Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Osteoarthritis of the knee (OAK) is a common and severe disease. Current treatments provide temporary pain relief, demonstrating unmet need. PCRX-201 is a high capacity, nonintegrating, nonreplicating adenovirus serotype 5 vector for IA injection in patients with OAK. In response to local inflammation, PCRX-201 expresses interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, an inhibitor of interleukin-1 signaling, under control of an inducible promotor to reduce pain and disability and potentially slow structural progression. This open-label phase 1 trial (NCT04119687) investigated the safety and efficacy of PCRX-201 and is currently in long-term follow-up.
Methods: Participants aged 30-80 years (N=72) with OAK (Kellgren/Lawrence [K/L] grade 2-4) satisfying ACR criteria were eligible. The first cohort received ultrasound-guided IA injection of PCRX-201 in the target knee at 1 of 3 doses (n=36). To explore the benefit of immune modulation to maximize vector tolerability and transduction, the second cohort received pretreatment with IA methylprednisolone 40 mg immediately before PCRX-201 administration at the same doses (n=36). We report adverse events (AEs); efficacy outcomes, including WOMAC index pain score (WOMAC-A), stiffness score (WOMAC-B), and Knee Injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS); and radiographic changes and MRI changes up to 104 weeks.
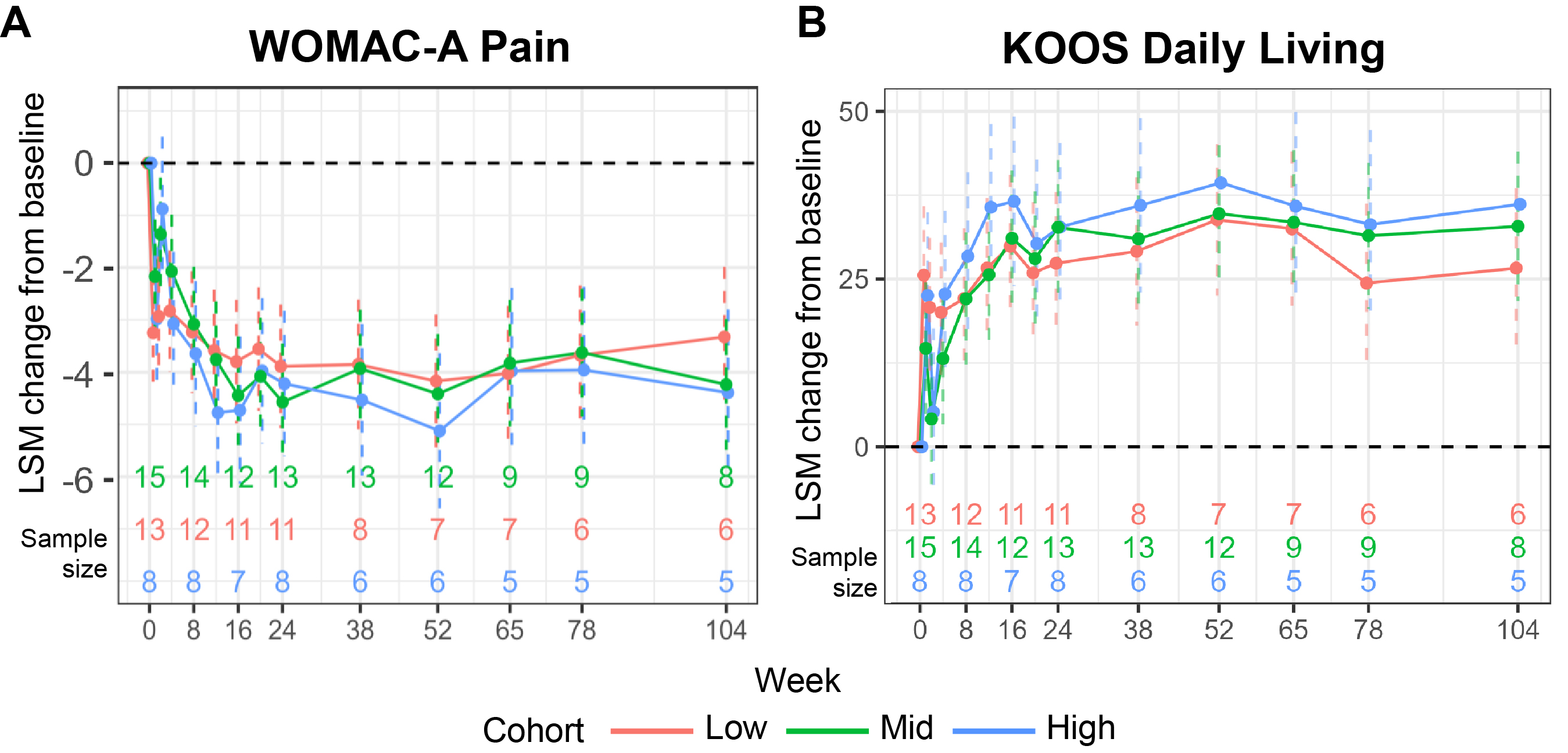
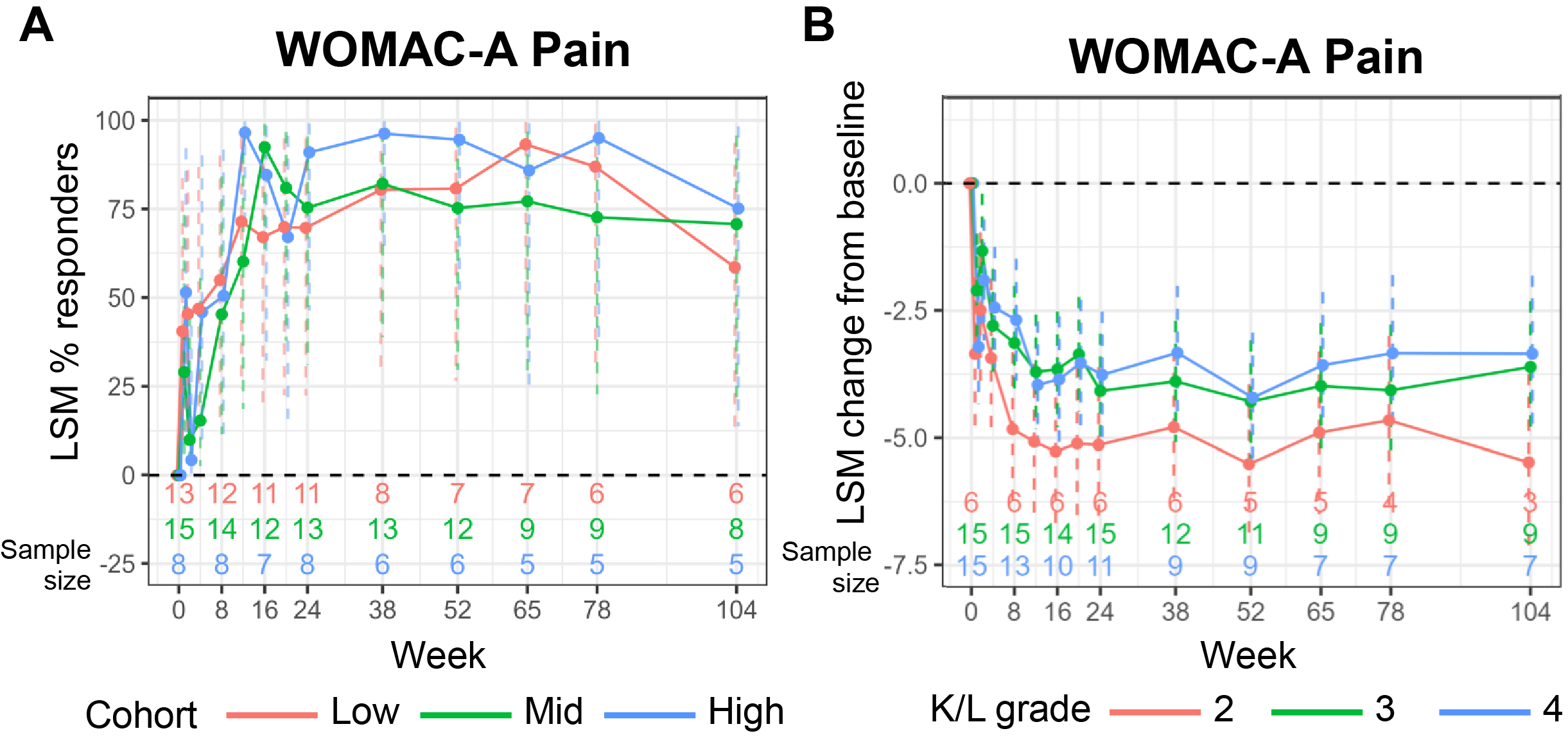
Results: No procedure- or treatment-related serious AEs were reported. Dose-related index knee effusion was the most commonly reported AE, occurring less frequently in the pretreated (13/36 [36%]) versus the not pretreated cohort (22/35 [63%]) as observed. Pain and function benefits were observed at all doses and across both cohorts, with the greatest improvements in the pretreated cohort (Figure 1); subsequent results focus on this cohort. In the pretreated cohort, the least squares mean (LSM) improvement from baseline was 3.3-4.4 of 10 points (48%-65%) for WOMAC-A (Figure 1A); and 3.7‑5.0 points (53%-72%) for WOMAC-B. LSM improvements from baseline in KOOS were similar (Figure 1B). Across doses in the pretreated cohort, pain response (defined as ≥50% reduction in WOMAC-A from baseline) was observed as early as 2-8 weeks after administration by >40% of participants and by 16 weeks in >70% of participants (Figure 2A). Participants in the pretreated cohort with K/L grade 3 or 4 had LSM reductions from baseline in WOMAC-A of 3.7 and 3.5 points, respectively (both 54% improvement), while those with K/L grade 2 had an LSM reduction of 5.5 points (81% improvement; Figure 2B). Structural assessment at week 104 demonstrated that disease progression with PCRX-201 did not differ significantly from expected natural progression; however, longer follow-up is needed.
Conclusion: A single IA injection of PCRX-201 in the index knee had an acceptable safety profile with improvements in pain across K/L grades to 104 weeks, indicating sustained clinical efficacy. From these data, future studies will employ steroid pretreatment. These results support further investigation of PCRX-201 in OAK in randomized, double-blind, active-controlled studies planned for 2025.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cohen S, Conaghan P, Hochberg M, Kivitz A, Joy N, Jackson D, Nakazawa M, DiGiorgi M, Slonin J. Sustained Clinical Effects After a Single Intra-articular Injection of PCRX-201 for Moderate-to-Severe Osteoarthritis of the Knee [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-clinical-effects-after-a-single-intra-articular-injection-of-pcrx-201-for-moderate-to-severe-osteoarthritis-of-the-knee/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustained-clinical-effects-after-a-single-intra-articular-injection-of-pcrx-201-for-moderate-to-severe-osteoarthritis-of-the-knee/