Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: It has been demonstrated that patient reported questionnaires including disease activity, functional impairment, anxiety and depression were correlated each other. However the causal relationships among activity, function and quality of life (QoL) in AS patients has never been evaluated before. Therefore we aimed to investigate the causal relationships among factor structures (Activity, Function and QoL) in AS patients by using Structural Equations Modeling (SEM) approach.
Methods: BASDAI, BASFI and Short Form 36 (SF 36) were used for the assessment of disease activity, function and QoL. All questionnaires simultaneously employed. BASDAI and BASFI were answered by both 10-cm VAS and numeric rating scale (NRS) format. Data analysis presented here was performed by VAS scores. Activity, Function and QoL were our latent variables (i.e. factor structures). A latent model was created that demonstrating the causality among these three factor structures by means of SEM approach in Lisrel 8.8 medium. Besides, Function was also tested for mediating role between Activity and QoL. Both model fit and parameter fit values were assessed against statistical significance of the proposed model.
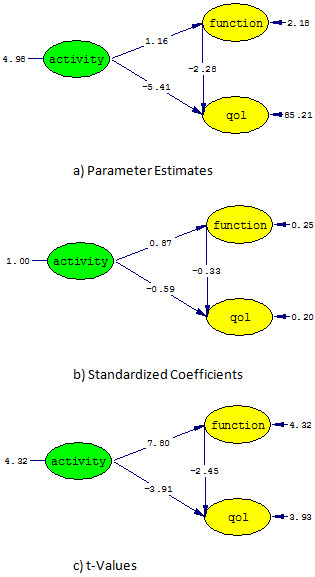
Results: A total 114 consecutive patients with AS (87 [76%] male, mean age was 39.8 ± 10.9 years) according to the modified NY criteria were included in the study. Mean (±SD) BASDAI, BASFI, SF-36 physical component summary, and SF-36 mental health component summary score were 3.6 ± 2.6, 3.3 ± 3.0, 53.1 ± 25, and 59.2 ± 19.9 respectively. Significance of parameters of about relationships between factor structures, factor loadings of latent variables by observed variables, error terms of observed variables are all tested by t-test and results are found as significant (p<0.05). Proposed model is demonstrated in Figure-1. According to that model, QoL can be significantly (|t|>1.96 and P<0.05) explained by both Activity and Function. Additionally, Function plays a mediating role that reflects the indirect effect of Activity on QoL. Direct and indirect effects are shown in Equation Model (RMSEA=0.089, c²/df =1.9, RMR=0.055, GFI=0.74, AGFI=0.69, NFI=0.95 and NNFI=0.97) and parameter fit (for all parameters |t|>1.96 and P<0.05) results satisfied allowable limits. NRS answering formats of BASDAI and BASFI were also produced similar results.
Conclusion: Our results show that proposed model is significant and both disease activity and function can explain the QoL in patients with AS. Function has also a mediating role as indirect effect of disease activity on QoL . This model can be utilized for the estimation of quality of life in AS patients in clinical practice or clinical trials.
Figure 1: Structural equations model
Disclosure:
S. Akar,
None;
S. Erdem,
None;
K. Akat,
None;
D. Solmaz,
None;
I. Sari,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-contribution-of-disease-activity-on-function-and-quality-of-life-in-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-investigating-causality-by-using-structural-equation-model/