Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Gout is the commonest form of inflammatory arthritis and is caused by the longstanding elevation of serum uric acid levels causing crystal deposits. monosodium urate deposits are the hallmark sign of gouty arthritis, and tendons in many sites represtents a potential target for urate deposits.
Methods: The current study was based on a cross sectional hospital-based survey, conducted among patients presenting at outpatient rheumatology clinics between August 2018- March 2019
Inclusion criteria:
First attack of acute gouty arthritis, diagnosed according to 2015 ACR/EULAR Gout Classification Criteria.
Age 45 years or less.
Exclusion criteria:
Patients with other causes of arthritis, either degenerative or inflammatory.
Previous related joint surgery, malalignment, congenital or acquired joint abnormality.
Metabolic or endocrinopathies: Diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, thyroid dysfunctions.
Chronic renal or hepatic diseases.
Grouping: Group I: 65 patients with acute gouty arthritis, Group II: 20 normal subjects as a control group. All patients were subjected to the following: Full clinical assessment, of 5 tendon sites, Achilles, Infrapatellar, Quadriceps, Triceps, and Supraspinatus tendons. Blood assay for serum uric acid level.
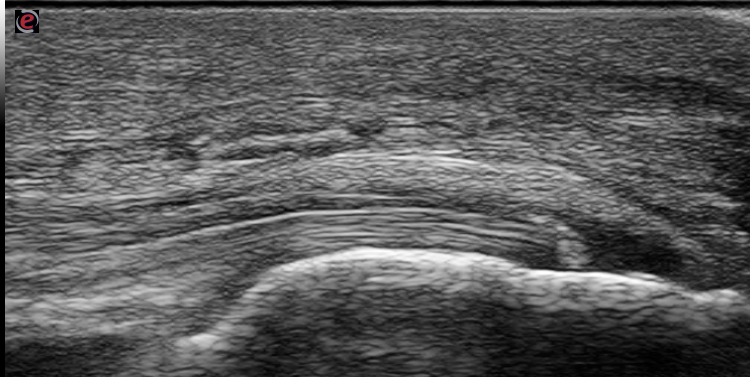
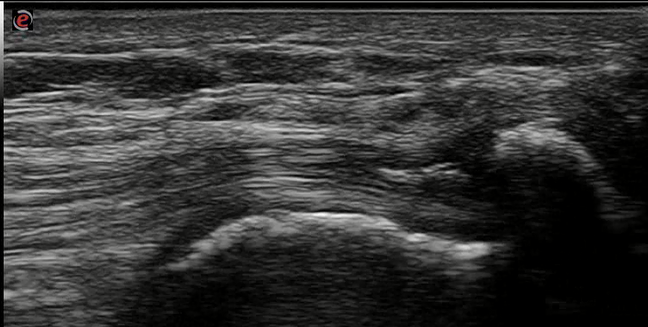
Ultrasonography:was performed for 5 tendon sites; Achilles, infrapatellar ligament, quadriceps, Triceps, supraspinatus tendons. All tendons were evaluated bilaterally according to the EULAR guidelines for performing US in rheumatology. using a scanner with a multi-frequency 12 megahertz linear array transducer (Esaote MYLAB7&General electric Systems; LOGIQU-E). Ultrasonography (US) has been used to detect features of crystal deposits in the tendons, US elementary lesion defined sas intra-tendinous deposits, inhomogeneous, circumscribed, and hyperechoic shadows with or without posterior acoustic shadowing and may be surrounded by a small anechoic halo.
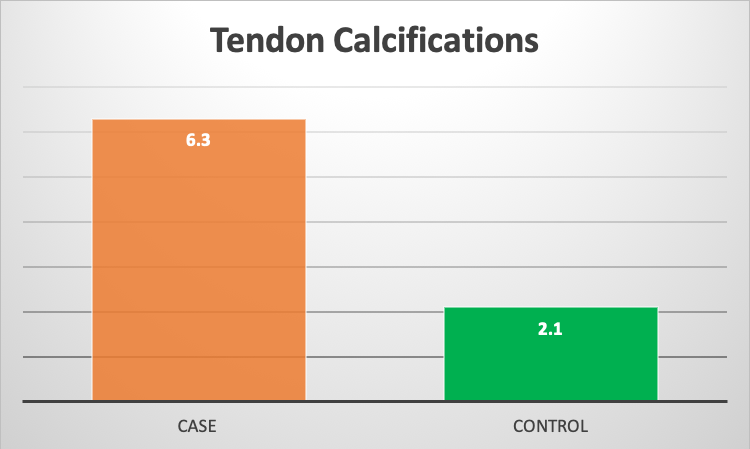
Results: both groups were matched as regards the age and BMI with no significant difference in means. In the study group; among 650 tendon sites examined by US calcifications were detected in 41 tendon sites
6.3
%. 19 at the Achilles tendon unilateral in 13 cases and bilateral in 3 cases, 7 at infrapatellar ligament, 2 at the quadriceps, 7 at the Triceps, and 6 at the supraspinatus tendon. In the other hand clinically, symptomatic tendons presented only in 6 tendon sites with 0.9 %. While in the control group; 190 sites examined by US, and calcifications were detected in 4 sites with 2.1%.
Conclusion: Tendons appears to be involved with the gouty urate deposits, and tendon calcifications could happen and detected early in the course of the disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abogamal A, abdallatif s, Hegazy M, Fathy k. Tendons Involvement at Early Onset of Gouty Arthritis, Ultrasonographic Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tendons-involvement-at-early-onset-of-gouty-arthritis-ultrasonographic-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/tendons-involvement-at-early-onset-of-gouty-arthritis-ultrasonographic-study/