Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: Plenary II (0849–0854)
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 9:15AM-9:30AM
Background/Purpose: The 2009 ASAS classification criteria had sensitivity (Sn) of 83% and specificity (Sp) of 84% for a rheumatologist diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). Given the high prevalence of back pain, greater specificity would be desirable. The global Classification in Axial Spondyloarthritis Inception Cohort (CLASSIC) study was established as a combined initiative of ASAS and SPARTAN to validate the performance of the 2009 criteria according to prespecified Sn/Sp targets of ≥75%/≥90%.
Methods: CLASSIC recruited consecutive patients referred to a rheumatologist with current undiagnosed back pain of ≥3 months duration with onset ≤45 years of age. Diagnostic evaluations for axSpA were performed at 5 stages: Stage 5 provided all diagnostic information including centralized imaging review by two primary readers and an adjudicator, and served as reference standard. The cohort data were randomly divided into testing and validation datasets (50:50). The testing dataset was used to develop candidate criteria, while the validation dataset evaluated whether criteria achieved the Sn/Sp targets, using the stage 5 global diagnosis as the reference standard. Regression techniques (least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO), multivariable logistic regression (MLR)) were used to identify which SpA variables were independently associated with stage 5 diagnosis and for estimating the strength of this association according to LASSO coefficients. Final selection of SpA variables and their weighting was determined by expert consensus and the final proposal was selected by a vote of the combined ASAS and SPARTAN membership.
Results: CLASSIC included 1015 patients from 61 centers in 27 countries of whom 370 (36.5%) were diagnosed with axSpA per stage 5 global. The 2009 ASAS classification criteria did not meet the prespecified targets (Sn 82.4%, Sp 77.1%)1, indicating the need for revised criteria. MRI of the SIJ indicative of axSpA by global assessment of both active and structural lesions had the highest independent association with stage 5 diagnosis of axSpA followed by radiographic sacroiliitis. Selected clinical variables were HLA-B27, inflammatory back pain, inflammatory bowel disease, acute anterior uveitis, heel enthesitis, and dactylitis. Expert consensus led to the inclusion of psoriasis and replacement of dactylitis by elevated CRP. Two high-performing proposals in the testing dataset achieved the Sn/Sp targets in the validation dataset (Figures 1 and 2). The final proposal selected by the ASAS-SPARTAN vote (158 vs 151, 9 abstained) assigned weights for the selected SpA variables based on LASSO coefficients and achieved Sn of 79.5% and Sp of 90.4% in the validation dataset (Table).
Conclusion: The ASAS-SPARTAN revised classification criteria for axSpA achieved prespecified performance targets of ≥75% sensitivity and ≥90% specificity, emphasizing the central role of imaging and incorporating a more focused set of clinical variables compared to the 2009 ASAS criteria.
1. Maksymowych et al. Arthritis Rheumatol 2024;76 (suppl 9):0820
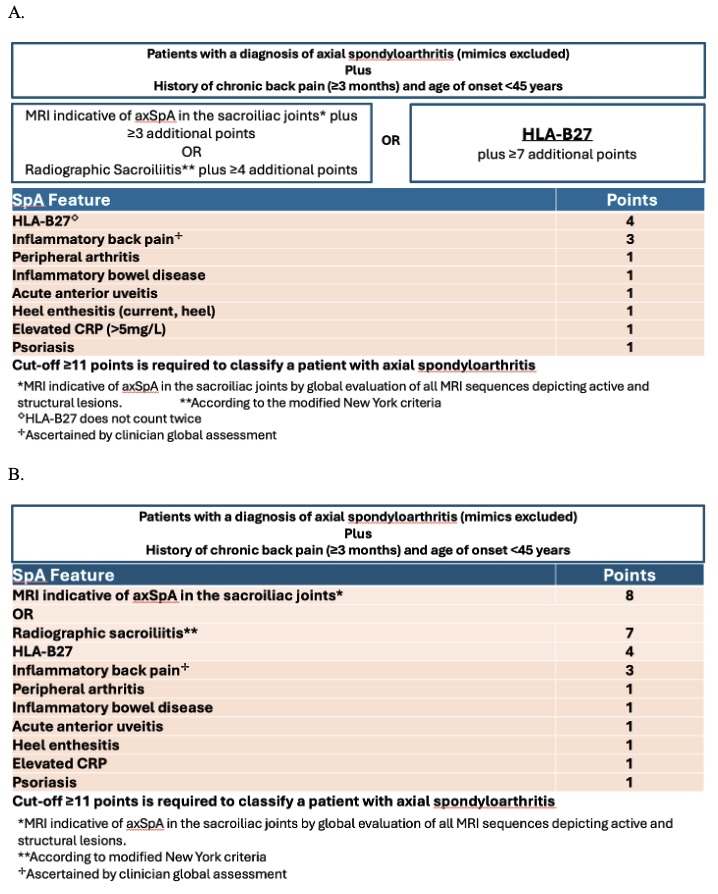 Figure 1. ASAS-SPARTAN revised classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis in A. Tree, and B. Table, formats.
Figure 1. ASAS-SPARTAN revised classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis in A. Tree, and B. Table, formats.
.jpg?3) Figure 2. Rejected alternative proposal for axial spondyloarthritis classification criteria in A. Tree, and B. Table, formats.
Figure 2. Rejected alternative proposal for axial spondyloarthritis classification criteria in A. Tree, and B. Table, formats.
.jpg) Table. Sensitivity and specificity of A. ASAS-SPARTAN revised classification criteria, and B. Rejected proposal, for final rheumatologist diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis
Table. Sensitivity and specificity of A. ASAS-SPARTAN revised classification criteria, and B. Rejected proposal, for final rheumatologist diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis
Disclosures: W. Maksymowych: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, BMS, 2, 5, 6, Boehringer-Ingelheim, 2, Celgene, 2, Chief Medical Officer for CARE ARTHRITIS, 4, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; D. van der Heijde: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Alfasigma, 2, ArgenX, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, Eli-Lilly, 2, Grey-Wolf Therapeutics, 2, Imaging Rheumatology BV, 4, Janssen, 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, Takeda, 2, UCB Pharma, 2; L. Caplan: None; R. Landewé: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, Eli Lilly, 2, Janssen, 2, Joint Imaging BV, 12, Director, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, Rheumatology Consultancy BV, 12, Director, UCB, 2; L. Gensler: Acelyrin, 2, Eli Lilly, 2, Janssen, 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, UCB, 2, 5; P. Machado: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 6; A. Sepriano: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 6; F. van Gaalen: AbbVie, 2, BMS, 2, Eli Lilly, 2, Jacobus Stichting, 5, MSD, 2, Novartis, 2, 5, Stichting ASAS, 5, Stichting vrienden van Sole Mio, 5, UCB, 5; M. van Lunteren: None; B. Vandermeer: None; S. Akar: None; S. Aydin: AbbVie/Abbott, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 5, 6, Janssen, 5, 6, Novartis, 5, 6, Pfizer, 5, 6, UCB, 5, 6; X. Barliakos: Abbvie, 1, 2, 5, Advanz, 1, 2, Alexion, 1, 2, Alfasigma, 1, 2, Amgen, 1, 2, Astra Zeneca, 1, 2, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 1, 2, Celltrion, 1, 2, 5, Cesas, 1, 2, Clarivate, 1, 2, Eli-Lilly, 1, 2, Galapagos, 1, 2, Janssen, 5, Johnson and Johnspn, 1, 2, Moonlake, 1, 2, 5, Novartis, 1, 2, 5, Peervoice, 1, 2, Pfizer, 1, 2, Roche, 1, 2, Sandoz, 1, 2, Springer, 1, 2, Stada, 1, 2, Takeda, 1, 2, UCB Pharma, 1, 2, Zuellig, 1, 2; W. bautista molano: None; S. Bernard: None; R. BURGOS-VARGAS: None; J. Carrino: Arthritis & Rheumatology, 12, Editorial Board, Carestream, 4, Cartilage Imaging, 12, Editorial Board, Covera, 2, Image Analysis Group, 4, Image Biopsy Lab, 4, Radiology, 12, Editorial Board; A. Cauli: None; J. Chan: Abbvie, 2, 6, Celltrion, 2, 6, Eli-Lilly, 2, 6, Fresenius, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, Organon, 2, 6, UCB Pharma, 2, 6; A. Danve: AbbVie, 2, Amgen, 2, Eli Lilly, 5, Janssen, 2, Novartis, 2, 5; T. Diekhoff: Abbvie, 1, 6, Berlin Flame, 1, 6, Bracco, 2, 6, Canon MS, 2, 6, Eli-Lilly, 1, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, Merck/MSD, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, UCB Pharma, 1, 2, 6; M. Dougados: None; i. Eshed: None; W. Fong: None; R. García Salinas: AbbVie/Abbott, 2, 5, 6, Adium, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, Biogen, 2, 5, 6, Bristol-Myers Squibb(BMS), 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Raffo, 2, 5, 6, Roche, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; H. Haibel: Abbvie, 2, 6, Alfasigma, 5, GlaxoSmithKlein(GSK), 6, Janssen, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, Sobi, 5, 6, UCB Pharma, 2, 5, 6; N. Haroon: AbbVie, 2, Eli Lilly, 2, Janssen, 2, UCB, 2; K. Hermann: None; L. Jans: Abbvie, 6, Alfasigma, 6, Eli-Lilly, 6, Janssen, 6, Novartis, 6, UCB Pharma, 6; A. Jurik: None; U. Kiltz: AbbVie, 2, 5, Amgen, 2, 5, Biocad, 2, 5, Biogen, 2, 5, BMS, 2, 5, Chugai, 2, 5, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, Fresenius, 2, 5, Gilead, 2, 5, Grünenthal, 2, 5, GSK, 2, 5, Hexal, 2, 5, Janssen, 2, 5, MSD, 2, 5, Novartis, 2, 5, onkowissen.de, 2, 5, Pfizer, 2, 5, Roche, 2, 5, UCB, 2, 5, Viatris, 2, 5; T. Kim: None; R. Lambert: AbbVie, 2, CARE Arthritis and Image Analysis Group, 2; C. López Medina: None; E. Lubrano: AbbVie, 6, Amgen, 6, Eli Lilly, 6, GlaxoSmithKlein, 6, Johnson & Johnson, 6, Novartis, 6, UCB, 6; M. Magrey: AbbVie, 2, 5, Amgen, 5, BMS, 2, 5, Eli Lilly, 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, UCB, 2, 5; V. Majithia: None; H. Marzo-Ortega: AbbVie, 2, 6, Amgen, 2, 6, Biogen, 2, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Takeda, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; P. Mease: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Acelyrin, 2, 5, Amgen, 2, 5, 6, BMS, 2, 5, Century, 2, Cullinan, 2, Eli Lilly and Company, 2, 5, 6, Inmagene, 2, J&J Innovative Medicine, 2, 5, 6, MoonLake Immunotherapeutics, 2, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Sana, 5, Spyre, 5, Takeda, 2, UCB, 2, 5, 6; V. Navarro-Compan: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Alfasigma, 2, Bristol Myers Squibb, 2, 5, 6, Fresenius Kabi, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 5, 6, Janssen, 2, 5, 6, Lilly, 2, 5, 6, MoonLake, 2, 5, 6, MSD, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Roche, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; J. O'Neill: None; M. Ostergaard: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Amgen, 5, BMS, 2, 5, 6, Celgene, 2, 5, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Gilead, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, MEDAC, 6, Merck, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, Sandoz, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; S. Ozgocmen: None; S. Pedersen: None; F. Pimentel-Santos: None; D. Poddubnyy: AbbVie, 2, 5, 6, Biocad, 2, BMS, 6, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, 6, Gilead, 2, GSK, 2, Moonlake, 2, MSD, 2, 5, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, Samsung Bioepis, 6, UCB, 2, 6; F. Proft: AbbVie, 2, 6, Amgen, 2, 6, BMS, 2, 6, Celgene, 2, 6, Eli Lilly and Company, 2, 5, 6, Galapagos, 2, 6, Hexal, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, Medscape, 2, 6, MoonLake Pharma, 2, 6, MSD, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, Roche, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; S. Ramiro: AbbVie, 2, 5, Eli Lilly, 2, 5, Galapagos/Alfasigma, 2, 5, Janssen, 2, MSD, 2, 5, Novartis, 2, 5, Pfizer, 2, 5, Sanofi, 2, 5, UCB, 2, 5; M. Reijnierse: None; J. Reveille: Surf Therapeutics, 5; R. Schiotis: None; H. Tahir: Abbvie, 2, 6, Eli-Lilly, 2, 6, Janssen, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, UCB Pharma 2, 6; M. Tuite: GE Health Care, 2; F. Van den Bosch: Abbvie, 2, 6, Alfasigma, 2, Amgen, 2, 6, Eli Lilley, 2, Galapagos, 2, Grey Wolf Therapeutics, 2, Janssen, 2, 6, Merck, 6, Novartis, 2, 6, Pfizer, 2, 6, UCB, 2, 6; R. Wang: None; U. Weber: Eli-Lilly, 6, Novartis, 6; J. Wei: None; J. Sieper: Abbvie, 2, 6, Merck/MSD, 2, 6, Novartis, 2, 6; UCB Pharma, 2, 6; A. Deodhar: BMS, 2, 6, Eli Lilly and Company, 2, 5, 6, J&J, 2, 5, 6, Moonlake Immunotherapeutics, 2, Novartis, 2, 5, 6, Pfizer, 2, 5, 6, UCB, 2, 5, 6; M. Rudwaleit: AbbVie, 2, Boehringer Ingelheim, 2, Janssen, 2, 6, Lilly, 2, Novartis, 2, Pfizer, 2, UCB, 2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, van der Heijde D, Caplan L, Landewé R, Gensler L, Machado P, Sepriano A, van Gaalen F, van Lunteren M, Vandermeer B, Akar S, Aydin S, Barliakos X, bautista molano W, Bernard S, BURGOS-VARGAS R, Carrino J, Cauli A, Chan J, Danve A, Diekhoff T, Dougados M, Eshed i, Fong W, García Salinas R, Haibel H, Haroon N, Hermann K, Jans L, Jurik A, Kiltz U, Kim T, Lambert R, López Medina C, Lubrano E, Magrey M, Majithia V, Marzo-Ortega H, Mease P, Navarro-Compan V, O'Neill J, Ostergaard M, Ozgocmen S, Pedersen S, Pimentel-Santos F, Poddubnyy D, Proft F, Ramiro S, Reijnierse M, Reveille J, Schiotis R, Tahir H, Tuite M, Van den Bosch F, Wang R, Weber U, Cheng-Chung J, Sieper J, Deodhar A, Rudwaleit M. The Assessments in Spondyloarthritis International Society (ASAS) and Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network (SPARTAN) Revised Classification Criteria for Axial Spondyloarthritis: Development and Validation in the Classification of Axial SpA Inception Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-assessments-in-spondyloarthritis-international-society-asas-and-spondyloarthritis-research-and-treatment-network-spartan-revised-classification-criteria-for-axial-spondyloarthritis-developmen/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-assessments-in-spondyloarthritis-international-society-asas-and-spondyloarthritis-research-and-treatment-network-spartan-revised-classification-criteria-for-axial-spondyloarthritis-developmen/
