Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster I
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We previously showed
that bone marrow (BM) CD34+ cells from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients have
abnormal capacities to respond to tumor necrosis factor alpha and to
differentiate into fibroblast-like cells producing MMP-1, resembling type B synoviocyte. In addition, we have recently demonstrated
that the mRNA expression of nuclear factor kappa B1, Krüppel-like
factor 5 and FK506-binding protein 5 in BM CD34+ cells is significantly higher
in RA patients than osteoarthritis (OA) patients. Antibodies directed to citrullinated proteins are extremely specific for RA. Citrullination is catalyzed by a group of peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD) enzymes. PAD
family members are categorized into five isoforms (PAD1, 2, 3, 4 and 6).
Several studies have disclosed that PAD2 and PAD4 are expressed in rheumatoid
synovial tissue or in mononuclear cells of rheumatoid synovial fluid. Moreover,
Sp1 has been shown to regulate transcription of these PADI genes. The current
study therefore examined the mRNA expression of PADI2, PADI4 and Sp1
transcription factor in BM CD34+ cells from RA patients.
Methods: BM samples were obtained from 48 patients
with RA (6 males and 42 females: mean age 58.8 years) and 30 patients with OA
(3 males and 27 females: mean age 71.1 years), who gave informed consent, during joint operations via aspiration from iliac
crest. CD34+ cells were purified from the BM mononuclear cells by positive
selection with magnetic beads. The expression of mRNA for PADI2, PADI4 and Sp1
was examined by quantitative reverse transcription PCR and is shown as the
ratio of the copy numbers to those of b-actin mRNA.
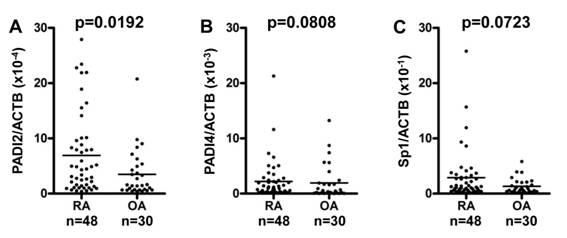
Results: The expression of mRNA for PADI2 was
significantly higher in RA BM CD34+ cells than OA BM CD34+ cells (Fig. A).
Compared to OA BM CD34+ cells, PADI4 and Sp1 gene expression levels of RA BM
CD34+ cells manifested no statistically significant increase (Fig. B and C). The
mRNA expression levels of PADI2, PADI4 and Sp1 were not correlated with serum
C-reactive protein or with the administration of methotrexate or oral steroid. PADI2 gene expression was significantly correlated with
PADI4 (p<0.0001, r=0.7143) and Sp1 (p<0.0001, r=0.7954) gene expression
in RA BM CD34+ cells.
Conclusion: These results indicate that the
enhanced expression of PADI2 mRNA in BM CD34+ cells plays a pivotal role in the
pathogenesis of RA, and might be closely associated with mRNA expression of PADI4
or Sp1.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nagai T, Tomita T, Yoshikawa H, Hirohata S. The Expression of mRNA for Peptidylarginine Deiminase Type 2 and Type 4 in CD34+ Cells of the Bone Marrow in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-expression-of-mrna-for-peptidylarginine-deiminase-type-2-and-type-4-in-cd34-cells-of-the-bone-marrow-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-expression-of-mrna-for-peptidylarginine-deiminase-type-2-and-type-4-in-cd34-cells-of-the-bone-marrow-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/