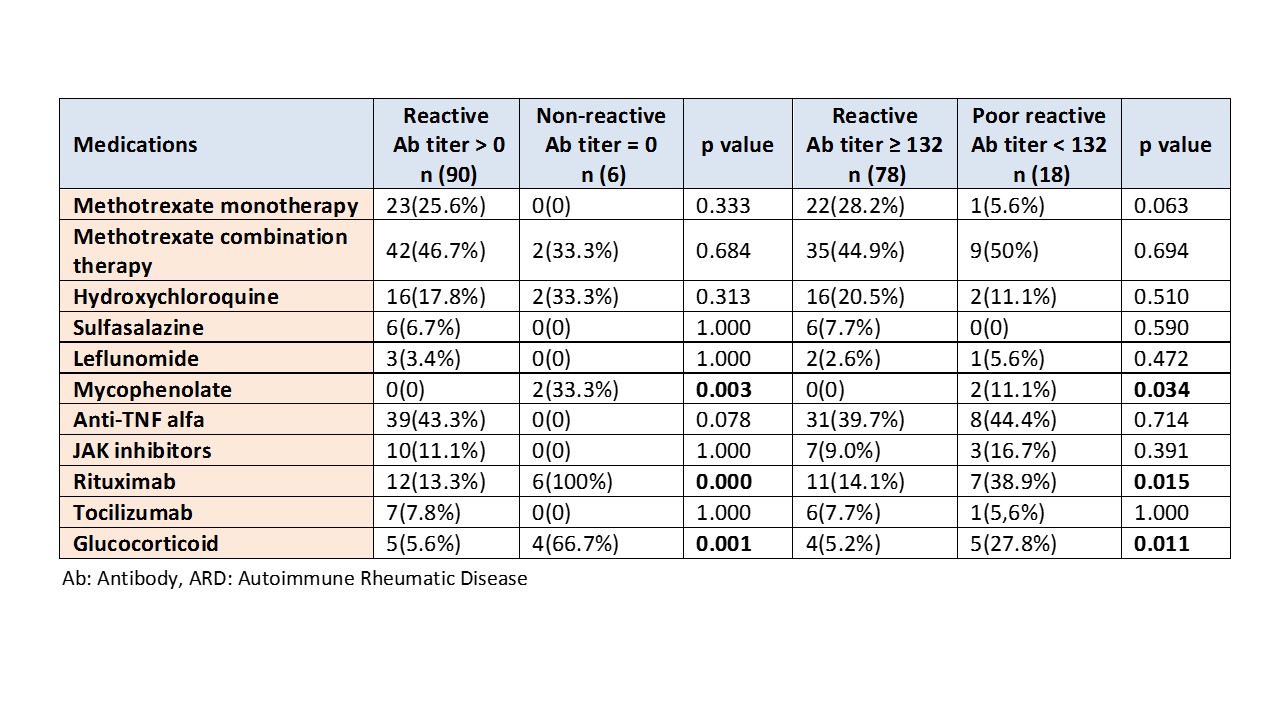 The immunomodulators used in ARD patients stratified according to humoral response post 2 doses of mRNA-based SARS-CoV2 vaccines
The immunomodulators used in ARD patients stratified according to humoral response post 2 doses of mRNA-based SARS-CoV2 vaccines
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alsaed O, Satti E, Muthanna B, Veettil S, Ashour H, Alkuwari E, Al Emadi S. The Humoral Immunity of mRNA-Based SARS-CoV2 Vaccine in Autoimmune Rheumatic Disease Patients Receiving Immunomodulators [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-humoral-immunity-of-mrna-based-sars-cov2-vaccine-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-patients-receiving-immunomodulators/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-humoral-immunity-of-mrna-based-sars-cov2-vaccine-in-autoimmune-rheumatic-disease-patients-receiving-immunomodulators/
