Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a highly heterogeneous disease. The response to therapy is variable among patients (ref.). Therefore, we need a tailored approach. Biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) are effective treatments for active PsA in adult patients with intolerance, contraindication or inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (csDMARDs). Our aim was to compare the molecular effects of adalimumab (ADA), guselkumab (GUS), and ustekinumab (UST) and to correlate these with clinical responses to therapy in PsA.
Methods: In this multicentre prospective randomized trial (TNFα and IL-23 blockers gene expression ratios in PsA synovium – TIGERS study, NCT04261010), csDMARD-resistant PsA patients were divided into three subgroups according to their randomly received bDMARD (ADA, GUS, UST), and stratified in two groups (oligo-PsA and poly-PsA). We assessed disease activity clinically and biologically at baseline (BL) and every 6 weeks through week 24 (W24). The psoriatic arthritis response criteria (PsARC) was used to assess clinical response to therapy at W24. Patients underwent needle arthroscopy for knee synovial biopsy and blood sample collection at BL and W24 after initiation of a bDMARD. We performed RNA sequencing (NGS – Illumina) using the BL and W24 synovium and blood samples (Paxgene). The local institutional review board and regulatory authorities approved the study.
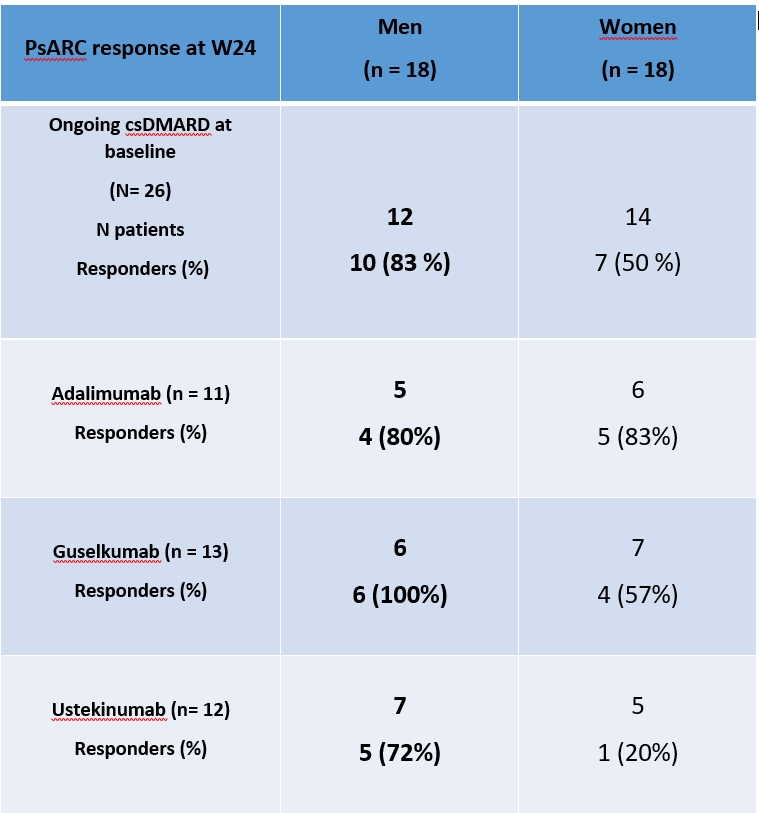
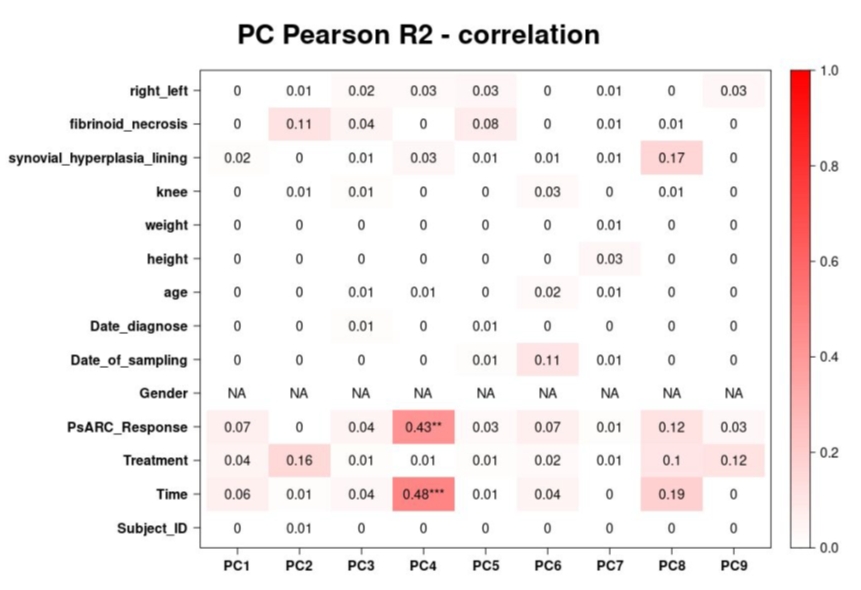
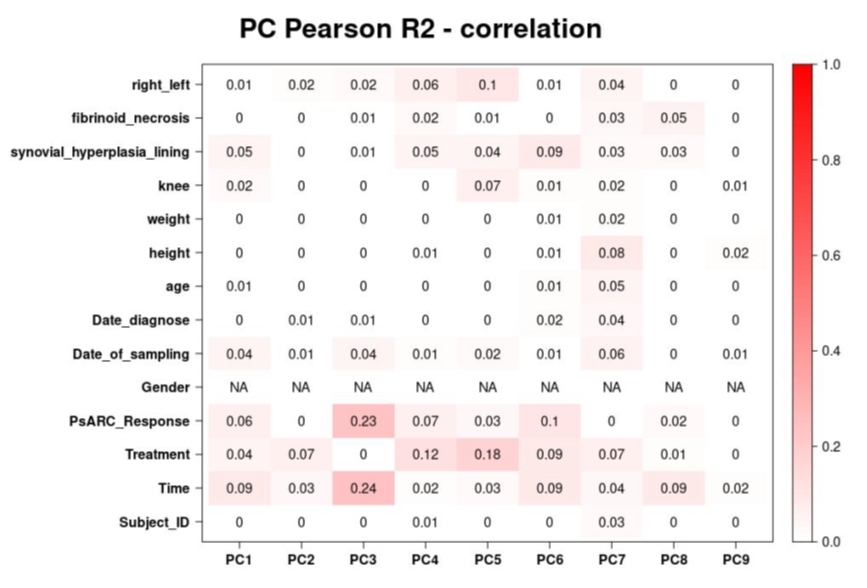
Results: We assessed 36 patients; 50% were men. Mean (SD) age was 48.5 (13.8) years, and mean (SD) disease duration was 45.5 (47.3) months. Seventy-five percent had a polyarticular phenotype. At W24, the PsARC response rate was 70% for the whole group, and 82% for ADA, 77% for GUS, and 50% for UST subgroups. In the whole group, 15 men (83.3 %) were responders compared to 10 women (55.6 %). Table displays PsARC outcomes at W24 stratified by gender and treatment. The synovial transcriptomic data represented by the principal component (PC) analysis and Pearson correlation was associated with PsARC response at W24 only in men (figures 1 and 2 for men and women, respectively).
Conclusion: In the TIGERS study, men responded better to IL-23 blockers both clinically and based on their synovial gene expression profile, even if we should be cautious regarding the sample size. Additional analyses are ongoing to better characterize the pathways involved in this sex-specific and/or gender-related differences. This could be useful in tailoring our therapeutic strategy in PsA.
Reference:
Coates LC, van der Horst-Bruinsma IE, Lubrano E, Beaver S, Drane E, Ufuktepe B, Ogdie AR. Sex-Specific Differences in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Review. J Rheumatol. 2023 Apr; 50(4):488-496.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
KRUG P, De Sousa Leite a, Lecouvet F, stoenoiu M, Nzeusseu Toukap A. Synovial Transcriptomic Sex-Specific Differences in the Response to Biologics in Psoriatic Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-transcriptomic-sex-specific-differences-in-the-response-to-biologics-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-transcriptomic-sex-specific-differences-in-the-response-to-biologics-in-psoriatic-arthritis-patients/