Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
Capsaicin (CAP) and Resiniferatoxin (RTX) are vanilloid receptor agonists that when given by intra-articular injections, can normalize Evoked Pain Scores (EPS) and Automated Dynamic Weight Bearing (ADWB) measures in carrageenan-induced acute inflammatory arthritis. To determine whether these vanilloid receptor agonists might have benefit in chronic inflammatory arthritis pain, we measured changes in ADWB and EPS due to joint pain in mice with Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA) induced chronic inflammatory arthritis with and without treatment with intra-articular (IA) injections of CAP and RTX.
Methods:
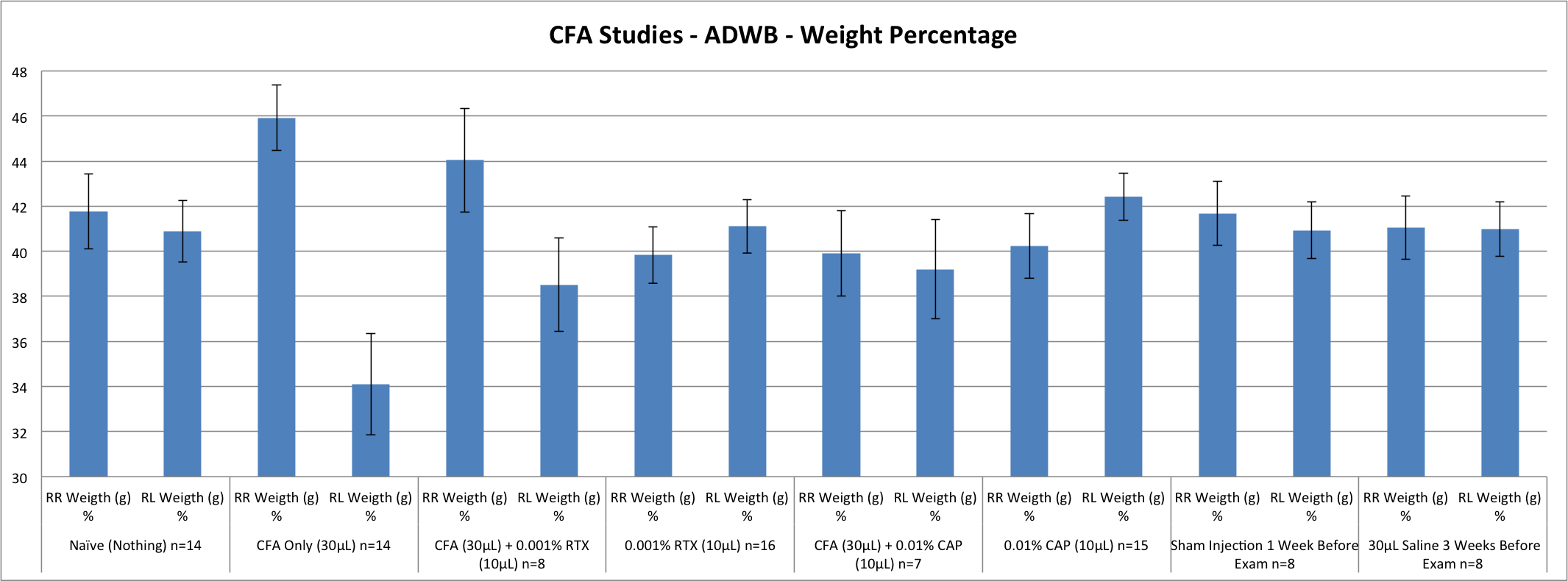
Chronic Inflammatory arthritis was produced by intra-articular injection of 30 µl of Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA) into the left knee of C57BL6 male mice 3 weeks prior to pain behavior testing. One group of mice was injected with IA RTX (10µl of 0.001%) 7 days prior to measurement of EPS and ADWB. Similarly, another group of mice were injected with 10µl of 0.01% IA CAP 7 days before pain behavior testing. Evoked pain behavior was measured by tallying fights and vocalizations per one minute with repeated palpation of the knee at 15.6 psi. ADWB (weight on each limb and time on each limb) was measured using an Automated Dynamic Weight Bearing apparatus (Bioseb, Vitrolles, France).
Results:
Chronic Inflammatory arthritis pain is demonstrated by increased EPS and reduced ADWB measures in the affected limb of arthritic mice. Na•ve mice have low EPS (0.5) and equal left to right DWB ratios for weight (1.01) and time (1.006). Chronic inflammatory arthritis induced by IA CFA resulted in a significantly increased EPS (3.5) and a decrease in left to right ADWB ratios for weight (0.76) and time (0.93) when compared with controls. Treatment with IA CAP 7 days prior to pain behavior testing resulted in improvement in EPS (1.38) and near normalization of left to right ADWB ratios for weight (0.99) and time (1.01) when compared to the chronic inflammatory arthritis model. Treatment with IA RTX 7 days prior to the exam led to improved EPS (1.67) and improved left to right ADWB ratios for weight (0.90) and time (0.98) when compared to the chronic inflammatory arthritis model. IA CAP alone and IA RTX alone did not have an impact on EPS or ADWB ratios when given 7 days prior to pain behavioral testing.
Conclusion:
Using ADWB and EPS, we were able to quantitate pain in a murine chronic arthritis model. Intra-articular CFA administration resulted in a significant increase in EPS and decreased ADWB measures in the affected limb. Treatment with CAP and RTX in these mice improved pain measures as assessed by EPS and ADWB measures. These results are comparable to those previously reported when mice were pretreated in an acute inflammatory arthritis model. The optimal dose of RTX and CAP for therapeutic benefit and duration of response has yet to be determined.
Disclosure:
J. Bert,
None;
C. W. Dorman,
None;
S. Frizelle,
None;
S. C. Funkenbusch,
None;
H. E. Krug,
None;
M. L. Mahowald,
None.
« Back to 2014 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-treatment-with-resiniferatoxin-and-capsaicin-on-dynamic-weight-bearing-measures-and-evoked-pain-responses-in-a-chronic-inflammatory-arthritis-murine-model/