Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Because the thoracic spine has traditionally been excluded from radiographic examinations of spinal damage in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) due to poor visualization, little is known about the extent and degree of involvement of the thoracic spine with syndesmophytes. In particular it is not known if thoracic syndesmophytes are often present in the absence of lumbar syndesmophytes. We used computed tomography (CT) to investigate the presence of syndesmophytes in the thoracic spine, and examined the concordance between thoracic syndesmophytes in CT scans and syndesmophytes on lumbar radiographs.
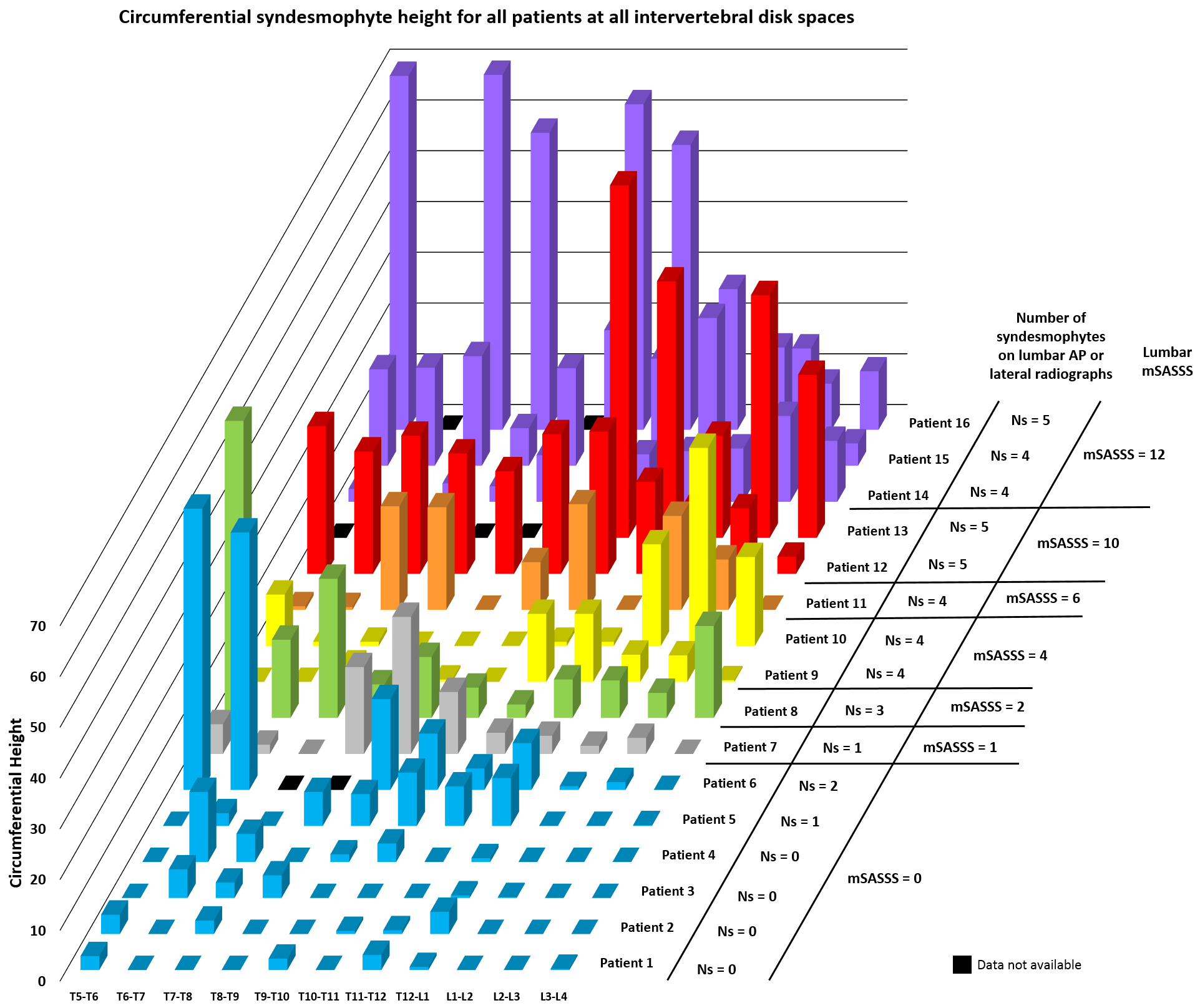
Methods: Sixteen patients with modified Stoke AS Spine Score (mSASSS) in the lumbar spine ranging from 0 to 12 underwent thoracic and lumbar spine CT scans and lumbar radiography. Using a validated semi-automated computer algorithm, we quantitated syndesmophytes in 11 intervertebral disk spaces (IDS) from T5-T6 to L3-L4 on CT scans. We measured syndesmophyte height in 72 angular sectors of 5 degrees around the vertebral rim. In each angular sector, we recorded the height of the tallest syndesmophyte and normalized it to the IDS height (a score of 0 indicating no syndesmophyte and a score of 1 indicating bridging). The 72 angular sectors were summed to form the circumferential height for each IDS (a score of 72 indicating complete fusion). Anterior-posterior and lateral radiographs of the lumbar spine were read for the presence or absence of syndesmophytes and bridging in lumbar IDSs.
Results: 94% of all patients had syndesmophytes at the thoracolumbar junction (Table). Syndesmophytes were slightly more frequent in the thoracic than lumbar spine. In the thoracic spine the average frequency of IDSs with syndesmophytes was 73%, compared to 69% in the lumbar spine. Bridging was more frequent and extensive in the more superior vertebral levels (p<0.005). There was low concordance between thoracic syndesmophytes on CT scans and lumbar syndesmophytes seen on radiographs (Figure). All 16 patients had thoracic syndesmophytes on CT but only 12 had visible lumbar syndesmophytes on radiographs. All 6 patients with lumbar mSASSS of 0 had thoracic syndesmophytes.
Conclusion: Syndesmophytes are common in the thoracic spine in AS, and are often present among patients without lumbar syndesmophytes on radiographs. The low concordance between thoracic syndesmophytes detected on CT and lumbar syndesmophytes seen on radiographs suggests that studies that rely on radiographic measures such as the mSASSS may underestimate the extent of bone proliferation, which may confound biomarker discovery.
|
Proportion of patients with any syndesmophyte |
Mean (std) circumferential height (0-72) |
Proportion of patients with any bridging |
Mean (std) extent of bridging (0-360) |
|
|
T5/T6 |
73% |
23.4 (25.9) |
60% |
137 (130) |
|
T6/T7 |
71% |
13.5 (15.6) |
50% |
83 (86) |
|
T7/T8 |
79% |
16.9 (20.5) |
50% |
117 (115) |
|
T8/T9 |
64% |
16.4 (17.4) |
50% |
92 (89) |
|
T9/T10 |
71% |
11.6 (9.17) |
50% |
70 (34) |
|
T10/T11 |
67% |
17.2 (18.7) |
47% |
92 (103) |
|
T11/T12 |
88% |
17.3 (21.2) |
38% |
149 (123) |
|
T12/L1 |
94% |
12.4 (14.0) |
44% |
81 (76) |
|
L1/L2 |
75% |
9.84 (7.66) |
13% |
43 (11) |
|
L2/L3 |
69% |
15.8 (15.2) |
38% |
88 (68) |
|
L3/L4 |
63% |
9.97 (10.4) |
19% |
33 (19) |
|
Ptrend |
0.96 |
0.16 |
0.003 |
0.005 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tan S, Ward M. Syndesmophytes in the Thoracic Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis As Detected By Computed Tomography and Association with Lumbar Radiographic Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/syndesmophytes-in-the-thoracic-spine-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-as-detected-by-computed-tomography-and-association-with-lumbar-radiographic-involvement/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/syndesmophytes-in-the-thoracic-spine-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-as-detected-by-computed-tomography-and-association-with-lumbar-radiographic-involvement/