Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2016
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis – Small Molecules, Biologics and Gene Therapy - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Several predictors of response to tocilizumab have been described. They include a low HAQ, high baseline CRP or NK levels and certain IL-6R polymorphisms. IL-6 and sIL-6R levels have also been considered as response predictors, but with contradictory results. However, the combination of them has not been studied.
Methods: Heparinized peripheral blood was obtained from 10 healthy donors and 63 RA patients meeting the ACR criteria. In all patients, RA was refractory to treatment with DMARDs, including methotrexate. Tocilizumab treatment was begun following European and Spanish guidelines. Plasma was collected prior to first infusion(baseline), at 4 and at 12w. Laboratory analysis included an haemogram, ESR, CRP, Igs, RF, ACPAs, IL-6 and sIL-6R concentrations. Clinical data collected was DAS28, SDAI, CDAI and EULAR response criteria. K-means clustering (SPSSv.18) analysis was applied to identify groups of patients based on IL-6 and sIL-6R concentrations.
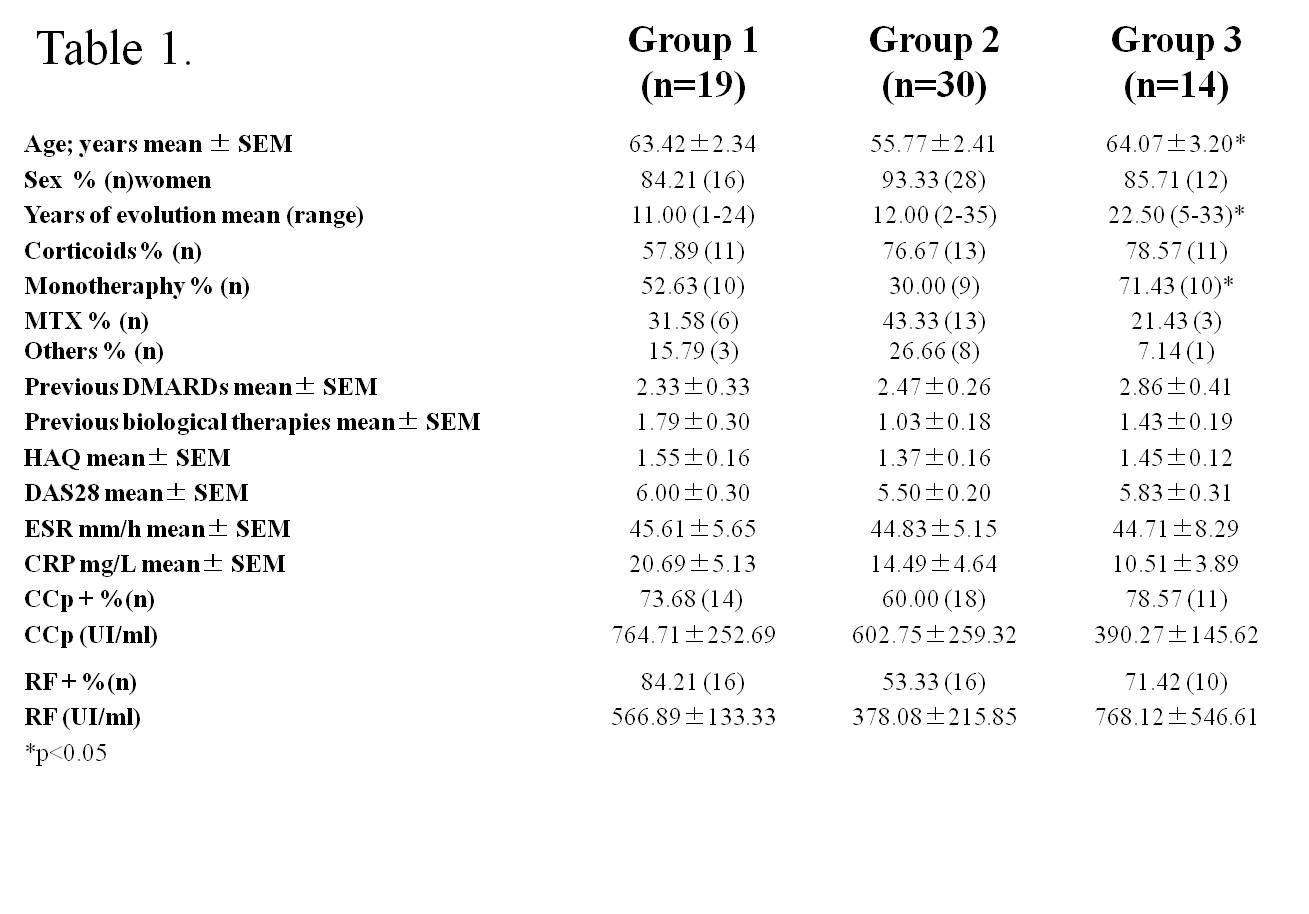
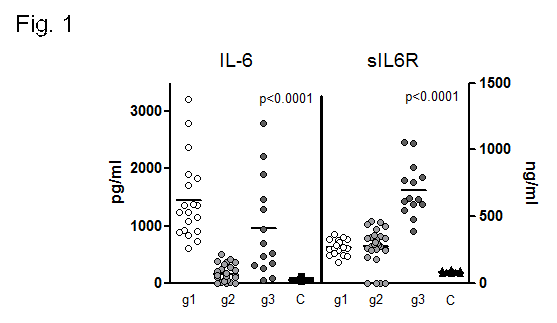
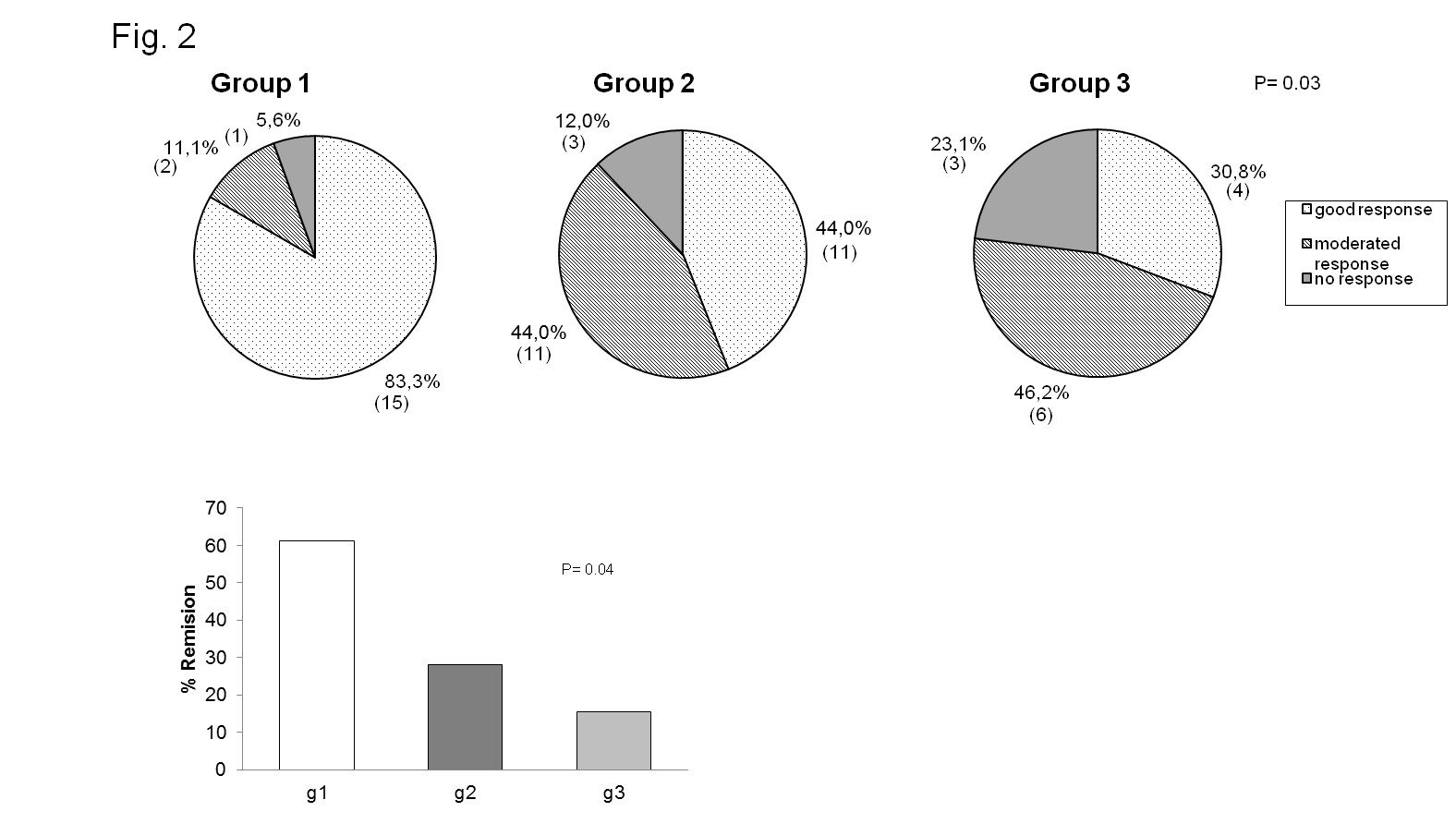
Results: Three statistical significant clusters of RA patients were defined by IL-6 and sIL-6R concentrations at baseline: Group 1 with the highest levels of IL-6 and low levels of sIL-6R; Group 2 with low levels of IL-6 and sIL-6R; and Group 3 with the highest levels of sIL-6R (fig. 1). Baseline clinical data of RA patients in each group are presented in Table 1. DAS28 was markedly reduced after 24 weeks of treatment in all groups of patients (group 1: 6.09±0.24 to 3.55±0.46 at t=24w, p=0.001; group 2: 4.68±0.32 to 2.66±0.22 at t=24w, p=0.001;group 3: 6.04±0.30 to 2.89±0.34 at t=24w, p=0.0001). Patients in group 1 achieved the highest rate of remission (60% vs.27% in group 2 and 18% in group 3,p <0.04) and the highest rate of good EULAR response (83,3% vs. 44% and 30.8% in group 3) (fig.2). IL-6 levels, that correlated with RF and IL-15 levels, SDAI and CDAI, did not substantially change after 12w of tocilizumab. On the other hand, sIL-6R levels increased significantly in most patients(93.6%) after 4w of tocilizumab. After 12w, sIL6R levels in all patients of group 1 were still high, and they decreased in 50% of patients of group 3. sIL-6R levels inversely correlated with leukocyte counts/mL and with VSG, PCR and DAS28.
Conclusion: Combination of biomarkers IL-6 and sIL6R is more useful to discriminate those patients with the best response outcome to tocilizumab than both of them separately.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Diaz-Torne C, Ortiz MA, Moya P, Hernández MV, Reina D, Castellvi I, De Agustin JJ, De La Fuente D, Corominas H, Sanmarti R, De Llobet Zubiaga JM, Vidal S. The Combination of IL-6 and IL-6 Receptor Levels As a Biomarker of Response to Tocilizumab in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-combination-of-il-6-and-il-6-receptor-levels-as-a-biomarker-of-response-to-tocilizumab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-combination-of-il-6-and-il-6-receptor-levels-as-a-biomarker-of-response-to-tocilizumab-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/