Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated condition that causes fibroinflammatory lesions, often presenting as pancreatitis, cholangitis, sialoadenitis, and retroperitoneal fibrosis. The epidemiology of IgG4-RD, as well as its management patterns, clinical outcomes, and healthcare resource utilization (HCRU) in the US remain unknown.
Methods: We performed a retrospective observational cohort study using the Optum Clinformatics claims database from 1/1/2009-12/31/2021. We identified IgG4-RD patients using a validated algorithm requiring ICD codes, IgG subclass tests, and treatment.1 Clinical awareness of IgG4-RD grew in this period, so contemporary incidence and point prevalence were measured 1/1/2015-12/31/2019, standardized to the US population. For each case, we risk-set sampled 10 comparators matched by age, sex, and race with a medical encounter ±3 days of the second IgG4-RD-related ICD-9 or -10 claim used to identify the case (index date). We assessed manifestations, treatments, and comorbidities one year prior to and including index date (baseline) and during follow-up which ended at disenrollment, death, or 12/31/2021. HCRU was assessed over the 12 months following the index date.
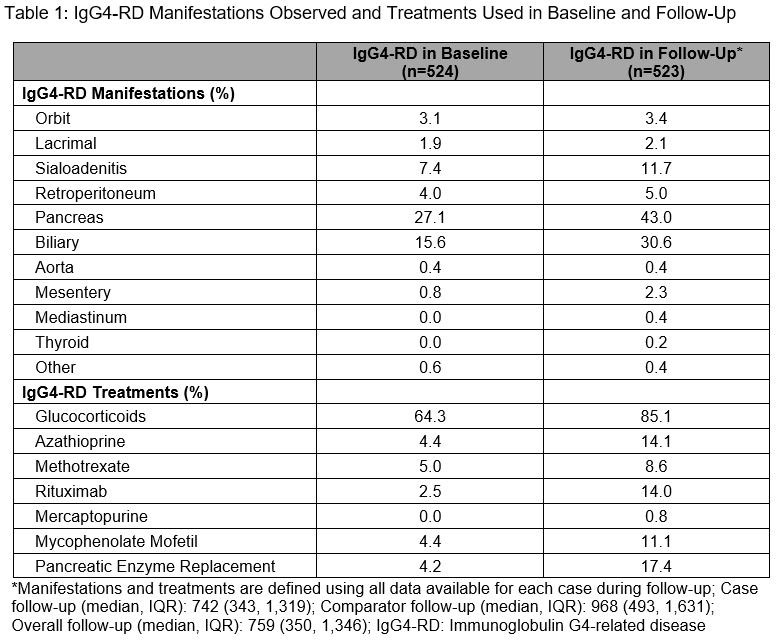
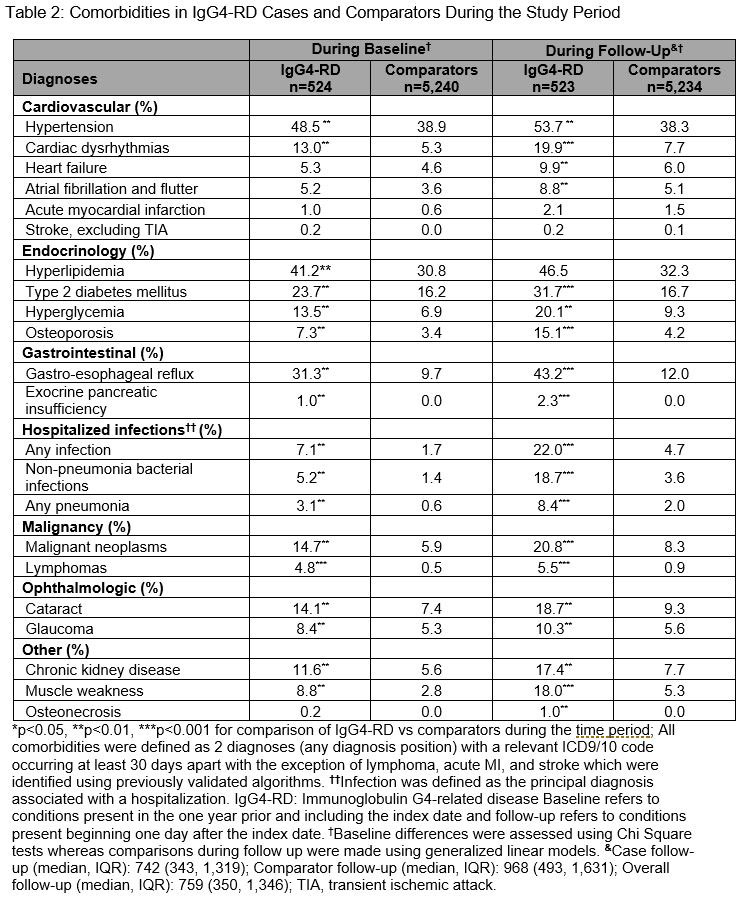
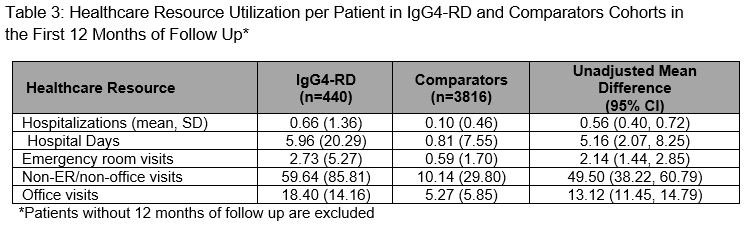
Results: We identified 524 IgG4-RD cases and matched 5,240 comparators. The mean age was 56.5 years; the majority were female (57.6%) and White (66%). Between 2015-2019, IgG4-RD incidence was 1.41/100,000 person-years and the period prevalence was 0.003%. During a median follow-up of 742 days, the most commonly affected organs (Table 1) based on ICD codes included the pancreas (43.0%), biliary tract (30.6%), salivary glands (11.7%), and retroperitoneum (5.0%). The most frequent treatments during baseline and follow-up were glucocorticoids (64.3% and 85.1%, respectively). Azathioprine (14.1%), rituximab (14.0%), mycophenolate (11.1%), and methotrexate (8.6%) were also used during follow-up. IgG4-RD cases had more comorbidities during follow-up than comparators (Table 2), especially hypertension (53.7% vs 38.3%), diabetes (31.7% vs 16.7%), infection (22.0% vs 4.7%), osteoporosis (15.1% vs 4.2%), neoplasms (20.8% vs 8.3%), and lymphomas (5.5% vs 0.9%; all P-values < 0.01). Pancreatic enzyme replacement was prescribed during baseline and follow-up in 4.2% and 17.4% of cases, respectively. IgG4-RD cases vs comparators had more outpatient and emergency room visits, and hospitalizations (Table 3).
Conclusion: In this first large-scale outcomes study of IgG4-RD in the US, we have found both the clinical and HCRU burdens are substantial. The prevalence of IgG4-RD is likely underestimated given the recent recognition of the disease entity. Nevertheless, IgG4-RD is at least as common as ANCA vasculitis and systemic sclerosis. Hepatobiliary disease was the most common manifestation and glucocorticoids the most frequent treatment, which are reflected in the excess comorbidity burden of IgG4-RD patients, including pancreatic insufficiency and glucocorticoid toxicities. These findings support the need for effective steroid-sparing therapies for IgG4-RD and studies evaluating malignancy in IgG4-RD.
1ACR Open Rheumatol. 2022;4:371.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wallace Z, Miles G, Smolkina E, Petruski-Ivleva N, Madziva D, Cook C, Fu X, zhang y, Stone J, Choi H. The Epidemiology, Clinical Outcomes, and Healthcare Resource Utilization of IgG4-Related Disease Among Commercially Insured People in the United States [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-epidemiology-clinical-outcomes-and-healthcare-resource-utilization-of-igg4-related-disease-among-commercially-insured-people-in-the-united-states/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-epidemiology-clinical-outcomes-and-healthcare-resource-utilization-of-igg4-related-disease-among-commercially-insured-people-in-the-united-states/