Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 28, 2025
Title: (1855–1876) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
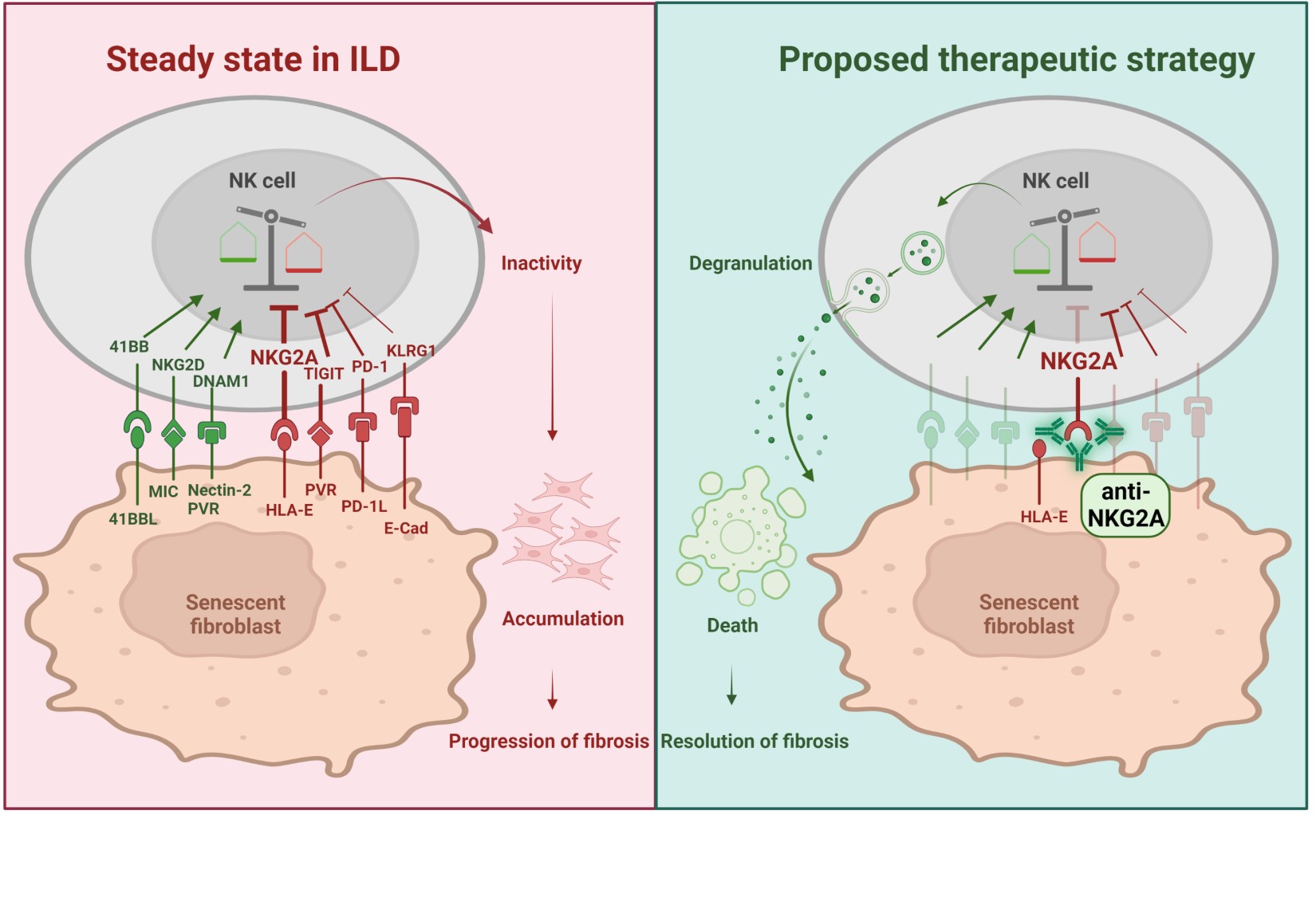
Background/Purpose: A key event driving pulmonary fibrosis in interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the accumulation of pathologic senescent myofibroblasts, thought to be promoted by insufficient clearance by exhausted NK cells. The aim of this study was to identify mechanisms of NK cell inhibition in pulmonary fibrosis with a focus on checkpoint receptors, which may represent novel targets for the treatment of age-related fibrotic disorders.
Methods: Transcriptomic datasets and spectral flow cytometry were applied to characterize pulmonary NK cells. The bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis model and in vitro cultures were used to investigate the effect of NKG2A-inhibition on lung fibrosis and the elimination of senescent primary human lung fibroblasts.
Results: Proteomics and transcriptomics analyses revealed that NKG2A exhibits the highest and most selective expression among NK checkpoints in human ILD. In preclinical models, blockade of NKG2A promoted resolution of established pulmonary fibrosis, as demonstrated by reduced collagen content and decreased number of senescent myofibroblasts. Importantly, we showed translational potential of this therapeutic approach to human disease by showing that NKG2A blockade with the checkpoint inhibitor monalizumab unleashed patient-derived NK cell activity and significantly increased lysis of human senescent myofibroblasts in vitro. Of note, monalizumab did not activate NK cells in absence of senescent myofibroblasts, ensuring selective killing and lowering the risk of unwanted generalized NK cell activation.
Conclusion: In summary, NKG2A checkpoint blockade selectively enhances elimination of senescent myofibroblasts by NK cells and promotes the resolution of fibrosis in preclinical models.
.jpg) Image 2: NKG2A blockade reduces lung fibrosis.
Image 2: NKG2A blockade reduces lung fibrosis.
A Schematic representation of the bleomycin mouse model and the timing of anti-NKG2A dosing. B Example results from histological analysis. C statistical summary of the experimental series; Ashcroft score (left) and hydroxyproline content were used as proxies of pulmonary fibrosis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Merkt W, Rodon L, Deicher F, Claus M, Lister R, Han H, Zhou Y, Sun Z, Horne A, Stuetz A, Kreuter M, kahn n, Schneider M, Haas S, Blank N, Lorenz H, Watzl C, Hübschmann D, Lagares D. Targeting the NK cell checkpoint NKG2A promotes lung fibrosis resolution by enhancing immune clearance of senescent myofibroblasts [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-the-nk-cell-checkpoint-nkg2a-promotes-lung-fibrosis-resolution-by-enhancing-immune-clearance-of-senescent-myofibroblasts/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-the-nk-cell-checkpoint-nkg2a-promotes-lung-fibrosis-resolution-by-enhancing-immune-clearance-of-senescent-myofibroblasts/