Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic inflammation in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) patients accelerates the process of atherosclerosis; this increases the risk of presenting a major cardiovascular (CV) event than the general population. The carotid ultrasound (US), a non-invasive diagnostic tool, has the ability of detecting subclinical atherosclerosis, but it is not available to all patients.
The aim of this study was to determine which is the best CV risk (CVR) algorithm to predict the presence of carotid plaque (CP) in PsA patients.
Methods: This was a cross-sectional and observational study. A total of 78 patients aged 40-75 years, who fulfilled the 2006 CASPAR classification criteria for PsA were included. The CVR of each patient was assessed by six different CVR algorithms, including: Framingham Risk Score (FRS)-lipids, FRS-body mass index (FRS-BMI), American College of Cardiology and American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) Risk Algorithm, Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation (SCORE), QRISK3 and Reynolds Risk Score (RRS). A carotid US was performed in all study subjects to identify the presence of CP. A ROC-curve analysis was done to establish the cut-off points of each algorithm to predict the presence of CP, calculating sensitivity, specificity and area under the curve (AUC) to determine the discriminative capacity. A p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
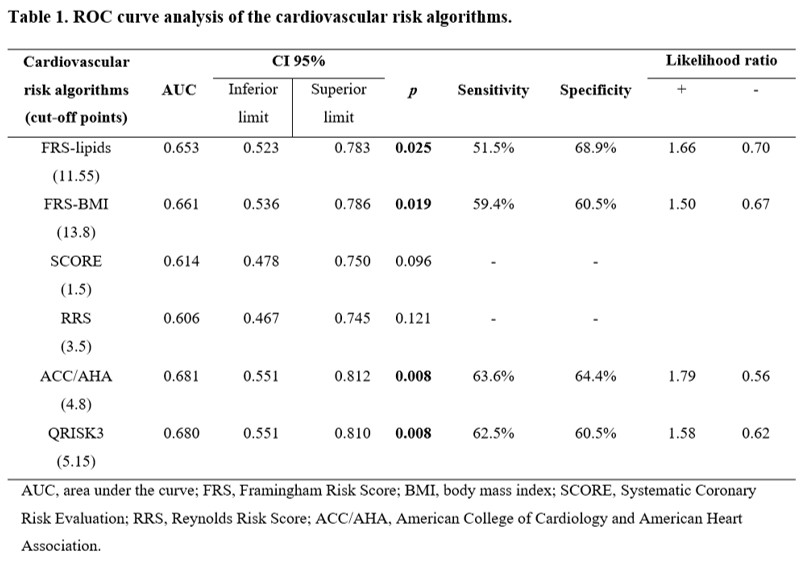
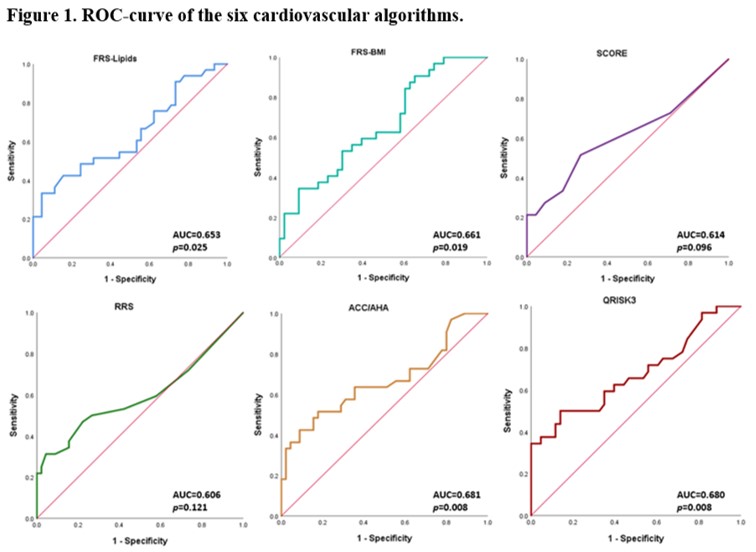
Results: Most patients were women (55.1%) with a mean age of 53.46 (±10.86) years. The prevalence of CP was 42.3%. Four of the six CVR algorithms showed the capacity of predicting CP in PsA patients. FRS-lipids showed an AUC 0.653 (0.523-0.783), p=0.025, a cut-off point ≥11.55, a sensitivity of 51.5% and specificity of 68.9%. FRS-BMI showed an AUC 0.661 (0.536-0.786), p=0.019, a cut-off point ≥13.8, sensitivity of 59.4% and specificity of 60.5%. ACC/AHA showed an AUC 0.681 (0.551-0.812), p=0.008, a cut-off point ≥4.8, sensitivity of 63.6% and specificity of 64.4%. QRISK3 showed an AUC 0.680 (0.551-0.810), p=0.008, a cut-off point ≥5.15, sensitivity of 62.5% and specificity of 60.5% (Table 1, Figure 1).
Conclusion: The best CVR algorithm to predict CP in PsA patients was the ACC/AHA risk score. However, there is a need of lower cut-off points to have the capacity of identifying patients classified in the low-moderate risk, according to these algorithms, with subclinical atherosclerosis, who would benefit from an opportune treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guajardo-Jauregui N, Colunga-Pedraza I, Azpiri-Lopez J, Galarza-Delgado D, Rodriguez-Romero A, Flores-Alvarado D, Loya-Acosta J, Meza-Garza A, Cardenas-de La Garza J, Lugo-Perez S, Castillo-Treviño J. The Best Cardiovascular Risk Algorithm to Predict the Presence of Carotid Plaque in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-best-cardiovascular-risk-algorithm-to-predict-the-presence-of-carotid-plaque-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-best-cardiovascular-risk-algorithm-to-predict-the-presence-of-carotid-plaque-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/