Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Mechanistic differences between biologic DMARDs are poorly understood. Exploring these mechanisms includes assessing the role of HLA-DRB1 alleles containing the shared epitope (SE), which are present in 85% of anti-CCP2+ patients (pts) with RA,1 and changes in immune cell subsets relevant in RA. In a head-to-head (H2H) study, abatacept (ABA) markedly altered immune cell subsets in pts with RA.2 In the present study, numerically higher efficacy responses with ABA versus adalimumab (ADA) were reported after 24 weeks (wks) in the overall population, specifially in SE+ pts.3 In the analysis reported here, we explored the relationship between HLA-DRB1 SE genotype and the effects of ABA or ADA on immune cell subsets and disease activity.
Methods: This H2H, single-blinded trial (NCT02557100) in biologic-naïve pts with active RA enrolled anti-CCP+ ( >3x upper limit of normal), RF+ adults with early (≤12 months of symptoms), moderate-to-severe RA (ACR/EULAR 2010 criteria). Pts were randomized 1:1 to SC ABA 125 mg wkly or SC ADA 40 mg every 2 wks (both with stable MTX) for 24 wks. Pts were grouped by HLA-DRB1 SE genotype (−, no SE allele; +, ≥1 SE allele). Efficacy was assessed to Wk 24 by proportions of ACR20/50/70 responders in ABA versus ADA arms by SE status. Changes in immune cell subsets with ABA versus ADA were measured by flow cytometry to Wk 24 in the overall population and by SE status. Benjamini–Hochberg procedure with a 10% false positive discovery rate was used to select significant immune cell subsets in the overall population.
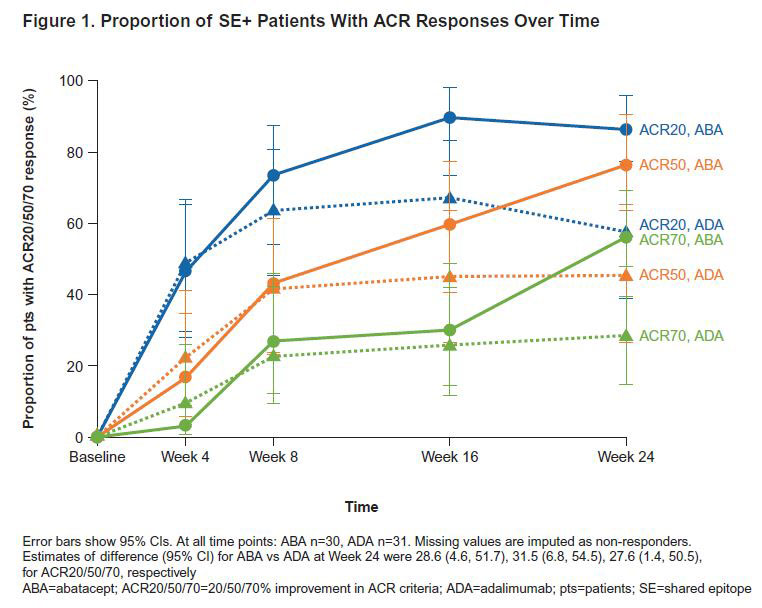
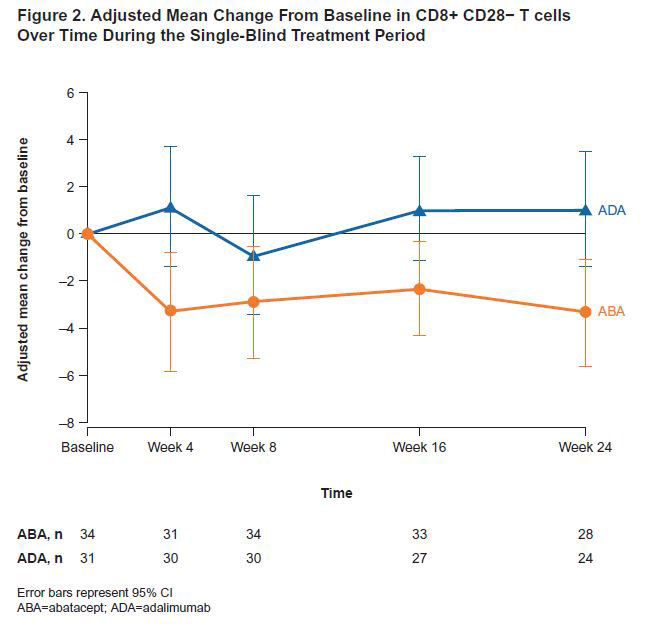
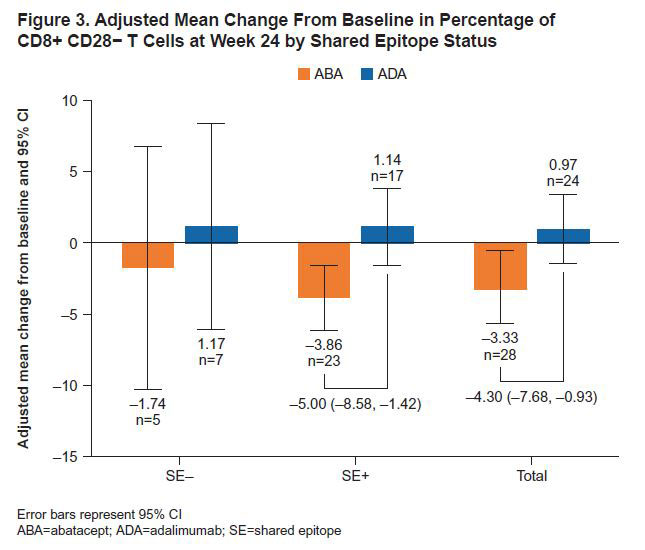
Results: 80 pts were treated: 40 ABA (9 SE−, 30 SE+, 1 SE unknown) and 40 ADA (9 SE−, 31 SE+). Baseline characteristics were similar between treatment (tx) arms. Mean (SD) age, disease duration and DAS28 (CRP) were 46.0 (14.4) years, 5.5 (2.6) months and 5.2 (1.1), respectively; 75% were female. SE+ pts versus SE− pts had greater (mean [SD]) CRP (16.1 [27.8] vs 4.8 [3.5] mg/L), anti-CCP2 (1216.6 [1525.1] vs 368.1 [433.6] U/mL) and RF levels (148.5 [130.1] vs 78.2 [44.2] kU/L); other characteristics were similar. SE+ pts had similar or numerically higher ACR20/50/70 responses with ABA versus ADA as early as Wk 8 and sustained to Wk 24 (Figure 1). At Wk 24, ABA significantly changed the proportions of key immune cell subsets versus ADA (tx difference [95% CI]): naïve CD4+ T cells (8.7 [5.6, 11.7]; p< 0.0001), naïve CD8+ T cells (6.3 [1.9, 10.7]; p=0.0059), CD8+ CD28− T cell (−4.3 [−7.7, −0.9]; p=0.0136; Figure 2), CD4+ effector memory T cells (−4.4 [−7.6, −1.2]; p=0.0086) and regulatory T cells (−1.6 [−2.2, −0.9]; p< 0.0001) in the overall population. The differential reduction in CD8+ CD28− T cells by tx group in the overall population was driven by the SE+ pts (Figure 3).
Conclusion: In this anti-CCP2+ early RA population, abatacept was effective in SE+ pts and had a significant effect on key immune cell subsets involved in adaptive immune response, relevant in RA, versus adalimumab.
References:
- Jiang X, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2015:67;352–1363.
- Nakayamada S, et al. Rheumatology 2018:57;164–174.
- Rigby W, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2019:78. Abstract 263.
Protocol manager: Marianne Peluso, BMS; Medical writing: Lola Parfitt, Caudex, funded by BMS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Buckner J, Bykerk V, Holers V, Bridges S, Rigby W, Gao S, Nys M, Ray N. The Effect of HLA-DRB1 Risk Alleles (Shared Epitope) on Changes in Immune Cell Subsets and Disease Activity Following Treatment with Abatacept versus Adalimumab in Seropositive Biologic-Naïve Patients with Early, Moderate-to-Severe RA: Data from a Head-to-Head Single-Blinded Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-hla-drb1-risk-alleles-shared-epitope-on-changes-in-immune-cell-subsets-and-disease-activity-following-treatment-with-abatacept-versus-adalimumab-in-seropositive-biologic-naive-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effect-of-hla-drb1-risk-alleles-shared-epitope-on-changes-in-immune-cell-subsets-and-disease-activity-following-treatment-with-abatacept-versus-adalimumab-in-seropositive-biologic-naive-patients/