Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 5, 2017
Title: Plenary Session I
Session Type: ACR Plenary Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Methotrexate (MTX), a widely used immune-suppressive agent, decreases vaccine response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We investigated whether a temporary MTX discontinuation for 2 weeks after vaccination improves the efficacy of seasonal influenza vaccination in RA patients.
Methods: In this prospective, multicenter, randomized, parallel-group trial, RA patients taking stable dose of MTX were randomly assigned at a ratio of 1:1 to continue MTX (MTX-continue group) or to suspend MTX for 2 weeks after vaccination (MTX-hold group). All participants were vaccinated with seasonal quadrivalent influenza vaccine containing H1N1, H3N2, B-Yamagata, and B-Victoria. The primary outcome was frequency of satisfactory vaccine response, defined as ≥4-fold increase in hemaglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titer at 4 weeks after vaccination against ≥2 of 4 vaccine strains. Secondary endpoints included seroprotection rate, fold-change in antibody titers relative to baseline in geometric mean titer (GMT).
Results: We enrolled 320 patients between Oct 7, 2016 and Jan 9, 2017. The modified intention-to-treat population consisted of 316 patients (156 in the MTX-continue group and 160 in the MTX-hold group). Higher proportion of patients in MTX-hold group achieved satisfactory vaccine response compared to MTX-continue group (75.5% vs. 54.5%, p < 0.001) (Figure). Post-vaccination seroprotection rate was higher for all 4 antigens in the MTX-hold group than the MTX-continue group (H1N1: 75.6% vs. 86.3%, p=0.016; H3N2: 62.2% vs.78.1%, p=0.002; B-Yamagata: 74.4% vs. 88.1%, p=0.002; B-Victoria: 60.9% vs. 75.6%, p= 0.005). Similarly, the MTX-hold group achieved higher fold increase of post-vaccination HI antibody titer in GMT [95% CI] for each antigen (H1N1: 4.6 [3.7- 5.7] vs. 6.7 [5.4 – 8.3], p=0.017; H3N2: 4.3 [3.5 – 5.3] vs. 8.0 [6.4 – 9.9], p <0.001; B-Yamagata: 3.1 [2.6 – 3.8] vs. 5.6 [4.7- 6.6], p<0.001; B-Victoria: 2.9 [2.4- 3.4] vs. 5.7 [4.9 – 6.7], p<0.001). Vaccine was well tolerated. Disease activity after vaccination did not differ between both groups.
Conclusion:
Temporary MTX discontinuation for 2 weeks after vaccination improves the immunogenicity of seasonal influenza vaccination in RA patients without increasing RA disease activity.
Trial registration: [www.clinicaltrials.gov, protocol number NCT02897011].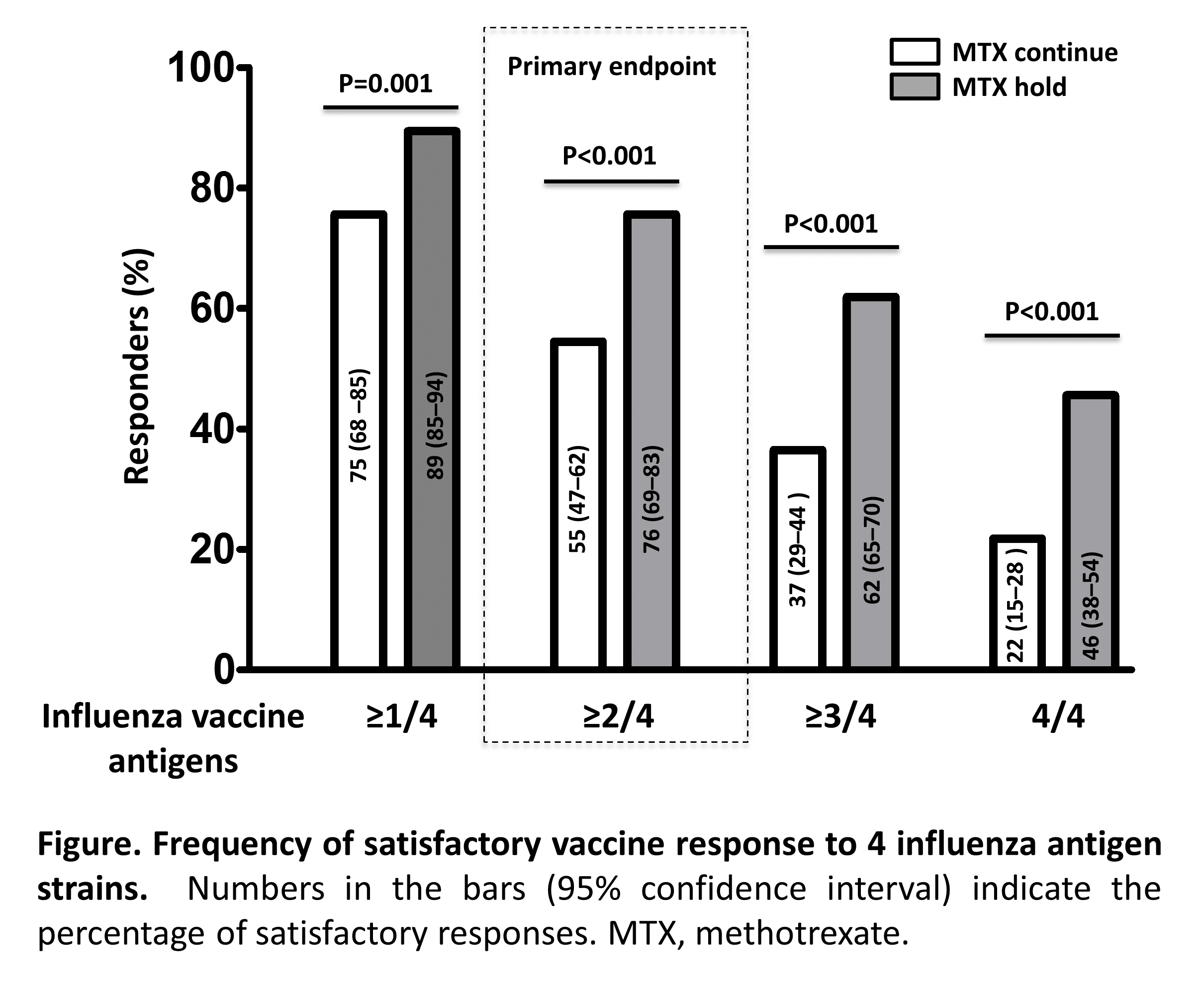
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park JK, Shin K, Ha YJ, Lee YJ, Lee EY, Song YW, Choi Y, Winthrop K, Lee EB. Temporary Methotrexate Discontinuation for 2 Weeks Improves Immunogenicity of Seasonal Influenza Vaccination in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/temporary-methotrexate-discontinuation-for-2-weeks-improves-immunogenicity-of-seasonal-influenza-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-randomized-clinical-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/temporary-methotrexate-discontinuation-for-2-weeks-improves-immunogenicity-of-seasonal-influenza-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-a-randomized-clinical-trial/
