Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: To describe the epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in the Czech Republic (CZ)
Methods: We used the administrative database of the National Registry of Reimbursed Health Services (NRRHS) operated by the Czech Institute of Health Information and Statistics (IHIS) to estimate the incidence and prevalence of RA. NRRHS contains all administrative claims data collected for purposes of health system management as part of all public medical insurance plans for the period 2010-17. Data on all Czech citizens seeking healthcare are captured in this billing database, as medical insurance is mandatory in CZ. Cases of RA were identified using the following algorithm: at least 2 physician service claims (over 1 year) with ICD-10 code for RA (M05, M06) as the main diagnosis, with at least 1 of these claims originating from a rheumatologist AND at least one prescription for an oral glucocorticoid, csDMARD or bDMARD. We calculated crude and age and sex–standardized prevalence and incidence rates (with corresponding 95% confidence intervals [95% CIs]) among patients age ≥18 years over the period 2012–2017. The numerator represents all patients with RA, and the denominator represents all persons age >18 years living in CZ for the relevant year for prevalence or persons age >18 years at risk for incidence. Prevalent cases were carried forward for each year. We used a 2-year “run-in” period (2010-2011) to distinguish between incident and prevalent cases, allowing rates to be reported from 2012 onward. All analyses were performed by IHIS using Vertica database and IBM SPSS statistical software, version 25.0.0.1.
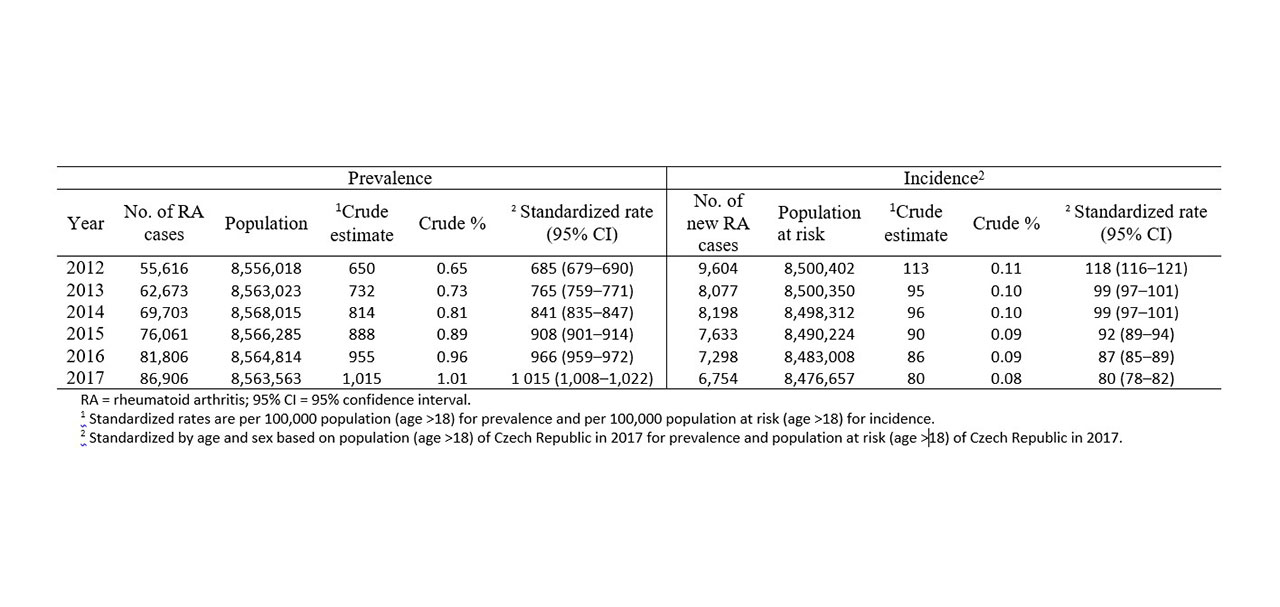
Results: As of 2017, there were 86,906 Czechs with RA, corresponding to a cumulative prevalence of 1.01%. Age and sex–standardized RA prevalence for population in 2017 increased over time from 685 (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 679 – 690) per 100,000 population (0.65 %) in 2012 to 1,015 (95% CI 1,008 – 1,022) per 100,000 population (1.01 %) in 2017. Age and sex–standardized incidence per 100,000 population ranged from 118 (95% CI 116 – 121) in 2012 to 80 (95% CI 78-82) in 2017. See table 1. Mean (SD) age at diagnosis was 59 (14) years, and 73% cases were female. The direction of the time trends in incidence and prevalence were similar across various age groups and both sexes, and the slopes of the curves appeared to be steeper in older individuals.
Conclusion: Over a 6-year period, we observed an increase in RA prevalence over time. This rise may be attributed to the increasing time to ascertain cases, increasing survival, and/or an increase in the aging background population. Incidence appears to decreasing.
Disclaimer: This study was supported by the project of MHCR for conceptual development of research organization 00023728
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Závada J, Bezděková M, Uher M, Jarkovský J. The Epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis in the Czech Republic [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-epidemiology-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-czech-republic/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-epidemiology-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-the-czech-republic/