Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SpA Including PsA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: The 2009 ASAS classification criteria had sensitivity of 83% and specificity of 84% for a rheumatologist diagnosis of axSpA. However, their implementation revealed varying prevalence estimates, inconsistent genetic associations, and lower clinical trial response rates prompting the global Classification in Axial Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort study (CLASSIC). These shortcomings are largely due to misuse of the ASAS 2009 criteria as diagnostic criteria. Higher levels of specificity were considered desirable. CLASSIC was established as a combined initiative of ASAS and SPARTAN to test the performance of the 2009 criteria, which were to be considered validated if prespecified sensitivity/specificity targets of ≥75%/≥90% were met, or alternatively, to be revised if these targets were not met.
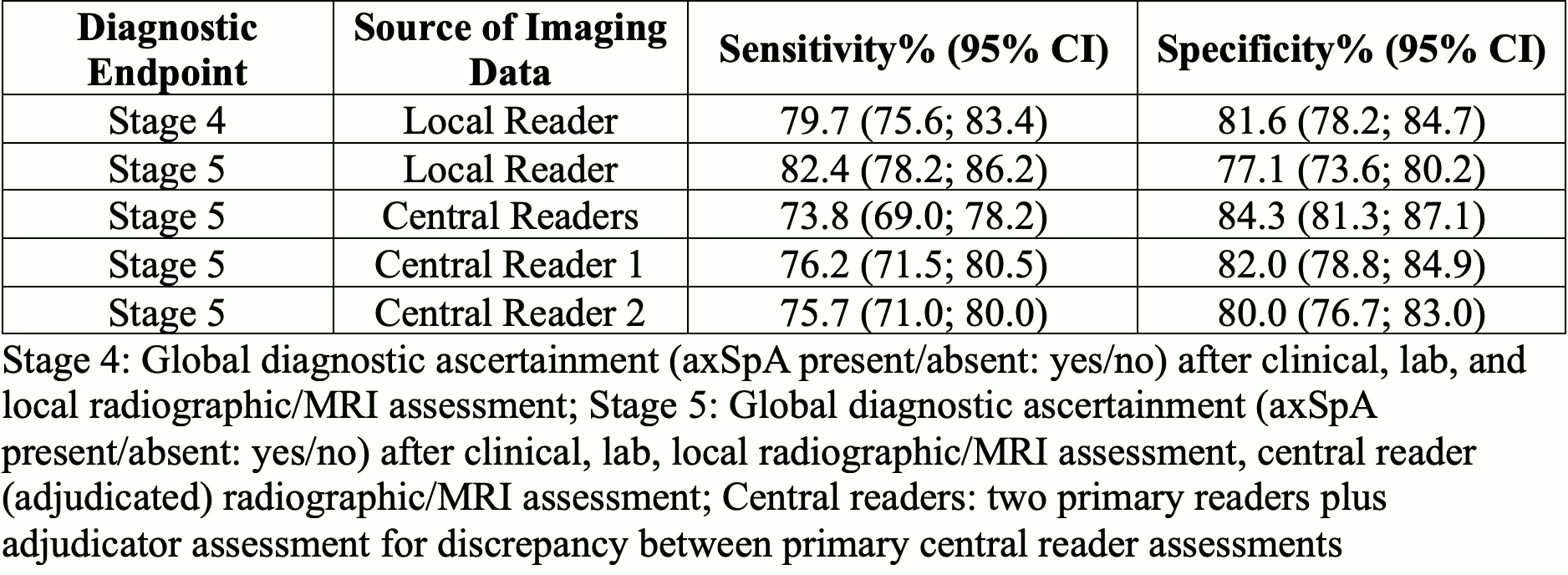
Methods: CLASSIC was a prospective study that recruited consecutive patients referred to a rheumatologist with current undiagnosed back pain suspicious for axSpA of ≥3 months duration with onset ≤45 years of age. Diagnostic assessements were performed at multiple stages to determine the presence/absence of axSpA: Stage 1. After the history and physical exam; Stage 2. After review of CRP and HLA-B27; Stage 3. After review of pelvic radiograph; Stage 4. After review of MRI by local radiologist; Stage 5. After central review of all imaging by 2 primary readers and an adjudicator (for prespecified discrepancies between central readers). The primary endpoint was attainment of specificity of ≥90% and sensitivity of ≥75% by the 2009 criteria in the entire population. If unmet, revised criteria would aim for these targets using stage 5 global diagnosis (after central imaging assessment) as the gold standard.
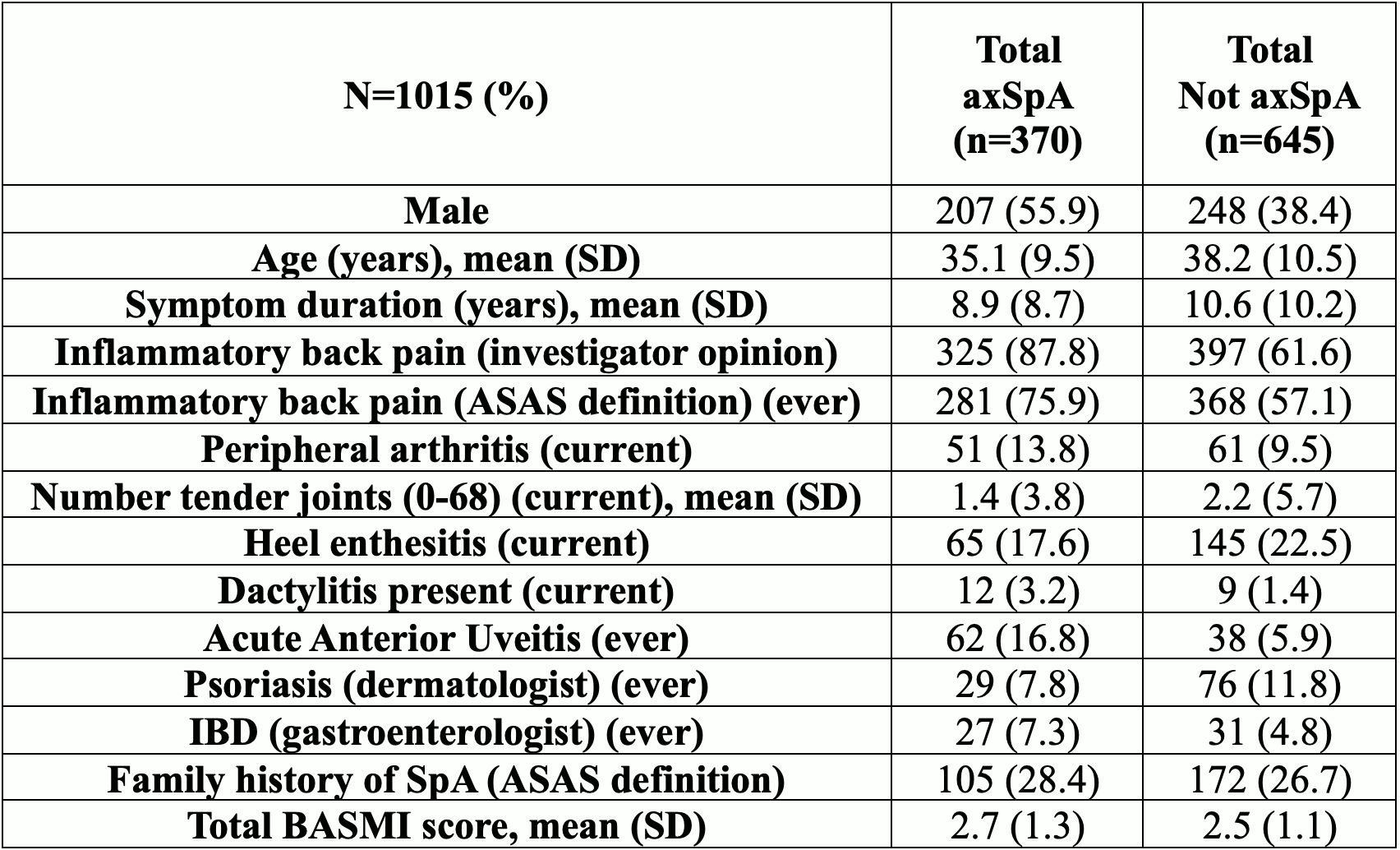
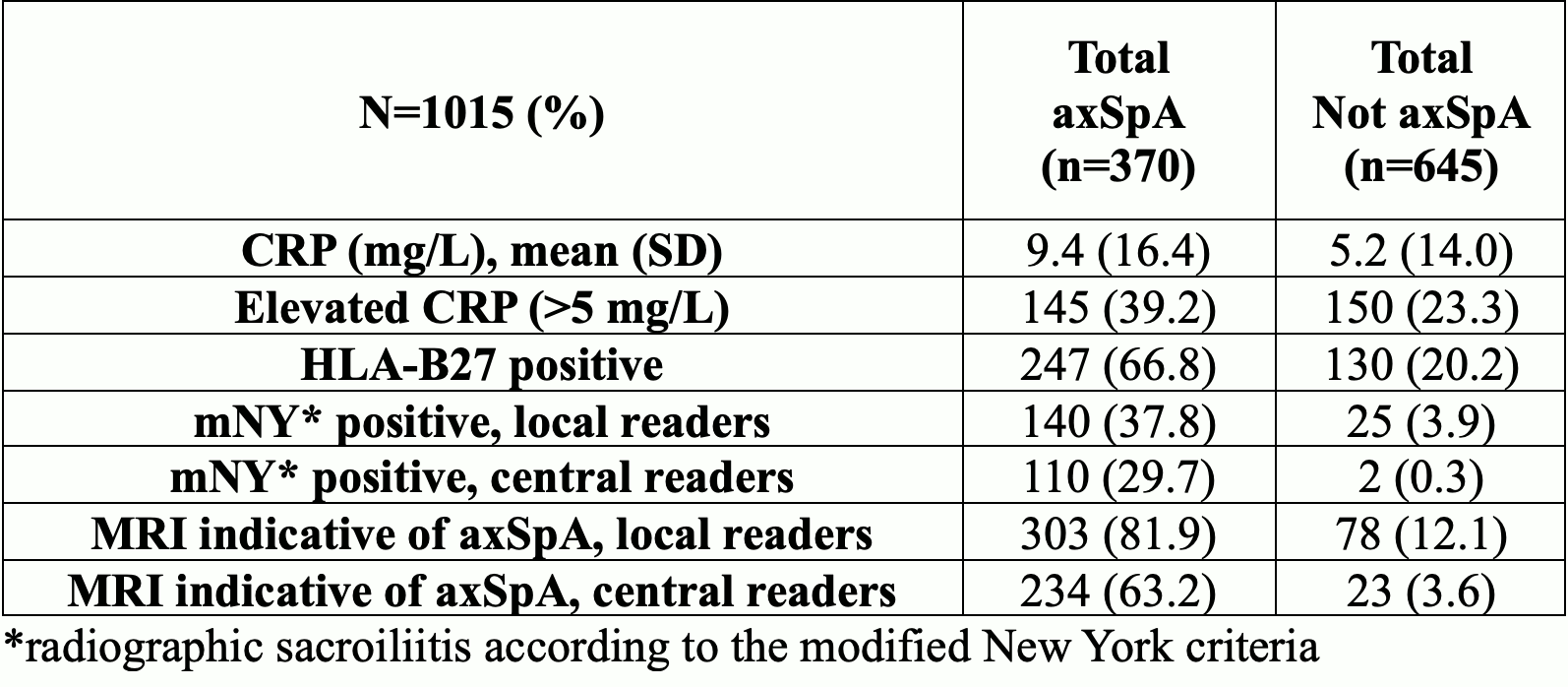
Results: CLASSIC included 1015 patients from 61 centers in 27 countries (501 from North America) of whom 370 (36.5%) were diagnosed with axSpA per stage 5 global. Among clinical variables, patients with axSpA versus non-axSpA included significantly more cases who were male (55.9%), had inflammatory back pain (88% vs 66%), current peripheral arthritis (14% vs 10%), dactylitis (3% vs 1%), and history of acute anterior uveitis (17% vs 6%) (Table 1). Tender joints, enthesitis, psoriasis, and family history were non-discriminatory. For lab and imaging measures, elevated CRP >5mg/L (39% vs 23%), positive HLA-B27 (67% vs 20%), radiographic sacroiliitis (30% vs 0.3%) and MRI indicative of axSpA (62% vs 2%) were significantly more frequent in cases with axSpA vs non-axSpA (Table 2). Sensitivity of the 2009 criteria varied from 73.8-82.4% and specificity varied from 77.1-84.3% depending on source of imaging data and stage 4 vs 5 global diagnostic evaluation (Table 3).
Conclusion: The 2009 ASAS classification criteria did not meet the set targets of 75% sensitivity and 90% specificity in the CLASSIC cohort, indicating the need for revision aimed at attaining these targets.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, van der Heijde D, Caplan L, Landewé R, Gensler L, Machado P, Sepriano A, van Gaalen F, van Lunteren M, Vandermeer B, Sieper J, Deodhar A, Rudwaleit M. The Classification in Axial Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort Study: Performance of the 2009 Assessments in Spondyloarthritis International Society Classification Criteria [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-classification-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-inception-cohort-study-performance-of-the-2009-assessments-in-spondyloarthritis-international-society-classification-criteria/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-classification-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-inception-cohort-study-performance-of-the-2009-assessments-in-spondyloarthritis-international-society-classification-criteria/