Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2015
Title: Biology and Pathology of Bone and Joint Poster I: Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CAAT/enhancer-binding
protein-beta (C/EBPb) is known to be a transcription factor regulating IL-1b-induced
catabolic pathways, including the expression of matrix metalloproteinases
(MMPs), in chondrocytes. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) was
reported to inhibit interleukin (IL)-1b signaling in chondrocytes. However, the
effect of SOCS1 on C/EBPb has not been explored.
Methods: To investigate the
interaction between SOCS1 and C/EBPb, we established human chondrocyte-like
SW1353 cell lines with overexpression or knockdown of SOCS1 or C/EBPb. MMP-1,
MMP-3, MMP-13, and C/EBPb transcripts were measured by using quantitative
real-time PCR. The expression of C/EBPb and cAMP response element-binding
protein (CREB) protein was evaluated by immunoblot. To evaluate the binding of
C/EBPb to MMP-13 promoter, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was
performed.
Results: Both SOCS1 and C/EBPb
were involved in transcription of MMP-3 and MMP-13. When SW1353 cells were stimulated
with IL-1b, C/EBPb levels were significantly increased by SOCS1 knockdown and
decreased by SOCS1 overexpression (Fig. 1). Also, the same change in IL-1b induced
C/EBPb expression was observed in SOCS1 transfected human articular
chondrocytes (Fig. 1). But, C/EBPb overexpression or knockdown did not change
the levels of IL-1b-inducible SOCS1 (Fig. 1). SOCS1 did not affect the
ubiquitination of C/EBPb, but it regulated the levels of C/EBPb mRNA and
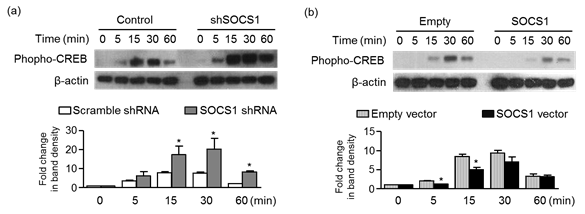
suppressed the phosphorylation of CREB1, an active transcription factor of C/EBPb
(Fig. 2). In addition, p38 MAPK, a target of SOCS1, was involved in the
phosphorylation of CREB1. The ChIP assay confirmed that SOCS1 overexpression resulted
in reduced binding of C/EBPb to MMP-13 promoter.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate
that SOCS1 down-regulates p38-CREB-C/EBPb pathway resulting in suppression of MMPs
expression in chondrocytes.
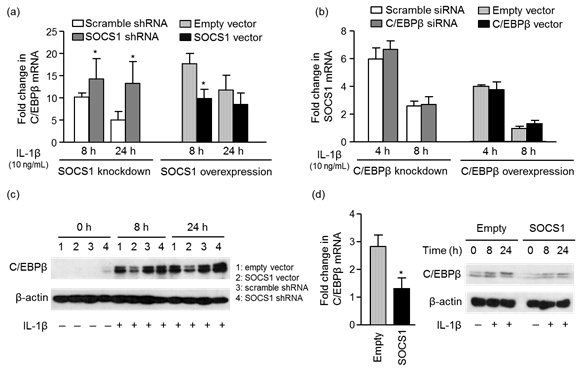
Fig.
1. SOCS1
knockdown increased and SOCS1 overexpression decreased IL-1b induced C/EBPb
mRNA and protein expression in SW1353 cells (a, c), but C/EBPb knockdown or
overexpression showed no alteration in SOCS1 transcript levels (b). In SOCS1-overexpressed
human articular chondrocytes, IL-1b-induced C/EBPb mRNA and protein expression showed
the same trends (d).
Fig.
2. Effects
of SOCS1 on phosphor-CREB levels in SW1353 cells.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ha YJ, Choi YS, Kang EH, Shin K, Hur J, Song YW, Lee YJ. Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1 Inhibits Interleukin-1β Induced Matrix Metalloproteinases Expression in Human Chondrocytes By Modulating p38-CREB- C/Ebpβ Pathway [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/suppressor-of-cytokine-signaling-1-inhibits-interleukin-1-induced-matrix-metalloproteinases-expression-in-human-chondrocytes-by-modulating-p38-creb-cebp-pathway/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/suppressor-of-cytokine-signaling-1-inhibits-interleukin-1-induced-matrix-metalloproteinases-expression-in-human-chondrocytes-by-modulating-p38-creb-cebp-pathway/