Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 17, 2024
Title: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Although diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is classically defined in the thoracic spine and the elderly population, there are case reports on the overlap between cervical DISH and spondyloarthritis (SpA), especially in a younger population (1). Our aim was to compare the frequency of cervical DISH in SpA vs age and sex-matched controls to see whether there is a true increased frequency and if the presence of SpA impacts the onset age of DISH.
Methods: The SpA population included patients who were diagnosed with axial or peripheral SpA, followed at the Arthritis Centre and had cervical spine x-rays for screening purposes in keeping with the standard of practice of a single rheumatologist between 2016-2020. The control group included patients who presented to the Emergency Department and had a cervical spine x-rays for any reason, and there were four control patients for each SpA patient who were age and sex-matched. An investigator meeting on the definitions took place prior to the study, followed by an agreement exercise. Two radiologists independently scored the cervical spine radiographs for the level of confidence for the presence of DISH, on a scale between 0-5. The ICC of the two radiologists were 0,935. For the study, the radiographs were read by one of the two radiologists; equally distributing the cases and controls among the two radiologists. The confidence of Grade 3 was considered as DISH positive.
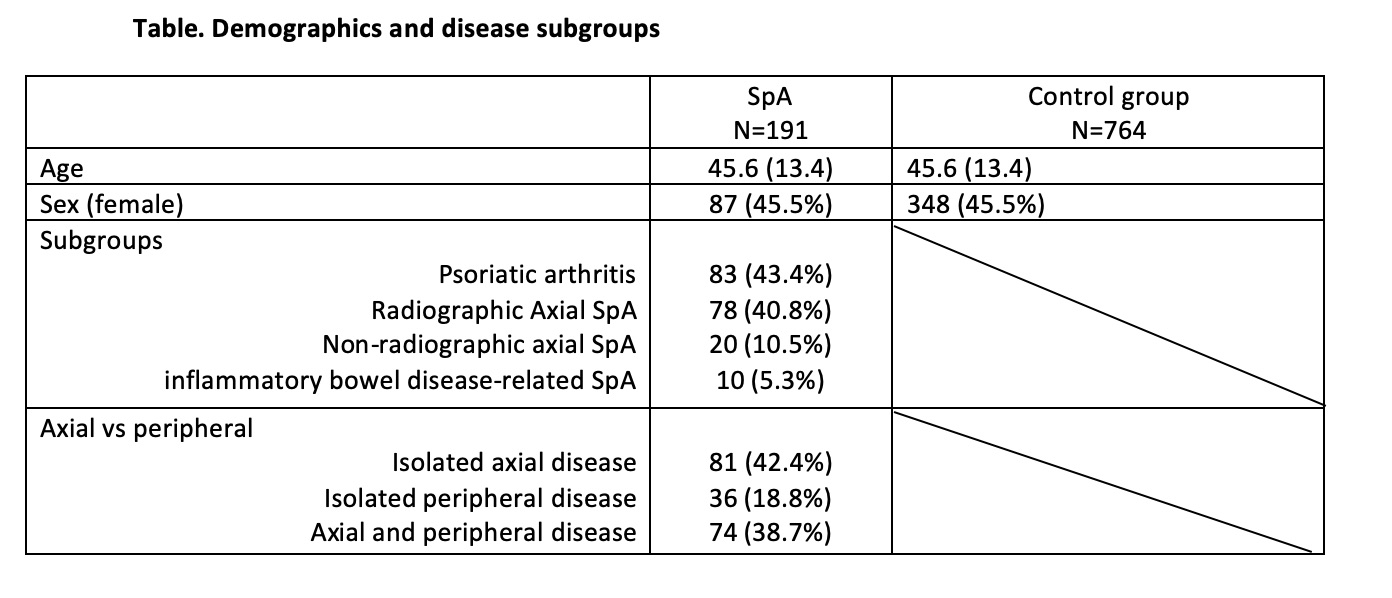
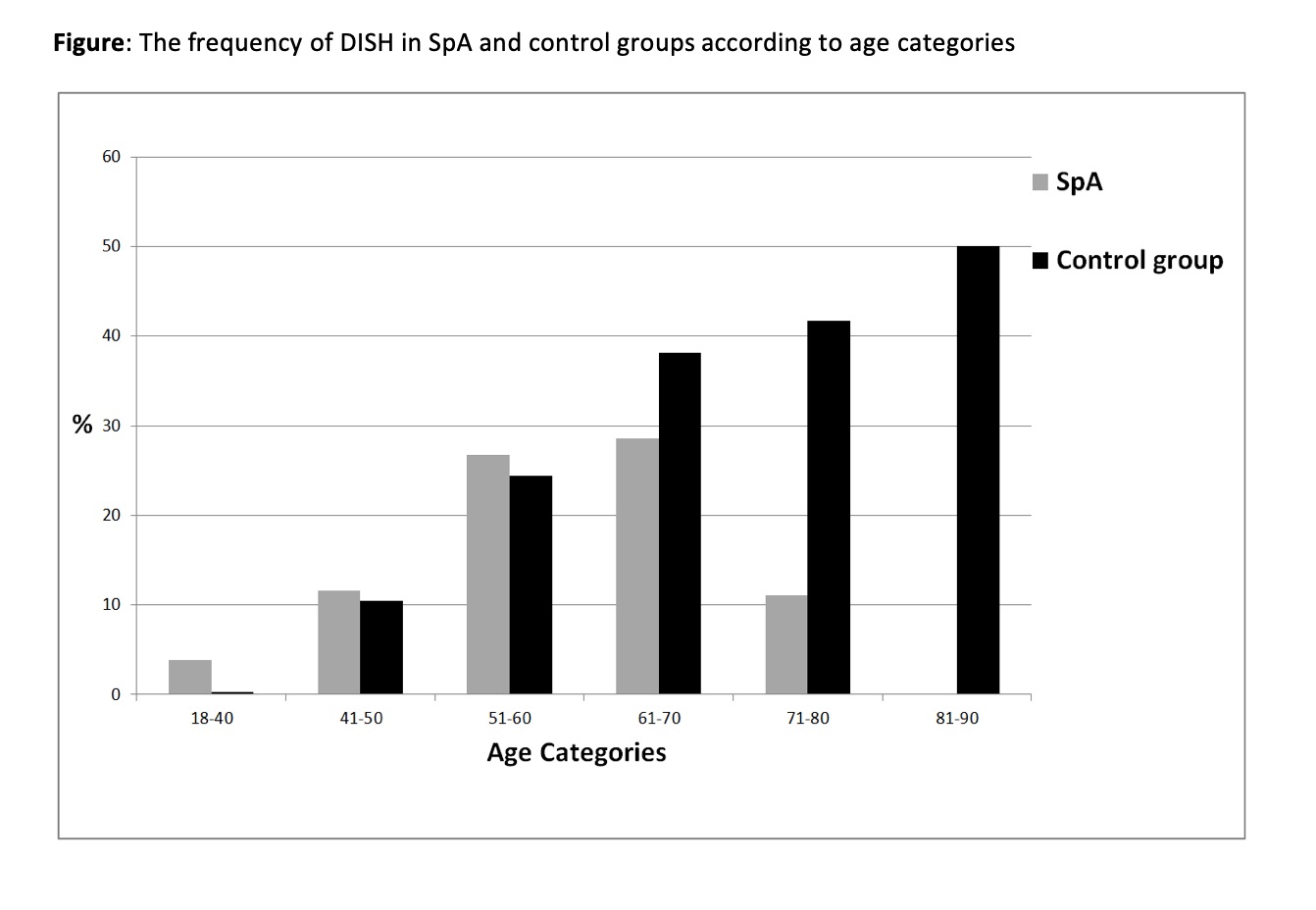
Results: One hundred ninety-one SpA and 764 age- and sex-matched controls were included (table). DISH was observed in 26 (13.6%) SpA patients and 108 (14.1%) controls, with similar frequencies (p=0.852). The age of DISH+ patients was statistically significantly lower in the SpA group than the control group (median (IQR); 54 (16) vs 59 (13); p=0.026), also reflected by the age categories (Figure). DISH was higher in males then females in both SpA (n:19/104 (18.3%) vs n:7/87 (8%); p=0.04) and control groups (n:74/416 (17.5%) vs n:35/348 (10.1%); p=0.003).
There were 143 (74.9%) SpA patients with known HLA-B27 status. The frequency of DISH in HLA-B27(-) SpA patients was higher than HLA-B27(+) SpA patients numerically (n=14/65 (21.5%) vs n=8/78 (10.3%); p=0.063). Interestingly, HLA-B27 had different effects on the presence of DISH in subgroups: AxSpA patients (radiographic and non-radiographic combined) had more DISH if they were HLA-B27 positive (12.5% vs 8.7%), unlike the psoriatic arthritis patients, who had DISH exclusively if they were HLA-B27 negative (28.2% vs 0%)
Conclusion: The frequency of DISH in SpA patients is similar to the general population. However, SpA patients develop DISH at an earlier age. Our observation on the differential impact of HLA-B27 on axSpA vs psoriatic arthritis may be a signal on the different mechanisms impacting the spine in both diseases.
Reference: Kuperus JS, et al., Rheumatology, 2018.
*Ummugulsum Gazel and Nicole Hryciw contributed equally to this study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gazel U, Hryciw N, Chahal B, Acikgoz S, Ayan G, Jibri Z, Sampaio M, Aydin S. The Frequency of Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) in Spondyloarthritis in Comparison to Age and Sex-matched Controls and Impact of SpA on Onset Age of DISH [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-frequency-of-diffuse-idiopathic-skeletal-hyperostosis-dish-in-spondyloarthritis-in-comparison-to-age-and-sex-matched-controls-and-impact-of-spa-on-onset-age-of-dish/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-frequency-of-diffuse-idiopathic-skeletal-hyperostosis-dish-in-spondyloarthritis-in-comparison-to-age-and-sex-matched-controls-and-impact-of-spa-on-onset-age-of-dish/