Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: We evaluated the effect of uric acid lowering therapy (ULT) in reducing the new development of comorbidities and the frequency of acute attacks in gout patients.
Methods: We retrospectively examined data of 200 patients who were diagnosed to have gout according to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria. The patients with at least 3 years of follow up during the period from January 1996 to December 2012 were divided into 2 groups; those whose mean serum uric acid level (sUA) < 6mg/dL (2012 ACR uric acid treatment target) and mean sUA °Ã 6mg/dL. Comorbidities of gout such as hypertension (HTN), type II diabetes mellitus (DM), chronic kidney disease (CKD), cardiovascular disease (CVD) and kidney stone were compared in each group at baseline and at last follow-up visit. Frequency of acute gout attacks were compared between the groups. Mann-Whitney U test and chi-square test was used to compare the variables between the 2 groups. McNemar's test was used to evaluate the treatment effects in comorbidities of gout in each group. A value of p < 0.05 was considered significant.
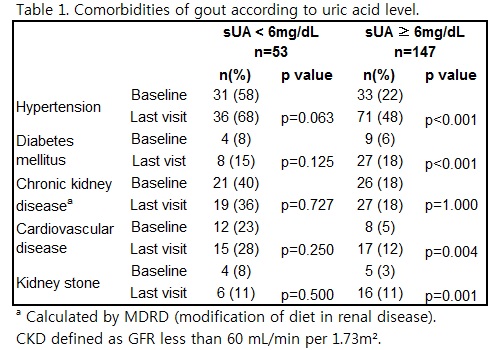
Results: Fifty-three patients were allocated to the adequately treated group (mean sUA < 6mg/dL) and 147 patients were allocated to the inadequately treated group (mean sUA °Ã 6mg/dL). Only 1 patient in the adequately treated group was woman. Patients in the adequately treated group was older (54 ± 13 years vs. 44 ± 12 years, p<0.001) with lower BMI (24.5 ± 4.5kg/m©÷ vs. 25.9 ± 4.5kg/m©÷, p=0.003) and kept higher medication possession rate (MPR) (94 ±10% vs. 61 ± 27 %, p<0.001) compared to the inadequately treated group. There was no difference in the duration of gout, ULT duration, tophi, family history of gout, smoking, alcohol, hypercholesterolemia between the groups. During the mean follow up period of 8 years, the yearly rate of acute attack (0.25 ± 0.39 vs. 0.47 ± 0.53, p<0.001) was lower in the adequately treated group compared to the inadequately treated group. New development of HTN, DM, CVD and kidney stone was lower in the adequately treated group compared to the inadequately treated group (Table 1). The frequency of CKD tended to decrease in the adequately treated group from 21 patients at baseline to 19 patients at last follow up visit.
Conclusion: Tight control of uric acid decreased the development of acute gout attacks and comorbidities of gout such as HTN, DM, CVD and urinary stone despite the same CVD risk factors. The renal function can be recovered by intensive ULT therapy.
Disclosure:
K. Joo,
None;
W. Park,
None;
S. R. Kwon,
None;
M. J. Lim,
None;
K. H. Jung,
None;
H. Joo,
None;
S. S. Kim,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-uric-acid-lowering-therapy-in-preventing-comorbidity-and-acute-attack-of-gout-a-retrospective-study/