Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : Substance P (SP) release and binding to NK-1 produces pain transmission. Neurotoxins (NT) that prevent release of SP, such as onabotulinum toxin (BoNT/A), and those that deplete SP, such as vanilloids (VAN), produce analgesia in chronic murine arthritis. This study evaluated the relationship of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) SP expression to pain and analgesia in murine arthritis treated with these NTs.
Methods: C57Bl6 male mice received intra-articular (IA) carrageenan, Complete Freund’s Adjuvant (CFA) or Collagenase (COL) to produce acute inflammatory, chronic inflammatory or chronic noninflammatory arthritis respectively. IA therapies were given at appropriate intervals before examination. Twelve-week-old mice were examined after arthritis induction. Evoked and spontaneous pain was quantitated. DRGs were harvested for immunohistochemistry (IHC) after pain assessment. SP expression was measured as % DRG neurons expressing SP.
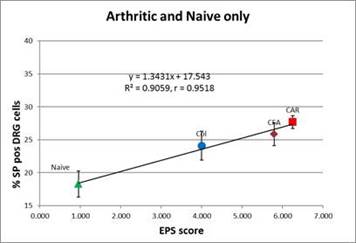
Results: Evoked pain in arthritic and naïve mice correlated with SP expression (R2=0.906, β=1.343). IA vanilloid agonists and antagonist reduced SP expression in a dose dependent manner in chronic inflammatory arthritis (CFA). IA BoNT/A reduced SP expression in CFA arthritis but significantly increased SP expression in COL arthritis at 4 weeks after induction but not at 6 weeks. None of the neurotoxins altered SP expression in non-arthritic mice.
Conclusion: Both SP depletion and release inhibition are analgesic in chronic murine arthritis. SP expression varied with NT mechanism of action in COL arthritis at 4 weeks. BoNT/A had different effects on SP expression in 4 week COL and CFA arthritis but SP expression in 6 week COL treated with BoNT/A was similar to that seen in BoNT/A treated CFA. The effect of NT on SP expression may depend on pathophysiology of pain production and chronicity. Understanding the effect of NT treatment on NK-1 expression will be important.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Krug H, Frizelle S, Blanshan N, Dorman CW, Mahowald M. The Effect of Intra-Articular Neurotoxin on Arthritis Pain and Substance P Expression in the Dorsal Root Ganglion: Results from Murine Arthritis Models [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-intra-articular-neurotoxin-on-arthritis-pain-and-substance-p-expression-in-the-dorsal-root-ganglion-results-from-murine-arthritis-models/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-intra-articular-neurotoxin-on-arthritis-pain-and-substance-p-expression-in-the-dorsal-root-ganglion-results-from-murine-arthritis-models/