Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2227–2256) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment: SpA Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biological and targeted synthetic therapies (ts/bDMARDs) have transformed the management ofPsoriatic arthritis (PsA).However, PsA might experience ts/bDMARD failure, (mainly due to inefficacy), and switching to another ts/bDMARD is the recommended strategy. In this aspect, there is a gap of knowledge regarding the correct treatment algorithms that can be followed after ts/bDMARDfailuredue to inefficacy.Objectives: To assess the incidence rate of switching between ts/bDMARDs due to inefficacy, and to analyze the role of the different types of ts/bDMARDs in the risk of switching due to inefficacy. Other factors were also evaluated.
Methods: A longitudinal retrospective study (2015-2022) of PsA patients with ts/bDMARDs from an outpatient rheumatology clinic of a tertiary hospital was conducted. Main outcome: switching between ts/bDMARDs due to inefficacy.Independent variable:exposure to ts/bDMARDs during follow-up: a) anti-TNF; b) Other Biologics: abatacept; anti-IL17; anti-IL-23; c)Janus kinase inhibitors(JAKi). Covariables: Sociodemographic, clinics, and treatment.Statistical analysis:To estimate ts/bDMARDsswitchingdue to inefficacy rates, survival techniques were used, expressing the incidence rate (IR) per 100 patients*year with their confidence interval at 95% [CI 95%].Cox bivariate and multivariate regression analyses were run to assess the role of the different ts/bDMRADs in switching due to inefficacy. Results wereexpressed ashazard ratio(HR) and 95%CI.
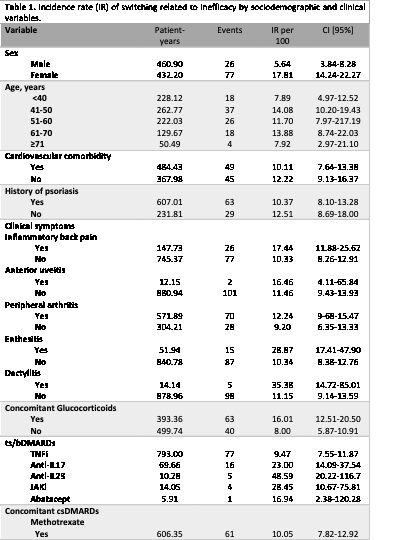
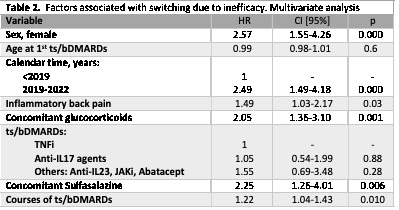
Results: 141 PsA on ts/bDMARDs were included, with an 893.09 patients*year follow-up. 52.48% were female and the mean age was 48.06±13.21 years. 262 courses of treatment were recorded andTNFi was the ts/bDMARDsmost used, flowed byanti-IL-17. 92% were associated to a conventional DMARD, being MTX the most frequent (76.1%). Duringthe study period, 56 patients (40%) presented 121 switches between ts/bDMARDs, and 103 were related to inefficacy. The IR of switching due to inefficacy was 11.53 [9.51-13.98] and anti-TNF was the drug with the lowest incidence (Table 1). In the bivariate analysis of switching due to inefficacy, all types of ts/bDMARDs but TNFi had more risk of switching, in the comparing analysis (HR IL-17 vs TNFi: 2.26 [1.17-4.36], p=0.014; others vs TNFi: 3.21 [1.59-6.45], p=0.001); however, this statistical significance was lost in the multivariate analysis after adjustment for age, sex, year of ts/bDMARDs prescription, and comorbidity: none type of ts/bDMARD had more or less risk compared to each other (Table 2). The model also showed the effect of gender, specific clinical symptoms, prescription year, therapy courses, and the negative influence of glucocorticoids or sulfasalazine on switching due to inefficacy.
Conclusion: This study suggests that long-term control of PsA requires therapeutic switching due to inefficacy. This investigation is able to give us useful information about the comparative effectiveness of ts/bDMARDs, not finding any statistical difference in switching due to inefficacy among different ts/bDMARDs in the multivariate analysis. This studyconfirms previously identified risk factors of switching due to inefficacy and proposes new ones.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Freites Núñez D, Rodriguez Laguna M, Hormigos martín C, Rosales z, Leon L, Candelas G, Rubio D, Otazu J, Fernandez B, Abasolo l. Switching Between Biologics and Targeted Synthetic Therapies Due to Inefficacy in Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/switching-between-biologics-and-targeted-synthetic-therapies-due-to-inefficacy-in-psoriatic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/switching-between-biologics-and-targeted-synthetic-therapies-due-to-inefficacy-in-psoriatic-arthritis/