Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The primary treatment goal for patients(pts) with rheumatoid arthritis(RA) is a state of sustained clinical remission(REM) or low disease activity(LDA).1,2 We assess long-term sustainability of response to upadacitinib(UPA), a JAK inhibitor, and adalimumab(ADA), both with background methotrexate(MTX), among pts with RA and prior inadequate response to MTX.
Methods: In the phase 3, randomized, placebo(PBO) and active-controlled SELECT-COMPARE trial, pts on stable background MTX received UPA 15 mg once daily, PBO, or ADA 40mg every other week. Pts not achieving 20% improvements in tender/swollen joint counts(Weeks 14-22) or LDA(CDAI ≤10 at Week 26) were rescued from UPA to ADA or PBO/ADA to UPA; all non-rescued PBO pts were switched to UPA at Week 26. This post hoc analysis evaluated clinical REM(CDAI ≤2.8; SDAI ≤3.3), LDA(CDAI≤10; SDAI≤11), and DAS28(CRP) < 2.6/≤3.2 at first occurrence before Week 72 or prior to treatment switch; additionally, these measures were evaluated at 3, 6, and 12 months after the first occurrence for total number of pts randomized to UPA(n=651) or ADA(n=327). Sustainability of response was evaluated by Kaplan-Meier only for pts who achieved REM/LDA and was defined as time to the earliest date of losing response at two consecutive visits, discontinuation of study drug, or losing response at time of rescue. The predictive ability of time to clinical REM/LDA was assessed using Harrell’s concordance (c)-index (for reference, an index ~ 0.5, indicates no ability to predict; an index of 1 or -1 would be a perfect prediction). The date of last follow up was 6 July, 2018, when all pts reached the Week 72 visit.
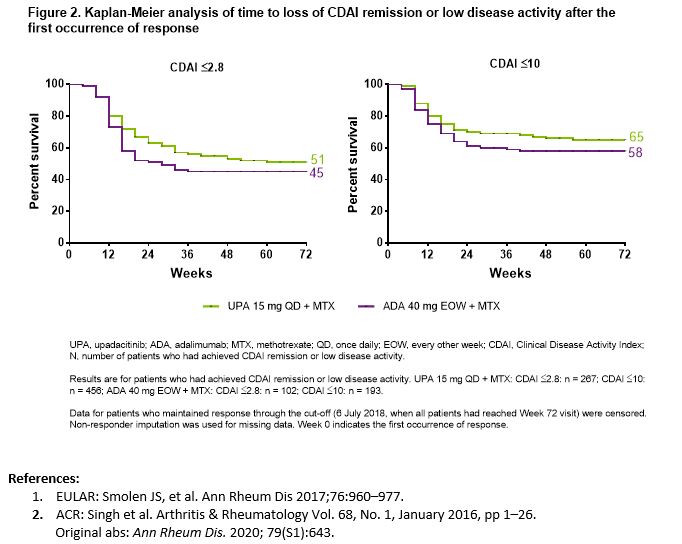
Results: Through Week 72, a significantly higher proportion of pts receiving UPA + MTX vs ADA + MTX achieved CDAI REM(41% vs 31%, p=.0035) as well as CDAI LDA(70% vs 59%, p=.0007). 26%/22% of pts randomized to UPA + MTX and 16%/14% of pts randomized to ADA + MTX achieved sustained CDAI REM at 6/12 months after the first occurrence. Additionally, 49%/46% of pts randomized to UPA + MTX and 36%/34% of pts randomized to ADA + MTX achieved sustained CDAI LDA at 6/12 months after the first occurrence(Figure 1). Time to initial clinical REM/LDA did not appear to be associated with sustained disease control. The c-indices (95% CI) for CDAI REM in the UPA +MTX and ADA + MTX groups were 0.528(0.48, 0.58) and 0.510(0.43, 0.59) and that of LDA were 0.601(0.56, 0.64) and 0.555(0.50, 0.61), respectively. Through last follow-up visit, 51% of UPA + MTX pts and 45% of ADA + MTX pts remained in CDAI REM while 65% of UPA + MTX pts and 58% of ADA + MTX pts remained in CDAI LDA, respectively(Figure 2). Similar results were observed across other disease activity measures(SDAI REM/LDA and DAS28(CRP) < 2.6/≤3.2).
Conclusion: A significantly greater proportion of pts with RA and prior inadequate response to MTX receiving UPA + MTX vs ADA + MTX achieved clinical REM or LDA across disease activity measures. REM and LDA were sustained through Week 72 in both treatment arms, with numerically higher proportions retaining response among UPA-treated pts.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nash P, Kavanaugh A, Buch M, Combe B, Bessette L, Song I, Song Y, Suboticki J, Fleischmann R. Sustainability of Response Between Upadacitinib and Adalimumab Among Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Prior Inadequate Response to Methotrexate [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustainability-of-response-between-upadacitinib-and-adalimumab-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-prior-inadequate-response-to-methotrexate/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sustainability-of-response-between-upadacitinib-and-adalimumab-among-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-prior-inadequate-response-to-methotrexate/