Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammatory synovitis, leading to invasion of synovial tissue into the adjacent cartilage matrix with degradation of articular cartilage and bone. Fibroblast-like synoviocyte (FLS) in RA synovium plays a key role by producing cytokines that perpetuate inflammation and proteases that contribute to cartilage destruction. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) is essential for signaling downstream of IL-1R/TLR superfamily which plays critical roles in the activation and proinflammatory effect of RA-FLS. We have reported that elevated synovial TRAF6 expression in RA correlated significantly with histological synovitis severity and cell density of subintimal mononuclear inflammatory cells. Here we aimed to investigate the TRAF6 expression and its role in the proinflammatory effect of RA-FLS.
Methods: Synovium from inflamed knees of active RA patients, and osteoarthritis (OA) as “less inflamed” disease control was collected by closed needle biopsy, and double immunofluorescence staining of TRAF6 and CD55 were tested. FLS were isolated from active RA synovium or OA synovium by modified tissue culture method. TRAF6 expression in primary cultured RA-FLS or OA-FLS was detected by immunofluorescence staining. TRAF6 in RA-FLS was depleted by Lentiviral-TRAF6-RNAi. The mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-a, IL-1b, IL-6 and IL-8, as well as MMP 3 and MMP13, was evaluated by Real-time PCR.
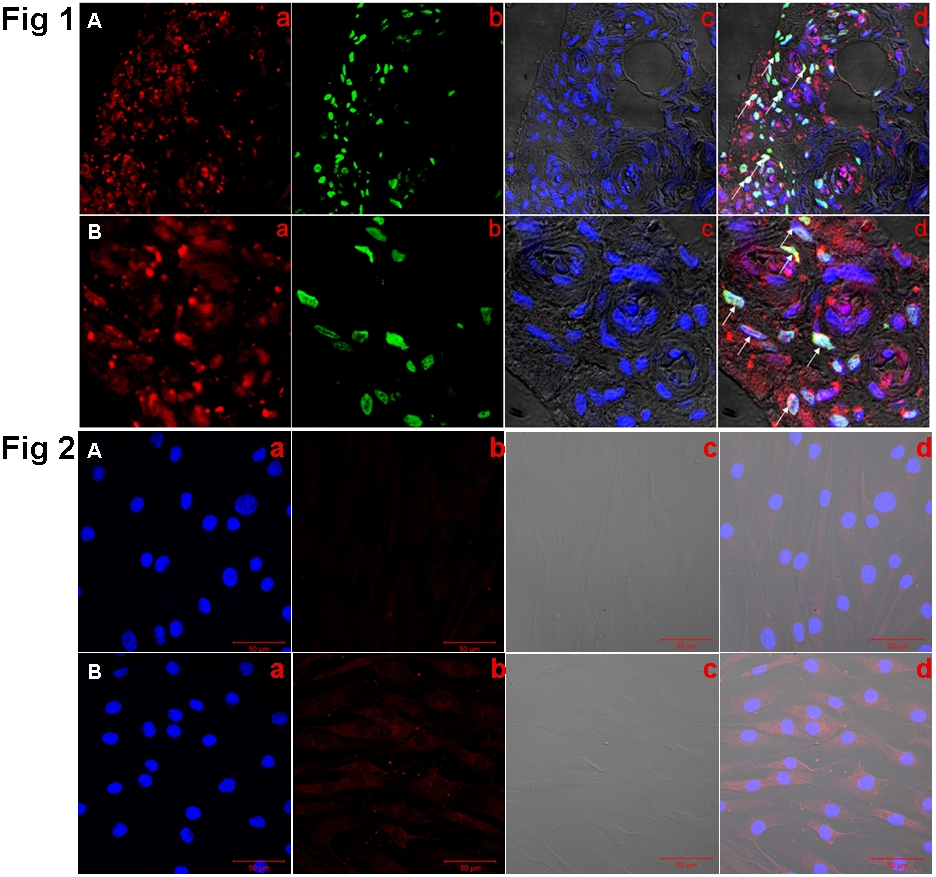
Results: (1) Double immunofluorescence staining showed TRAF6 was obviously expressed in CD55+ cells as well as some other CD55- cells in intimal and subintimal area of RA synovium (Fig 1). (2) Immunofluorescence staining showed obviously higher expression of TRAF6 in RA-FLS than in OA-FLS (Fig 2). (3) Lentiviral-TRAF6-RNAi infection effectively suppressed the expression of TRAF6 in RA-FLS. Suppression of TRAF6 attenuates the mRNA expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including TNF-a, IL-1b, IL-6 and IL-8, as well as MMP3 and MMP13 in RA-FLS.
Conclusion: Elevated TRAF6 was involved in the pathogenesis of synovial inflammation and the proinflammatory effect of RA-FLS. TRAF6-blocking might provide novel target for the treatment of RA.
Fig 1. Representative confocal microscopic images showed TRAF6 and CD55 by indirect double immunofluorescence staining in RA synovium (A, original magnification *400; B, original magnification *1200. a, TRAF6 (red); b, CD55 (green); c, DAPI (blue); d, merged a, b with c. The white arrows point to intimal and subintimal CD55/TRAF6 double+ cells).
Fig 2. Immunofluorescence staining of TRAF6 in primary cultures of FLS from OA and RA patients. RA-FLS stained significantly positive with TRAF6 than OA-FLS (A: OA-FLS, B: RA-FLS; original magnification *400. a, DAPI (blue); b, TRAF6 (red); c, neutral light; d, merged a, b with c).
Disclosure:
L. J. Zhu,
None;
J. J. Zhou,
None;
C. J. Zou,
None;
D. H. Zheng,
None;
X. N. Wei,
None;
J. D. Ma,
None;
Y. Q. Mo,
None;
L. Dai,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/suppression-of-tumor-necrosis-factor-receptor-associated-factor-traf-6-attenuates-the-proinflammatory-effect-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-fibroblast-like-synoviocytes/