Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: RA – Treatments Poster III: RA Treatments & Their Safety (1674–1710)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Piclidenoson, a highly selective A3 adenosine receptor (A3AR) agonist, demonstrated safety and efficacy in phase 2 clinical studies in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and psoriasis. Piclidenoson induces selective apoptosis of inflammatory cells via a molecular mechanism which entails de-regulation of the Wnt signaling pathway.
Methods: This randomized, double-blind, active- and placebo-controlled, parallel-group study enrolled patients with clinically active RA who were methotrexate (MTX)-naïve. Eligible patients were randomized to 4 groups in a 2:2:2:1 ratio: piclidenoson 1 mg; piclidenoson 2 mg; MTX; or matching placebo tablets/capsules. Piclidenoson or matching placebo tablets were administered every 12 h for up to 24 weeks of treatment. MTX or matching placebo capsules were administered once a week according to the dosing schedule. The primary endpoint was efficacy (noninferiority) of piclidenoson administered for 12 weeks relative to oral MTX, as assessed by the proportion of patients achieving a disease activity score (DAS) of low disease activity (LDA). Additional analyses of the primary efficacy parameter included comparison of each dose of piclidenoson to placebo at Week 12. Secondary endpoints included comparing response rates (ACR20, ACR50, and ACR70) between piclidenoson (each dose) and MTX or placebo. The study was designed to enroll 525 patients.
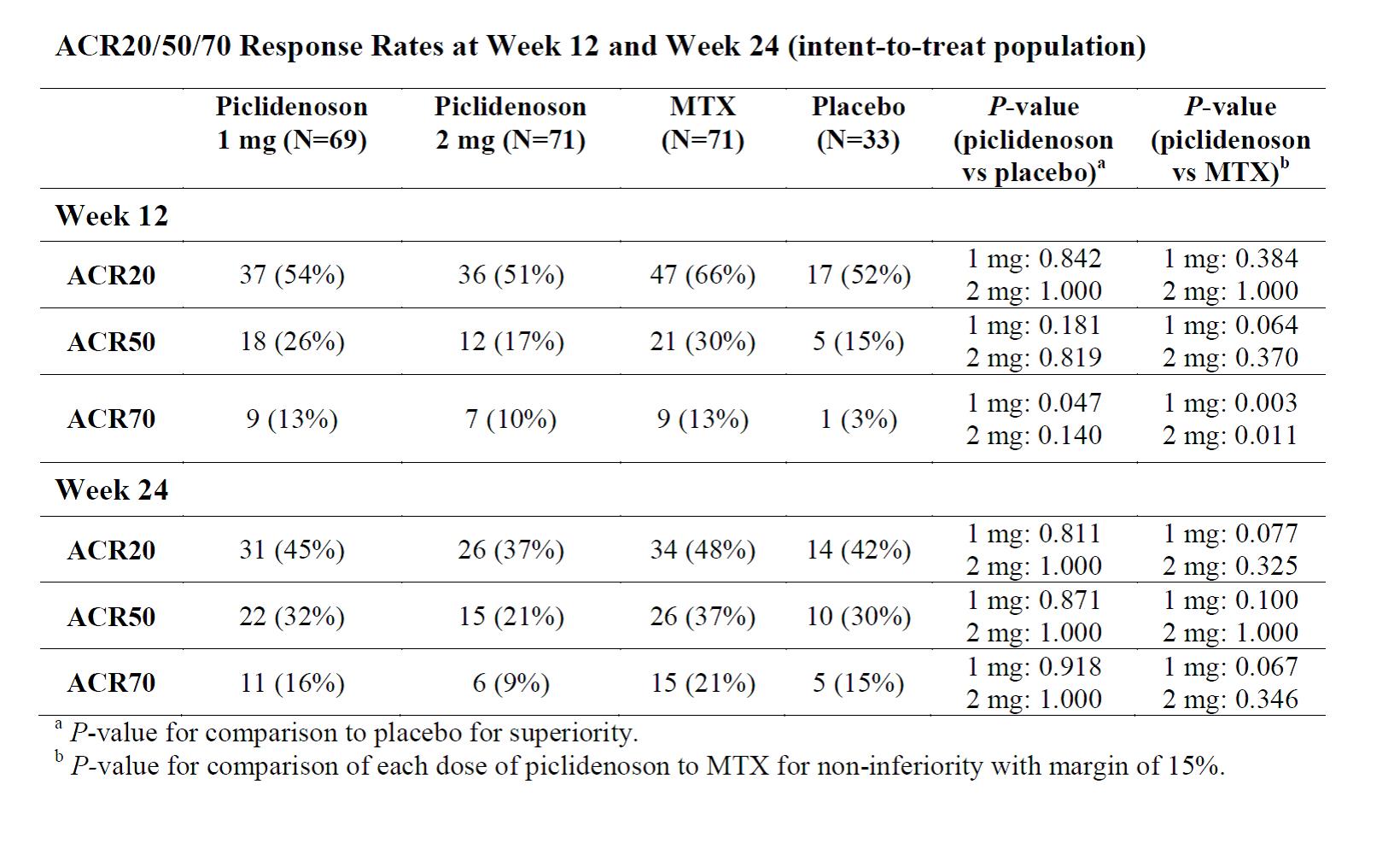
Results: Due to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, enrollment was paused and an interim analysis was performed after 50% of participants reached the Week 12 visit evaluation. The interim analysis included a total of 252 patients (72, 73, 73, and 34, in the piclidenoson 1 mg, piclidenoson 2 mg, MTX, and placebo groups, respectively). Patient demographics and baseline characteristics were overall similar between the groups. For the entire population included in the interim analysis, the median (range) age was 56 (18-75) years, and 197 (78%) were females. Piclidenoson was safe and very well tolerated. The proportion of patients experiencing any treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were similar for all groups (17%, 25%, 26%, and 29%, respectively) and the majority of TEAEs were mild. Although piclidenoson efficacy was significantly superior to placebo, the study did not meet the primary endpoint which was noninferiority vs MTX (Figure). At 12 and 24 Weeks, ACR20, ACR50 and ACR70 response rates were overall similar between the piclidenoson 1 mg (which was more effective than the 2 mg dose) and the MTX groups. The clinical benefits of piclidenoson 1 mg (as reflected in the ACR50 and ACR70 response rates) seemed more pronounced after 24 weeks (Table).
Conclusion: Piclidenoson was safe, but did not meet the primary endpoint in the current study; although it was superior to placebo in the DAS-LDA analysis. Since the primary endpoint was not met, the trial was discontinued by the sponsoring company.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Reitblat T, Gurman- Balbir A, Harpaz Z, Farbstein M, Silverman M, Kerns W, Fishman P. The Efficacy and Safety of Piclidenoson vs Methotrexate in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Phase 3 Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-efficacy-and-safety-of-piclidenoson-vs-methotrexate-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-efficacy-and-safety-of-piclidenoson-vs-methotrexate-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study/