Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: It has been reported that serum survivin level was an independent risk factor for predicting joint destruction in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The proto-oncogene BIRC5 generates alternative splicing variants, including wild-type (WT) survivin, survivin 2B, survivin delta-Ex3, survivin 3B and survivin 2-alpha. We herein examined which variants of survivin were expressed in the synovial tissues and blood samples of patients with RA and osteoarthritis (OA).
Methods: We observed the expression of survivin splicing variants in synovial tissues by the real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analyses, and serum survivin 2B was measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Moreover, to determine the effects of survivin splicing variants in fibroblasts, cell viability and chemosensitivity of an anti-metabolite were evaluated by overexpression experiments in a fibroblast model with the MTS and LDH assays.
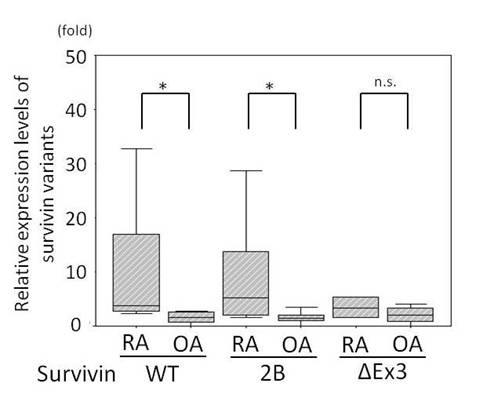
Results: We found that three types of splicing variant (WT survivin, survivin 2B and survivin delta-Ex3) were expressed in RA and OA synovial tissues by RT-PCR, and the WT survivin and survivin 2B mRNA expression levels in RA synovial tissues were higher than those in OA patients by real-time PCR (6 RA cases vs. 6 OA cases) (p=0.010 and 0.016, respectively). On the other hand, there was no significant difference in the survivin delta-Ex3 expression levels between the RA and OA synovial tissues (p=0.150) (Figure 1). In the IHC analyses, survivin delta-Ex3 was expressed in both RA and OA synovial tissues, while survivin 2B was strongly expressed in RA tissues and hardly expressed in OA tissues. In addition, the serum survivin 2B levels of RA patients were higher than those of OA patients and healthy controls (40 RA cases vs. 16 OA + controls cases) (mean 17.9 µg/ml vs. 6.1 µg/ml, p=0.019). Furthermore, double staining by IHC revealed that survivin and CD55 merged, so survivin was mainly expressed in synovial fibroblasts. Transfection experiments revealed that survivin delta-Ex3-overexpressing fibroblasts were fast-growing and their sensitivity to anti-metabolites was elevated compared with that of fibroblasts transfected with a vector plasmid. On the other hand, survivin 2B-overexpressing fibroblasts were fast-growing, but their sensitivity to anti-metabolites was not elevated compared with that of fibroblasts transfected with a vector plasmid.
Conclusion: The expression of survivin 2B in synovial tissue and serum samples was a specific biomarker of RA. In addition, survivin 2B-expressing fibroblasts were associated with proliferation and resistance to an anti-metabolite. Therefore, survivin 2B is a RA-specific molecule and might contribute to the rheumatoid synovial hyperplasia.
Figure 1. Relative expression levels of survivin splicing variants in synovial tissues from RA and OA
Results were presented relative to expression of the housekeeping gene Hprt. * Mann-whitney U test, p<0.05
Disclosure:
S. Mokuda,
None;
T. Miyazaki,
None;
J. Masumoto,
None;
M. Kanno,
None;
K. Takasugi,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-expression-of-proto-oncogene-survivin-splicing-variant-2b-in-synovial-tissues-and-blood-from-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/