Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: In the phase 3 studies, BE MOBILE 1 and 2, bimekizumab (BKZ), a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits interleukin (IL)-17F in addition to IL-17A, demonstrated sustained improvements in spinal pain, morning stiffness, and fatigue up to 52 weeks (wks) in patients (pts) with non-radiographic (nr-) axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) and radiographic (r-)axSpA (i.e., ankylosing spondylitis).1
We present 2-year data for pts continuing BKZ treatment in the joint, ongoing open-label extension (OLE) study, BE MOVING.
Methods: In BE MOBILE 1 (NCT03928704) and 2 (NCT03928743), pts were randomized to subcutaneous BKZ 160 mg every 4 wks (Q4W) or placebo (PBO); all received BKZ 160 mg Q4W from Wk 16. Pts completing either study at Wk 52 without meeting withdrawal criteria could enter BE MOVING (NCT04436640).
We report pooled data to Wk 104 across pts with nr-axSpA and r-axSpA from BE MOBILE 1 and 2. Mean values and change from baseline (CfB) in total and nocturnal spinal pain, morning stiffness (mean of Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index [BASDAI] questions [Q]5 and Q6), and fatigue (BASDAI Q1 and Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy [FACIT]-Fatigue subscale scores) are reported (multiple imputation [MI]).
The proportion of pts achieving different thresholds for low total and nocturnal spinal pain (scores < 4 or < 2) or FACIT-Fatigue response (≥8-point increase from baseline in pts with baseline score ≤44)2 are reported (non-responder imputation [NRI] and observed case [OC]). The proportion of pts achieving different thresholds for BASDAI Q1 severity, as established in a recent psychometric analysis,2 are presented based on MI data.
Results: Of pts originally randomized in BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA) and 2 (r-axSpA), 81.9% (208/254) and 86.1% (286/332) entered BE MOVING at Wk 52, respectively; 189 pts with nr-axSpA and 267 pts with r-axSpA completed Wk 104.
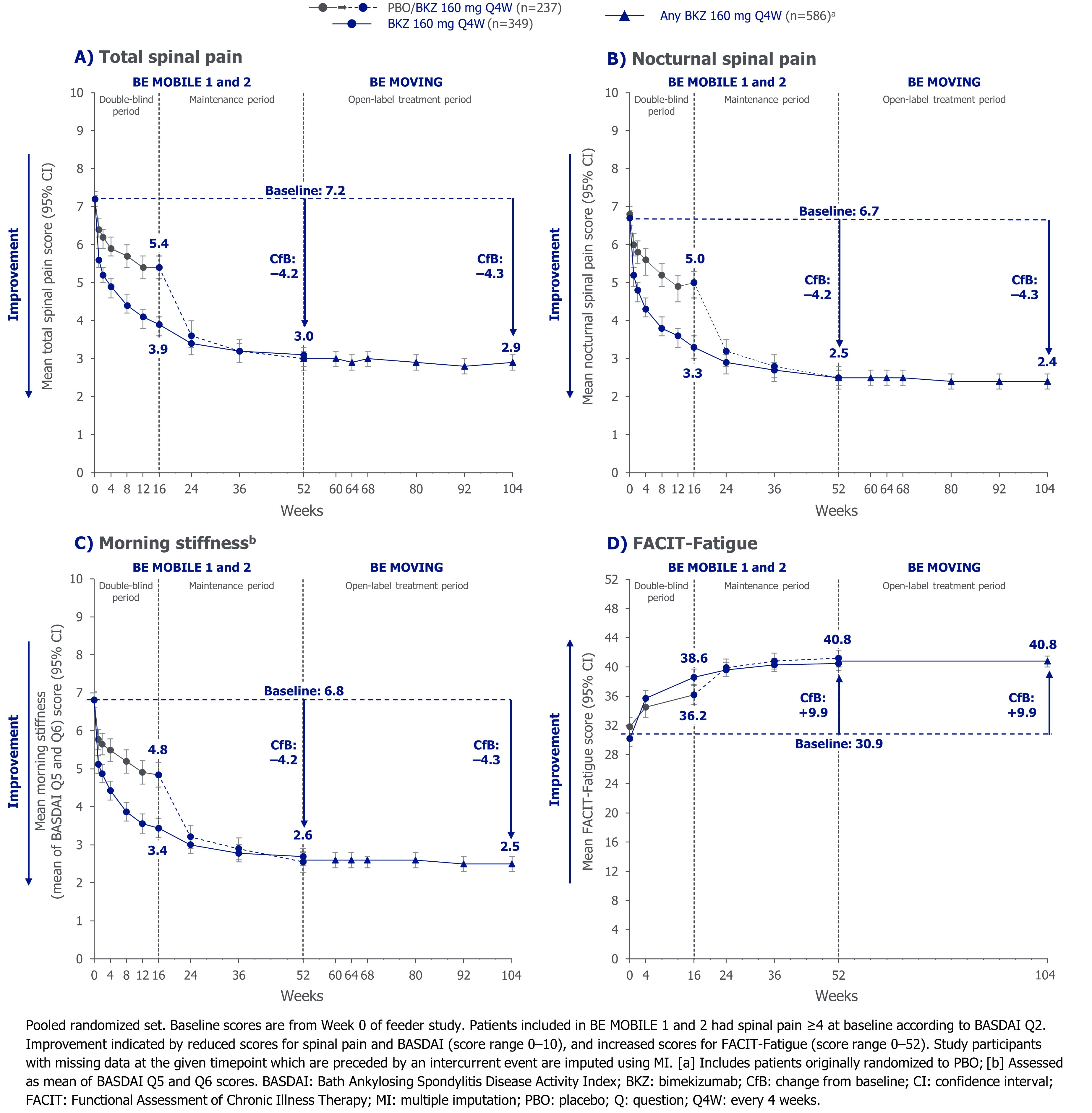
Improvements from baseline to Wk 52 were sustained to Wk 104 for total spinal pain, nocturnal spinal pain, and morning stiffness scores (CfB for all: –4.2 at Wk 52, –4.3 at Wk 104; Figure 1). Results were similar for BASDAI Q1 (CfB: –3.1 at Wk 52; –3.4 at Wk 104). Improved FACIT-Fatigue scores were sustained throughout the OLE (CfB: +9.9 at Wk 52 and Wk 104; Figure 1).
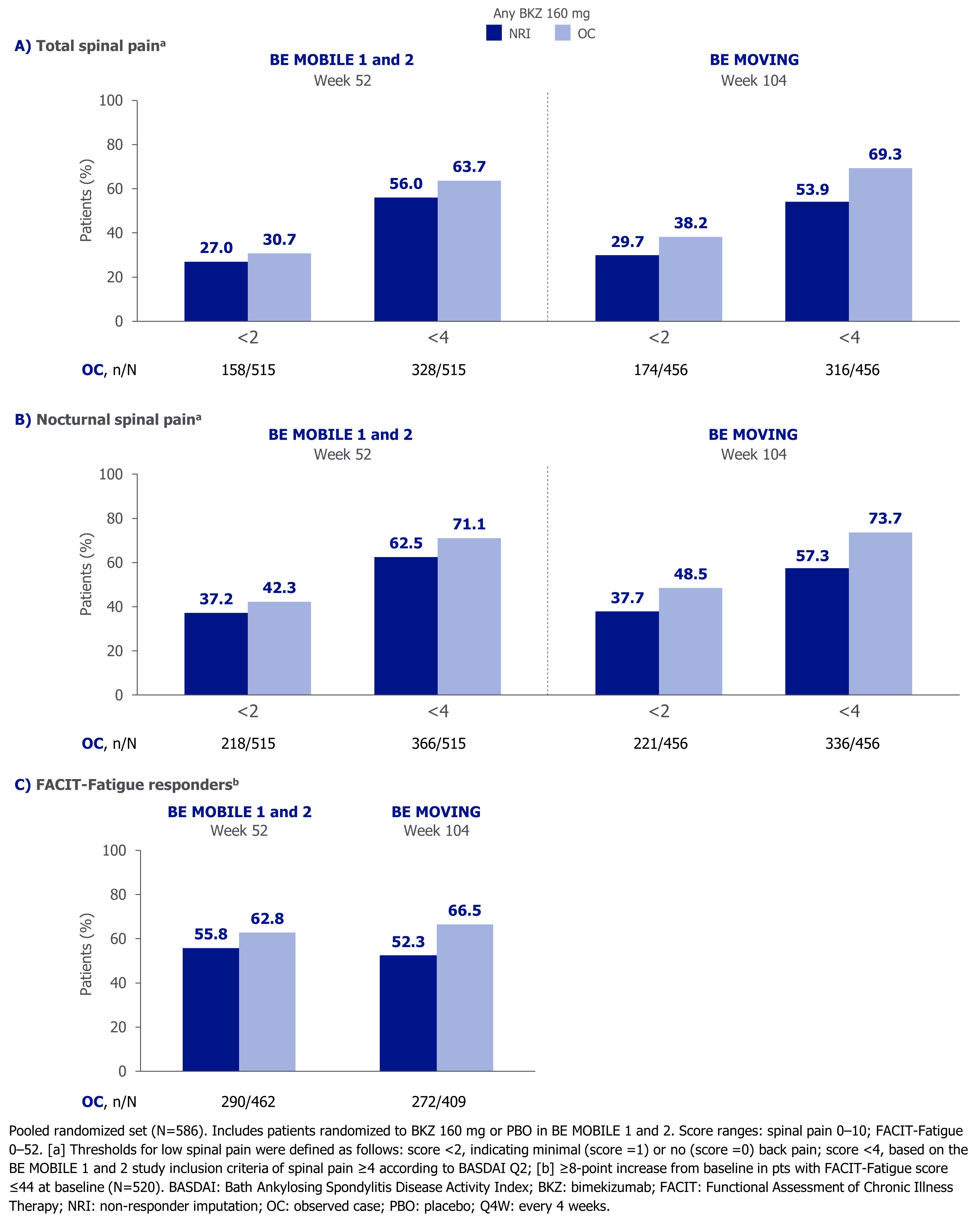
At Wk 52 and Wk 104, >50% of pts had total or nocturnal spinal pain scores < 4 (Figure 2). At the same timepoints, >25% and >35% of pts achieved scores < 2 for total and nocturnal spinal pain, respectively. More than 50% of pts were FACIT-Fatigue responders at Wk 52 and Wk 104 (Figure 2).
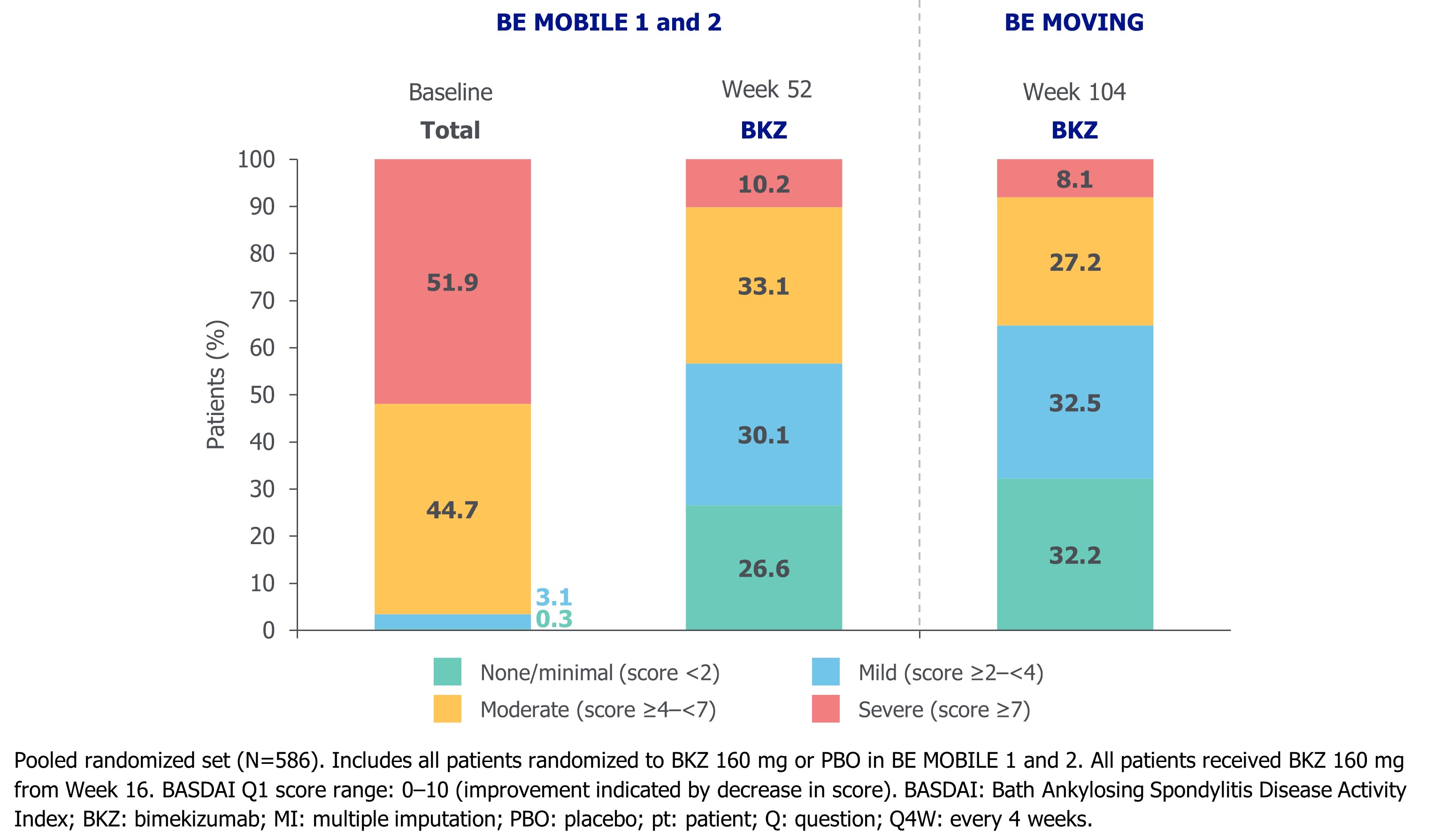
According to BASDAI Q1, 51.9% of pts had severe fatigue at baseline. By Wk 52, this decreased to 10.2% and most pts (56.7%) were considered to have mild or no/minimal fatigue. Improvements continued to Wk 104 (Figure 3).
Conclusion: Results from 2 years of treatment with BKZ demonstrated consistently sustained improvements in spinal pain, morning stiffness, and fatigue in pts across the full disease spectrum of axSpA. These findings support the longer-term maintenance of BKZ benefits on clinical symptoms, which are important to pts and have a substantial impact on their daily lives.
References: 1. Mease PJ. ACR 2023 [Poster 0510]; 2. de la Loge C. ICS Ghent 2024 [submitted].
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Marzo-Ortega H, Mease P, Dougados M, Dubreuil M, Magrey M, Rudwaleit M, D'Agostino M, de la Loge C, Massow U, Taieb V, Voiniciuc D, Deodhar A. Sustained Improvements with Bimekizumab in Patient-Reported Symptoms of Axial Spondyloarthritis: 2-Year Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-improvements-with-bimekizumab-in-patient-reported-symptoms-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-2-year-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-improvements-with-bimekizumab-in-patient-reported-symptoms-of-axial-spondyloarthritis-2-year-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/