Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with an increased risk of osteoporosis and osteoporotic fracture, but little is known about comparative risk of osteoporotic fractures between different biologic agents. We therefore aimed to investigate the comparative risk of osteoporotic fractures among RA patients who initiated TNF inhibitors (TNFi), abatacept, and tocilizumab.
Methods: We identified patients aged ≥ 40 years with at least two ICD-10 diagnosis codes for RA who initiated TNFi, abatacept, or tocilizumab from the 2002-2015 Korean National Health Insurance Service datasets. The primary outcome was a composite osteoporotic fracture endpoint of spine, hip, forearm or humerus requiring hospitalization. Secondary outcomes were vertebral and non-vertebral fractures. Follow-up period started from the day after the first dispensing date of the study drug to the earliest date among the following events: discontinuation of the study drugs, outcome occurrence, disenrollment, end of study dataset, or death. Propensity score (PS) matching with a variable ratio up to 10:1 was conducted for TNFi versus abatacept initiators and for TNFi versus tocilizumab initiators to adjust for baseline confounding. We estimated hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence interval (CI) of osteoporotic fracture risks comparing TNFi to abatacept or tocilizumab by Cox proportional hazard models stratified by a matching ratio.
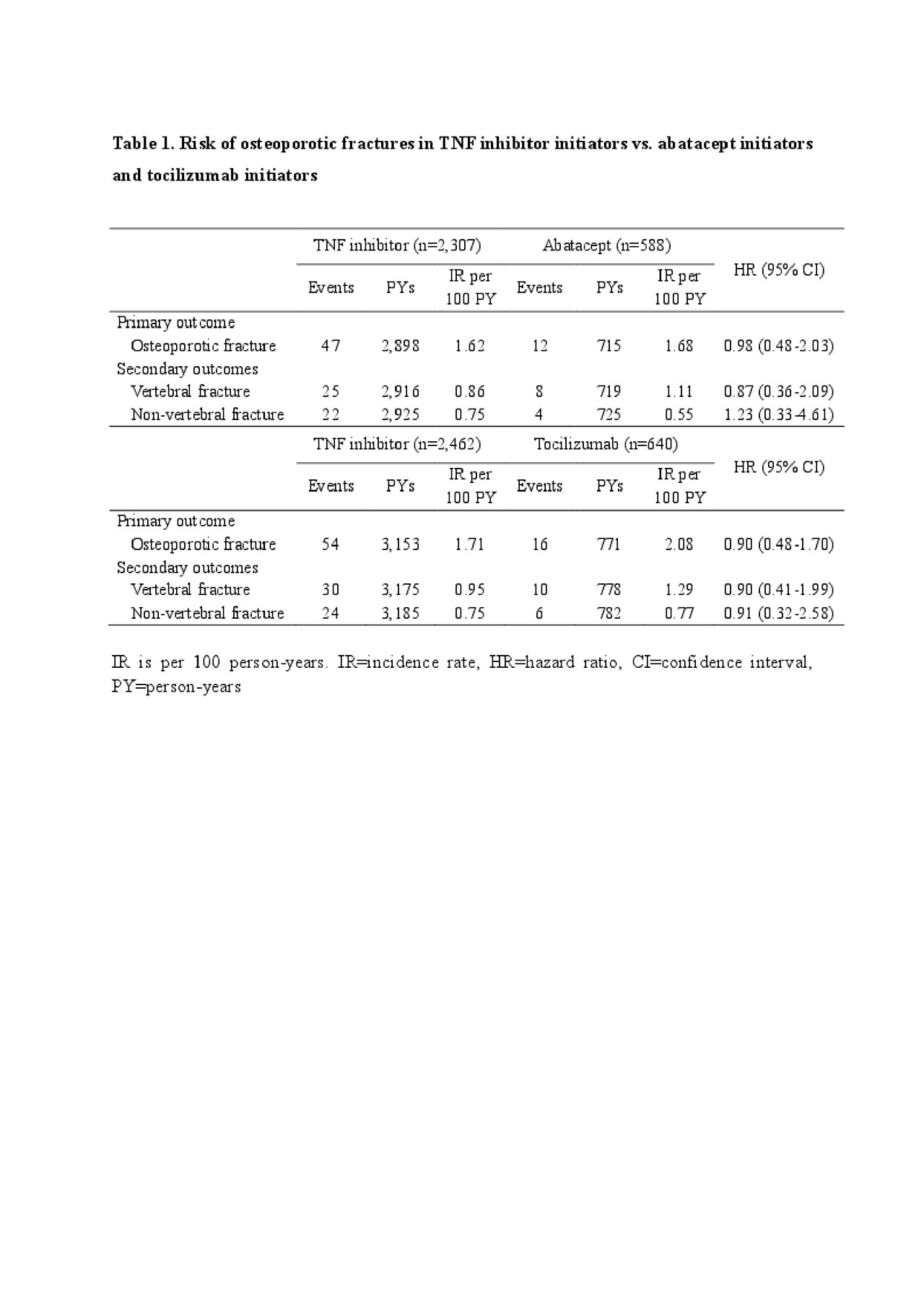
Results: We included 2,307 TNFi initiators and 588 abatacept initiators, and 2,462 TNFi initiators and 640 tocilizumab initiators in each PS-matched cohort. The incidence of the primary outcome per 100 person-years was 1.62 and 1.68 for initiators of TNFi and abatacept, and 1.71 and 2.08 for initiators of TNFi and tocilizumab, respectively. The HRs for the primary outcome were 0.98 (95% CI 0.48-2.03) comparing TNFi versus abatacept initiators and 0.90 (95% CI 0.48-1.70) comparing TNFi versus tocilizumab initiators. The adjusted risks of secondary outcomes were also comparable between RA patients initiating TNFi versus abatacept, or versus tocilizumab (Table 1).
Conclusion: We did not find a significant difference in the risk of osteoporotic fractures between TNFi and abatacept initiators, or between TNF inhibitor and tocilizumab initiators in this Korean population-based cohort study.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park E, Shin A, Dong Y, Ha Y, Lee Y, Lee E, Song Y, Kang E. The Comparative Risk of Osteoporotic Fractures Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Receiving TNF Inhibitors versus Other Biologics: A Nation-wide Cohort Study in Korea [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-comparative-risk-of-osteoporotic-fractures-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-tnf-inhibitors-versus-other-biologics-a-nation-wide-cohort-study-in-korea/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-comparative-risk-of-osteoporotic-fractures-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-receiving-tnf-inhibitors-versus-other-biologics-a-nation-wide-cohort-study-in-korea/