Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The aim of this systematic review is to determine the effects of IL-17 inhibitors on major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in patients with psoriasis (PsO) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
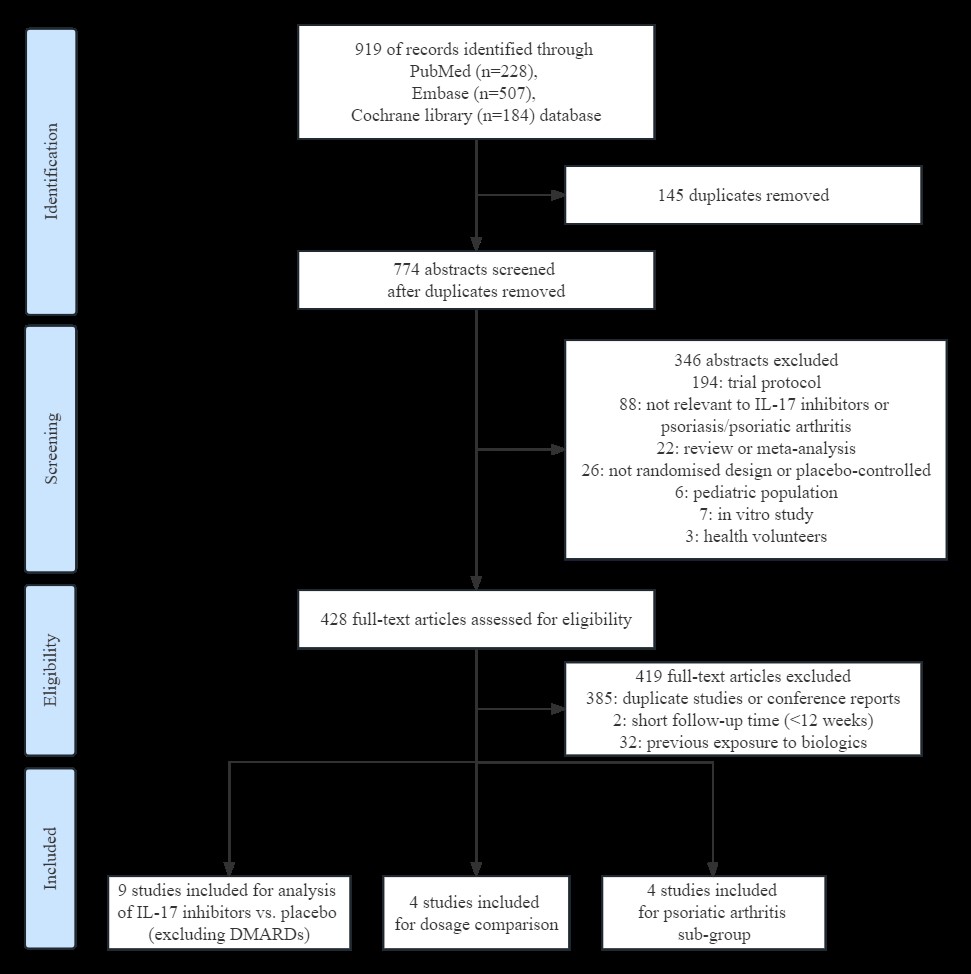
Methods: A search for randomized controlled trials of patients with PsO/PsA treated with IL-17 inhibitors that reported confirmed MACEs was conducted on December 7, 2022, in Medline, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for Randomized Controlled Trials. Two reviewers screened titles and abstracts and selected papers for full-text review. Trials that included the previous use of biologic disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs were excluded. Risk ratios were calculated by the Mantel-Haenszel random-effect method. Heterogeneity across studies was measured by χ2 test and I2 statistics. Funnel plot analysis was produced to detect potential publication bias.
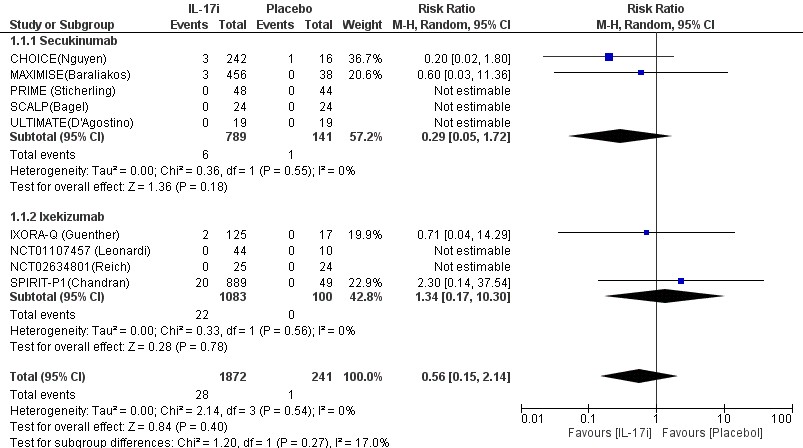
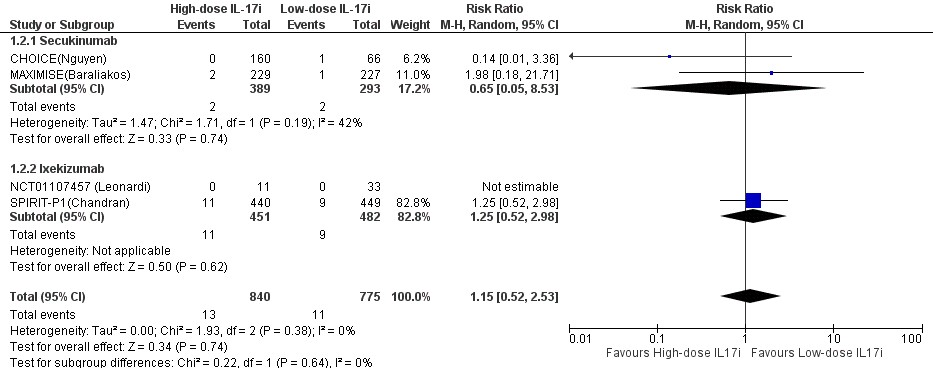
Results: Of the 919 references identified, 9 RCT studies were eligible for quantitative synthesis (n=2096 patients). The use of IL-17 inhibitors was not correlated with a statistically significant change in the risk of MACEs (Risk Ratio 0.56; 95% CI 0.15 to 2.14; p= 0.40). Subgroup analysis of secukinumab or ixekizumab also did not demonstrate changes in the risk for MACEs. Additionally, there was no detectable dose-dependent effect of IL-17 inhibitors on the risk of MACEs.
Conclusion: IL-17 inhibitor use is not correlated with a change in risk for major adverse cardiovascular in patients with PsO/PsA that have not previously received biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ni R, Zheng J, Guo R, Kumar B. The Effects of Interleukin 17 Inhibitors on Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients Naïve to Biologic Agents with Psoriasis or Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effects-of-interleukin-17-inhibitors-on-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-naive-to-biologic-agents-with-psoriasis-or-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-ran/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effects-of-interleukin-17-inhibitors-on-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-in-patients-naive-to-biologic-agents-with-psoriasis-or-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-review-and-meta-analysis-of-ran/