Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: Axial Spondyloarthritis (0908–0939)
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: A treat-to-target (T2T) strategy has been advocated for the management of axSpA although no consensus exists as to the most appropriate target or the outcome to be monitored to achieve this target. Structural damage assessed by radiography is not a feasible target in axSpA as it is insensitive to change. Functional impairment is associated with inflammation and structural damage and is assessed in axSpA using the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) Functional Index (BASFI). Sustained (≥6 mos duration) low BASFI (< 3) may therefore be an appropriate target for a T2T strategy in axSpA. There is also no consensus as to which outcome(s) should be monitored in a T2T strategy although there is agreement that the key domain is disease activity. The AS Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is recommended although the Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) is more feasible. Our objectives were to determine 1) to what degree duration of low disease activity impacts function and 2) which patient and disease characteristics predict sustained low BASFI focusing on a comparison of sustained (≥6 mos) low ASDAS versus BASDAI.
Methods: Biologic Treatment Registry Across Canada (BioTRAC) was a multi-centre, prospective, registry that collected real-world patient reported outcomes, clinical, and laboratory data on axSpA patients treated with infliximab or golimumab between 2002-2018. Data were collected every 6 mos. The impact of achieving low BASDAI (< 3) and/or ASDAS-inactive disease (ID) (< 1.3) at 6 and 12 mos, at only 6 or 12 mos, or at neither time point, and the interaction of CRP at 6 and 12 mos with BASDAI, on the BASFI score at 18 mos was analyzed by generalized linear models (GLM) adjusted for age, gender, baseline disease duration, and baseline BASFI. Generalized estimating equations (GEE) were used in univariate and multivariate analyses to test baseline patient demographic and disease characteristics, treatment, sustained low BASDAI and/or ASDAS-ID at 6 and 12 mos, in predicting low BASFI (< 3) between 12 and 18 mos.
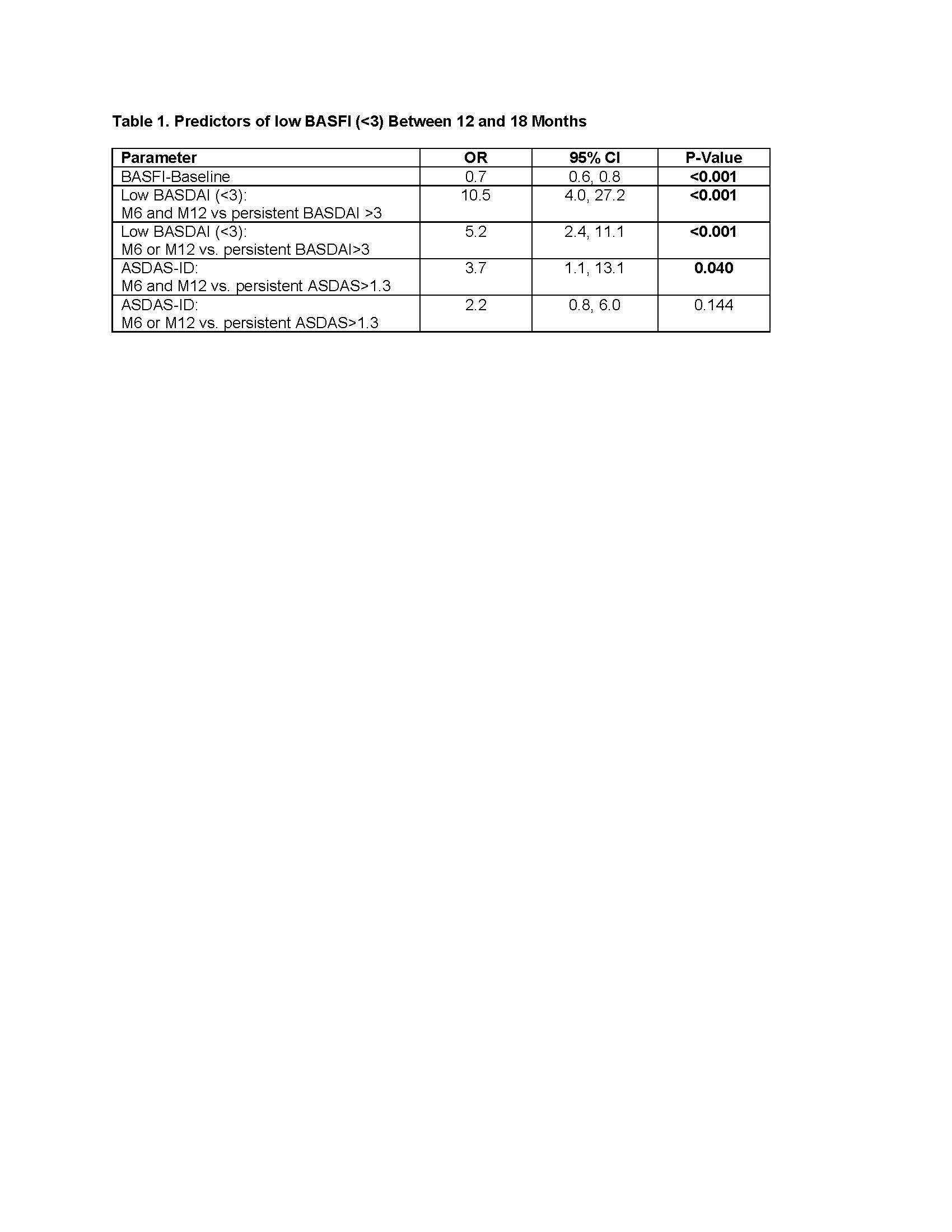
Results: A total of 1620 pts were enrolled, 33.7% and 15% with sustained low BASDAI and ASDAS-ID, respectively. In univariate GEE of baseline variables, only age and baseline BASDAI, BASFI, and ASDAS were significant predictors of sustained low BASFI. In univariate GEE of follow up variables, sustained low BASDAI and ASDAS-ID were also predictors. In multivariate GEE, sustained low BASDAI and baseline BASFI were the only predictors of low BASFI (Table 1). Sustained ASDAS-ID was a weak predictor when forced into the model.
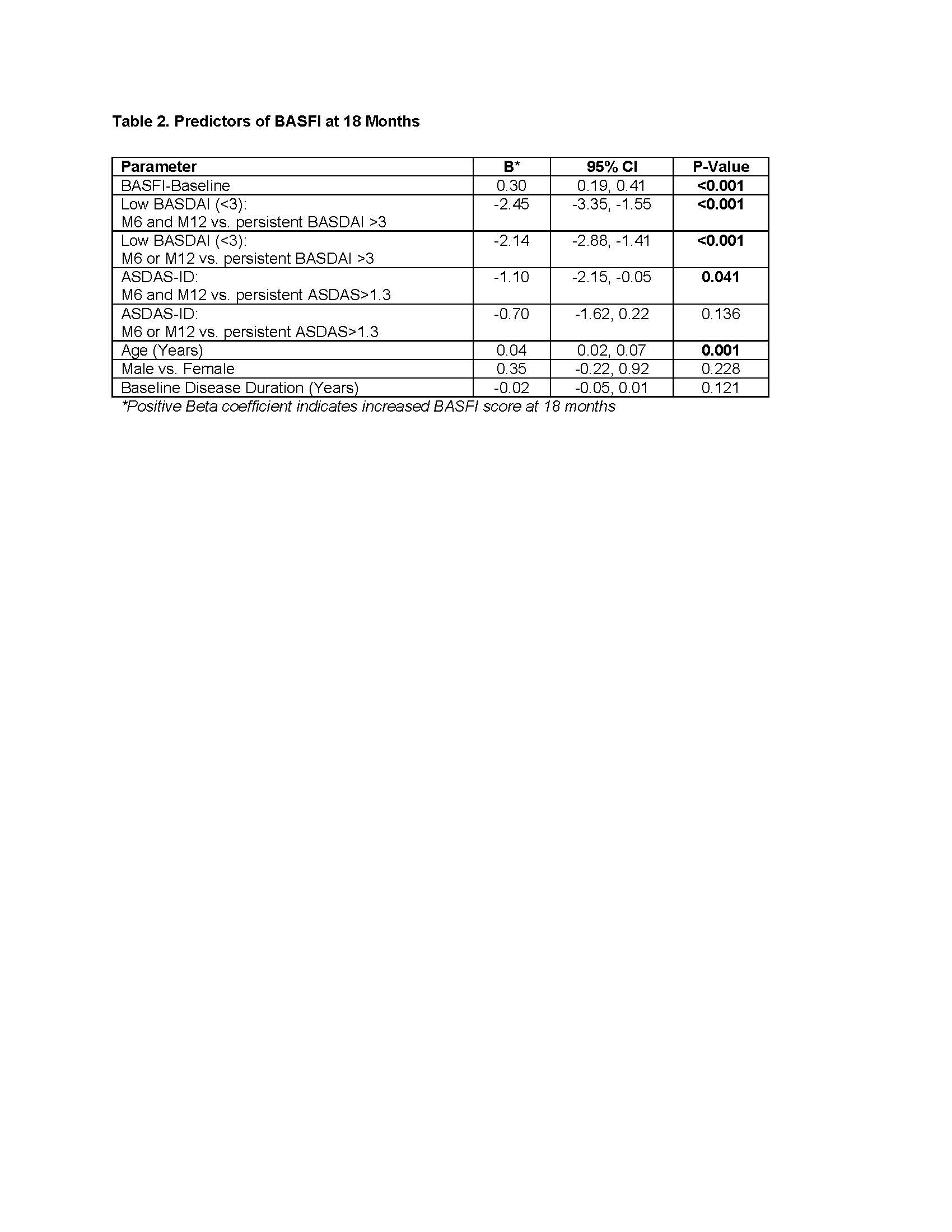
Similarly, in GLM models, sustained low BASDAI and baseline BASFI plus age were strong predictors of BASFI score at 18 mos, while sustained ASDAS-ID was a weak predictor (Table 2). A significant interaction was observed between duration of low BASDAI and normal CRP (< 5mg/L at 6 and 12 mos) with CRP remission identified as an independent predictor of function among patients on sustained low BASDAI.
Conclusion: Aiming for sustained low BASDAI (< 3) may be a valid and more feasible T2T treatment strategy than ASDAS-ID for routine care in axSpA. Further validation of these real-world findings is required to aid in achieving consensus on which outcome should be monitored in a T2T strategy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych W, Inman R, Bessette L, Rahman P, Rampakakis E, Asin-Milan O, Rachich M, Marrache A, Lehman A. Sustained Functional Remission in Axial Spondyloarthritis (axSpA): Which Are the Primary Outcomes That Should Be Targeted to Achieve This? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-functional-remission-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-axspa-which-are-the-primary-outcomes-that-should-be-targeted-to-achieve-this/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-functional-remission-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-axspa-which-are-the-primary-outcomes-that-should-be-targeted-to-achieve-this/