Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The past decade has witnessed the innovation of several biologics in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), most of which target B cells, including B-cell activating factor/a proliferation-inducing ligand (BAFF/APRIL) inhibitors. Telitacicept is a TACI–immunoglobulin fusion protein that neutralizes the activity of BAFF and APRIL by competitively inhibiting the TACI site, thereby suppressing the development and survival of plasma cells and mature B cells. The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of two differentBAFF/APRIL inhibitors, telitacicept and belimumab, in treating patients with active SLE in real world clinical practice.
Methods: Patients with active SLE who received telitacicept (n=72) or belimumab (n=103) from 2019 to 2022 at multiple centers in China were retrospectively reviewed, and the efficacy of telitacicept and belimumab was compared. Patients with renal and hematologic abnormalities were separately selected to confirm the treatment efficacy in these systems. Propensity score-based inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) was used to reduce selection bias. Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to identify the factors contributing to limited response.
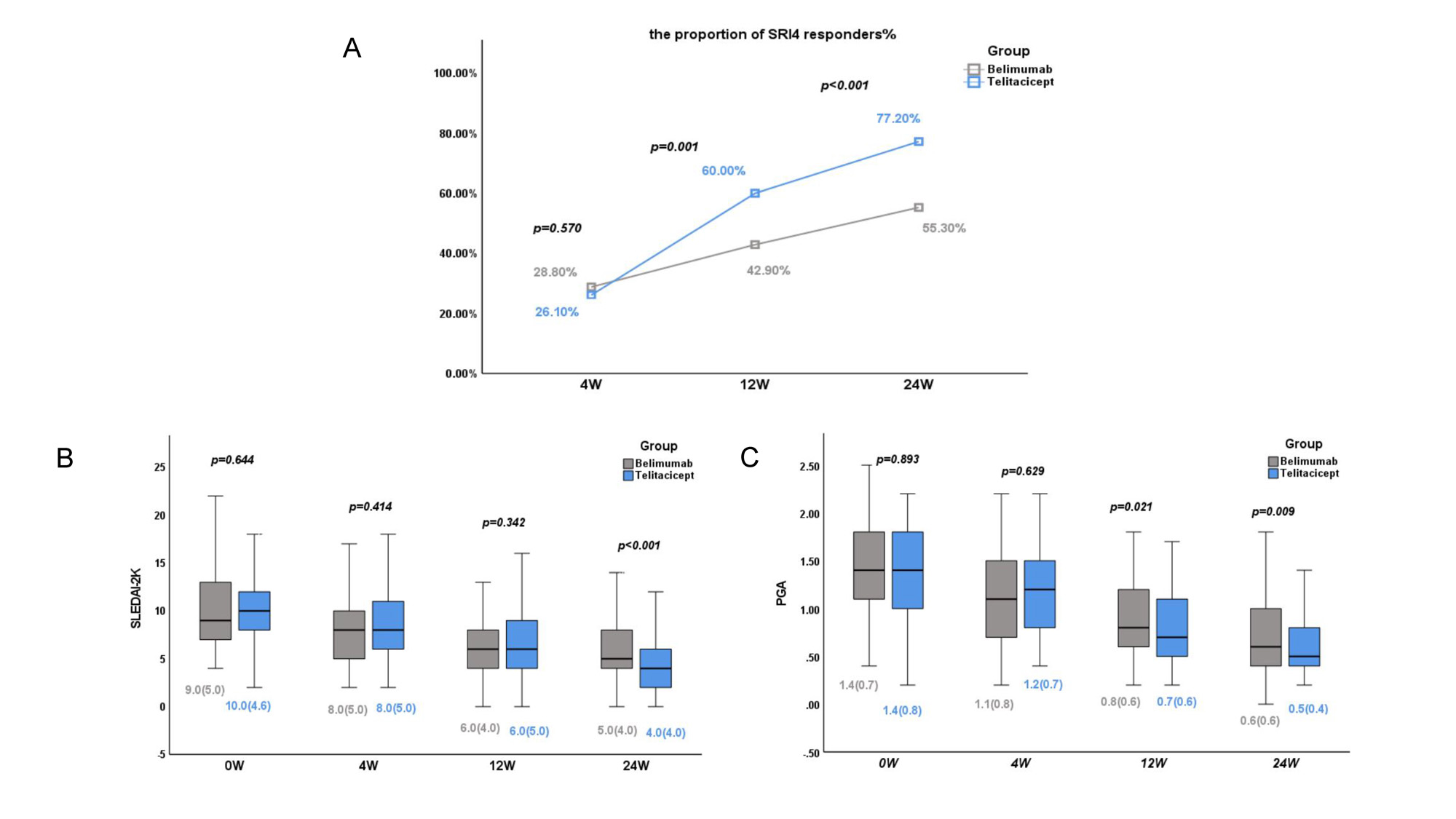
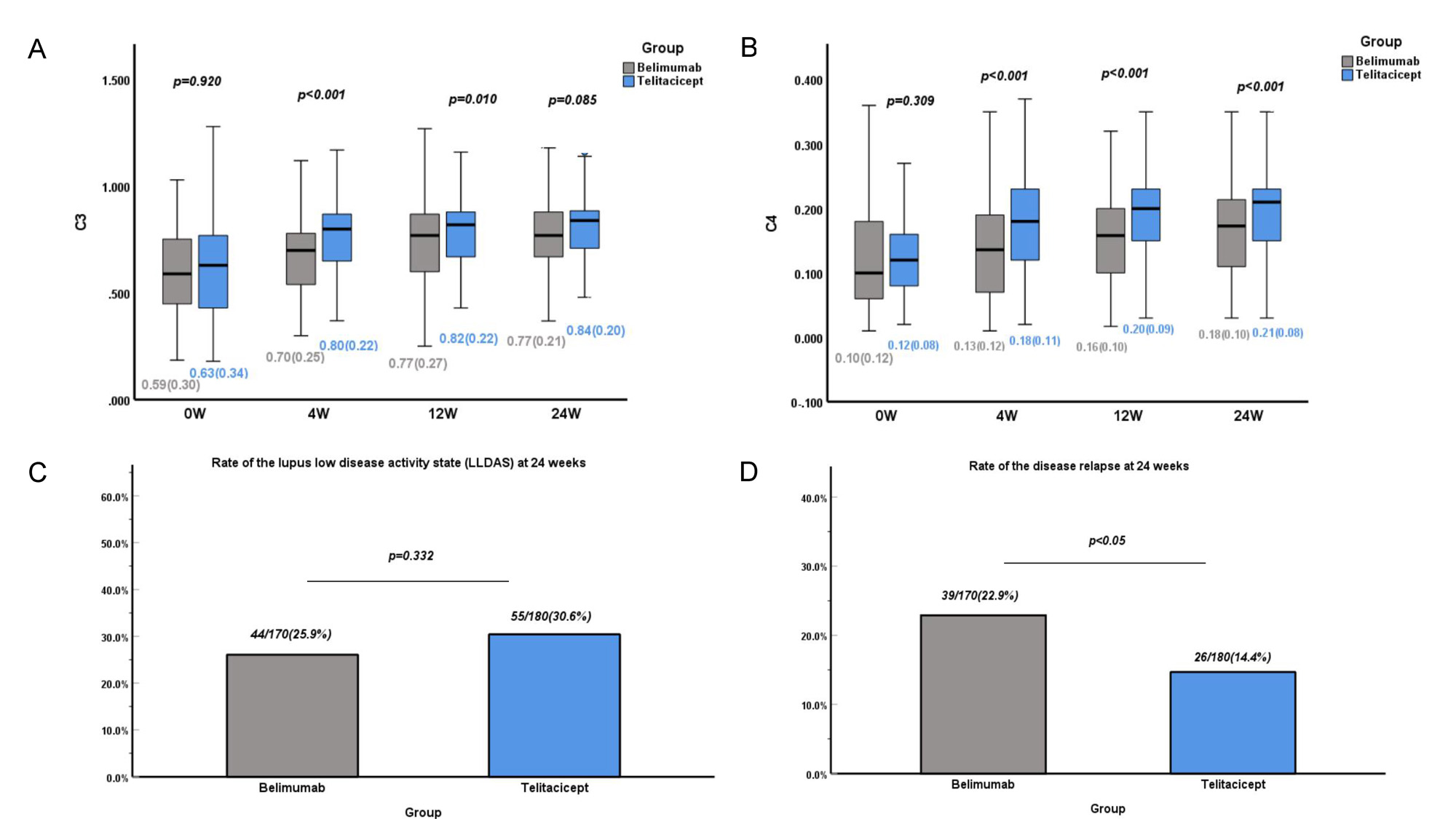
Results: No significant between-group differences in patient characteristics were observed after adjustment by IPTW. The proportion of SLE Responder Index 4 responders at 12 and 24 weeks was significantly higher in the telitacicept group (p < 0.05). Consistently, patients who received telitacicept had a significantly greater decrease in the SLEDAI-2K score and Physician Global Assessment score at 24 weeks (p < 0.05). No significant between-group difference in kidney efficacy was observed, but telitacicept produced greater improvement in patients with anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia at 24 weeks. Importantly, the telitacicept group had a lower incidence of adverse events, especially upper respiratory tract infections, than the belimumab group after the start of therapy (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Telitacicept showed better efficacy and safety than belimumab for patients with active SLE in multiple clinical centers. Further investigations in larger cohorts and head-to-head clinical trials are required to verify these findings.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chen Z, Jin H, Li Y, Wang G, Li X, Li Z, Niu L, Pan H. Telitacicept versus Belimumab for Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Retrospective, Multicenter, Real-world Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/telitacicept-versus-belimumab-for-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-retrospective-multicenter-real-world-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/telitacicept-versus-belimumab-for-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-a-retrospective-multicenter-real-world-observational-study/