Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:30AM-1:00PM
Background/Purpose: Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) secrete large amounts of type I interferon (IFN) and other cytokines upon activation. pDCs migrate to sites of active disease in lupus. VIB7734 is a monoclonal antibody that selectively targets pDCs for antibody-dependent cellular cytolysis.
Methods: VIB7734 was tested in a phase 1, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple ascending dose clinical trial (NCT03817424). Adult subjects were enrolled in 3 sequential cohorts and received placebo (n=9) or 5 mg (n=6, cohort 1), 50 mg (n=8, cohort 2), or 150 mg (n=8, cohort 3) of VIB7734. Cohort 1 enrolled subjects with SLE or Sjogren’s syndrome with no minimum disease activity requirement. Cohorts 2 & 3 included subjects with SLE or cutaneous lupus erythematosus (CLE) with a CLE Disease Area and Severity Index Activity score (CLASI-A) of ≥ 8. Subjects received VIB7734 or placebo subcutaneously every 4 weeks for 3 doses as an add-on to standard of care. In cohorts 2 and 3, a biopsy of affected skin was performed at baseline and Month 3. pDC levels were quantified in the blood and skin. The type I IFN signature was measured in blood. As a marker of IFN activity, myxovirus resistance protein A (MxA) was quantified within the epidermis as the percent of area reaching the positive staining threshold.
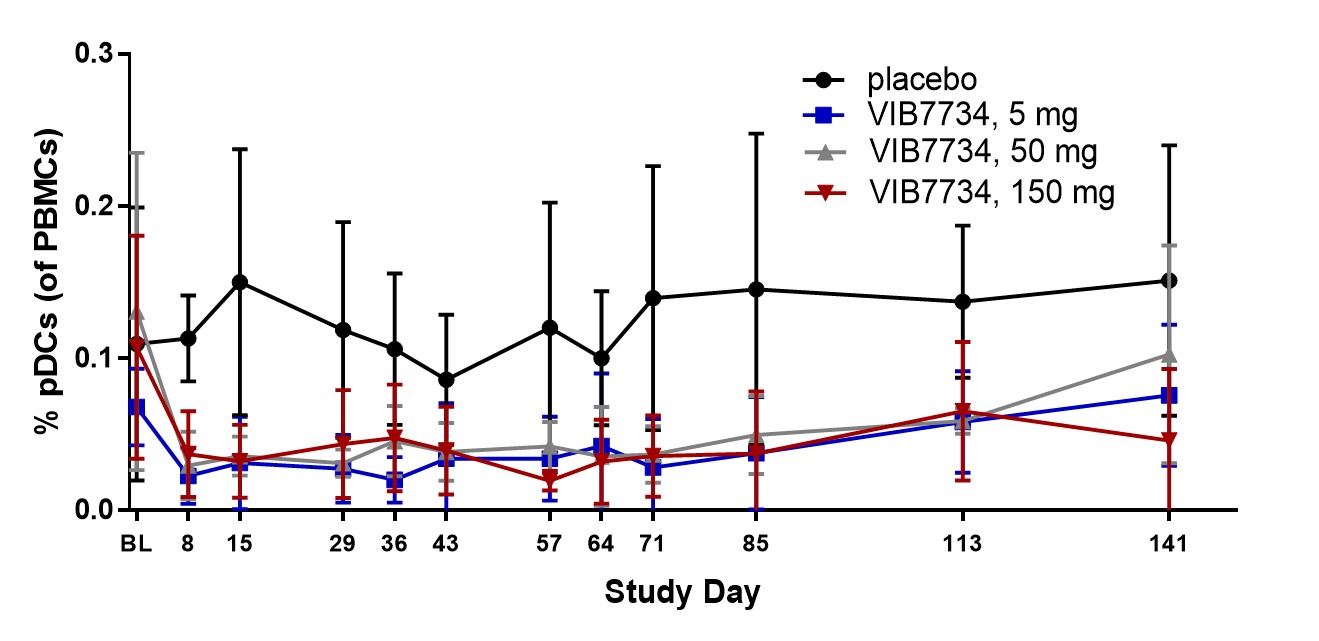
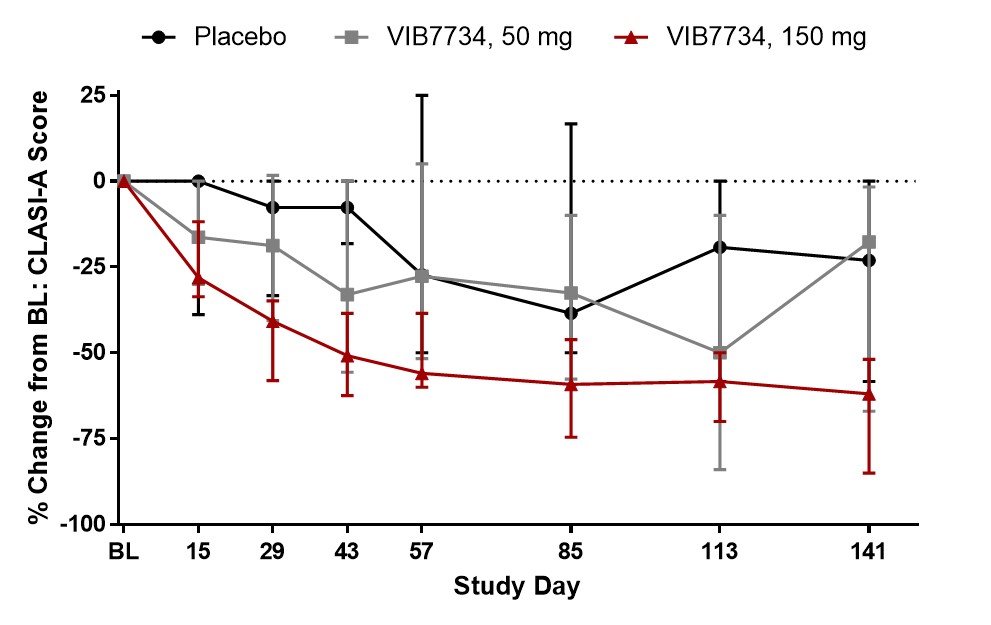
Results: 31 subjects were randomized and treated; all completed the study. Reductions in circulating pDCs were evident at Week 1 and persisted through the 3-month treatment period (Figure 1). A high type I IFN signature was present at baseline in 18 of 23 subjects (78%) in cohorts 2 and 3. The median change in IFN signature at Month 3 was -54% in the VIB7734 50 mg group, -83% in the VIB7734 150 mg group, and +8% in the placebo group. On the Month 3 biopsy the median change in pDC density was -87% for the 50 mg group, -99% for the 150 mg group, and -14% for the placebo group. The median area of MxA staining decreased with VIB7734 treatment (50 mg group: 50% to 1.7% affected area; 150 mg group: 90% to 1.1% affected area; placebo group: 5.5% to 18% affected area). The median change in CLASI-A from baseline to Month 3 was -5 in the 50 mg group, -9.5 in the 150 mg group, and -5 in the placebo group (Figure 2). At Month 3, a ≥50% improvement in CLASI-A was observed in 9 of 16 (56%) VIB7734-treated subjects and 2 of 7 (29%) placebo-treated subjects. No serious adverse events occurred in VIB7734-treated subjects. The proportion of subjects with an adverse event was similar in the VIB7734 and placebo groups (73% vs. 67%).
Conclusion: VIB7734 reduced blood and skin pDCs, thereby reducing type I IFN levels in blood and inflamed skin. More CLE subjects treated with VIB7734 than placebo had a clinically significant improvement in CLASI-A scores, and VIB7734 had an acceptable safety profile. Additional studies of VIB7734 in lupus are planned.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Werth V, Karnell J, Rees W, Mittereder N, Yan L, Wu Y, Drappa J, Illei G, Ratchford J. Targeting Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Improves Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus Skin Lesions and Reduces Type I Interferon Levels: Results of a Phase 1 Study of VIB7734 [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-improves-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-skin-lesions-and-reduces-type-i-interferon-levels-results-of-a-phase-1-study-of-vib7734/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/targeting-plasmacytoid-dendritic-cells-improves-cutaneous-lupus-erythematosus-skin-lesions-and-reduces-type-i-interferon-levels-results-of-a-phase-1-study-of-vib7734/