Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
To evaluate the impact of central sensitization (CS) on axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA) patients’ clinical and functional situation and quality of life.
Methods: Subjects with axSpA according to ASAS criteria and healthy controls were recruited. The central sensitization (CS) was evaluated by the central sensitization inventory (CSI). Quantitative sensory testing, which consists of pressure pain threshold (PPT), temporal summation (TS), and conditioned pain modulation (CPM), were applied. The algometer was used in all kinds of pain parameters’ assessment. The spinal hyperalgesia was evaluated from C3 and C7; T6 and T2; L3 and L5 levels. The sacroiliac PPT scores were obtained from 4 points. Trapezius muscle was used to evaluate distant control point. TS scores were evaluated over the trapezius muscle, sacroiliac joints, C7, T6, and L3 spine. In the evaluation of TS, a pressure as much the PPT value of each point was applied with pain pressure algometer ten times with a 1-second interstimulus interval. TS was calculated was by subtracting the rating at 0 seconds from the rating at 10 seconds. For the assessment of conditioned pain modulation (CPM), the first stimulus was applied to trapezius with the pressure that induced a pain intensity of 4/10 points on a VAS. After that, the right hand of the patient was immersed in 7 0C water for 20 seconds to create a conditioning stimulus. The second stimulus was applied to the trapezius. The ratio between the first and second VAS values was defined as CPM. Disease activity (BASDAI), disability (Istanbul Low Back Pain Disability Index: ILBPDI), quality of life (Ankylosing Spondylitis Quality of Life Questionnaires: ASQoL), sleep quality (Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index: PSQI), VASpain, depression (Beck Depression Inventory: BDI) and fatigue (Fatigue Severity Scale: FSS) were assessed. Comorbidities, fibromyalgia (Fibromyalgia Rapid Screening Tool: FIRST) were noted.
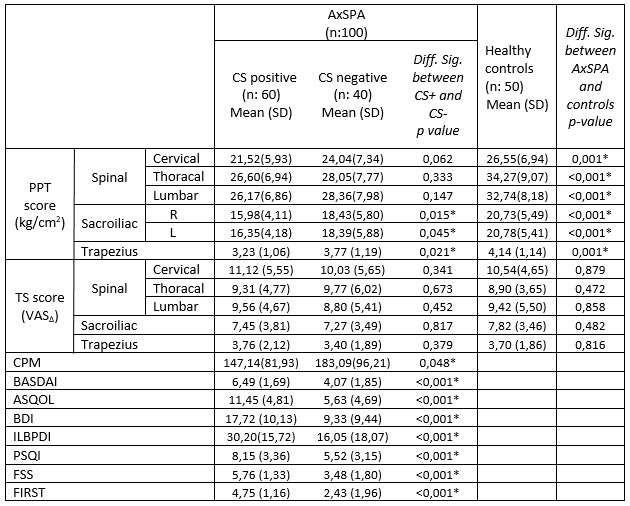
Results: One hundred patients (64 female) and 50 controls (32 female) were recruited. The mean age of patients and healthy controls were 42.31 (SS: 1.0) and 43.64 (SS:1.5), respectively. Central sensitization was detected in 60 of 100 AxSpA patients. When QST results were compared between the patient and control groups, all PPT scores were found lower (p< 0.05) in patients, but there was no significant difference between TS values. Regarding the comparison of the patients with and without CS, sacroiliac, and trapezius PPT scores were found lower in the patients with CS (p< 0.05). On the other hand, there was no significant difference between the groups in the mean measures of the other PPT and TS scores (p >0.05). CPM scores were significantly lower (p=0.048) and BASDAI, ASQoL, BDI, ILBPDI, PSQI, FSS, and FIRST scores were significantly higher (p< 0.001) in the patients with CS (Table). In regression analysis, female gender, morning stiffness duration, CPM, BDI, and FSS scores were detected as related parameters with CSI scores.
Conclusion: Central sensitization is an essential entity in axSpA patients, which affects their clinical and functional situation and quality of daily life negatively. The central sensitization assessment should be taken into consideration to determine the treatment strategy in axSpA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yücel F, Duruöz M. The Clinical and the Functional Impact of Central Sensitization on Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-and-the-functional-impact-of-central-sensitization-on-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-clinical-and-the-functional-impact-of-central-sensitization-on-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis/