Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) comprising radiographic (r-) and non-radiographic (nr)-axSpA is often associated with loss of mobility and impaired physical function. Established assessments of spinal mobility based on physical examination (BASMI) were shown to have limited reliability, whereas questionnaires (BASFI) are largely based on subjective perception of physical functioning. Epionics SPINE (ES) is a novel device that uses electronic sensors to measure spinal movements including range (RoM) and speed (RoK) of motion, it has already been validated in healthy individuals and in patients with mechanic back pain. The objective of this study was to evaluate the ES device for of the assessment of spinal mobility in patients with axSpA.
Methods: Spinal mobility was assessed in 153 individuals (40 nr- and 94 r-axSpA and 19 healthy controls (HC) using ES, BASMI, BASFI and other questionnaires. Mean scores were calculated to compare groups and modeling was performed using multivariable logistic regression.
Results: ES scores showed meaningful differences between axSpA patients and HC (all p< 0.001) and between r- and nr-axSpA (p< 0.01) (Table 1 and 2). In axSpA patients, ES results correlated negatively with BASMI (Fig.1) and patients with r-axSpA had worse spinal mobility than those with nr-axSpA. RoK and RoM decreased significantly with age. ES scores showed only a weak negative correlation with BASFI (r >-0.39) and almost no correlation with other patient reported outcomes (BAS-G, ASAS-HI, PCS, MCS all r between -0,26 and 0,28).
Conclusion:
ES measurements are a valid and objective measure to assess spinal mobility in patients with axSpA. Since rotation and time are new elements of assessment novel information is also provided. The exact measurement of spinal mobility in different planes with ES may improve our understanding of the functional status of patients with axSpA. It is likely that this will be more useful than standardized questionnaires only.
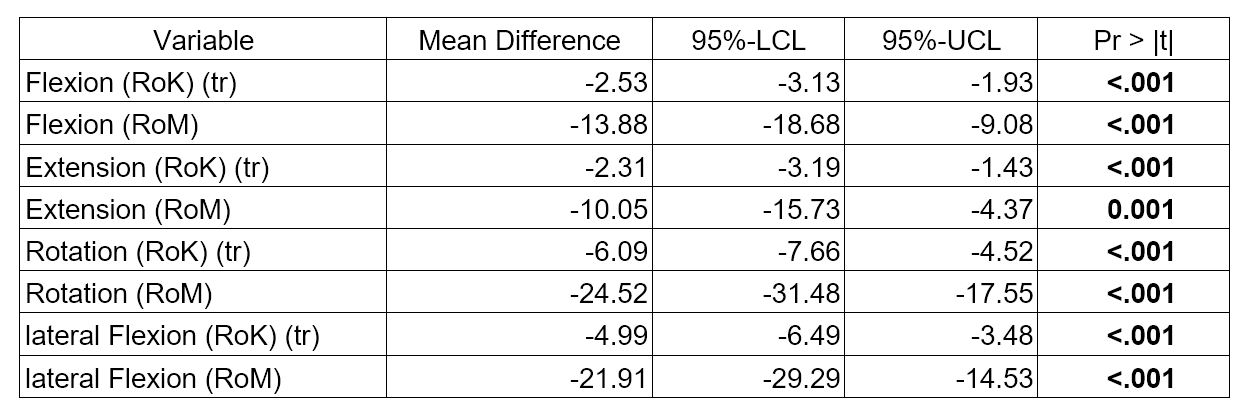 Table 1: Differences between axSpA and HC for ES scores (unadjusted analyses) axSpA: axial spondyloarthritis, ES: Epionics SPINE,HC: healthy controls RoM: Range of Motion, RoK: Range of Kinematics, (tr): log-transformed
Table 1: Differences between axSpA and HC for ES scores (unadjusted analyses) axSpA: axial spondyloarthritis, ES: Epionics SPINE,HC: healthy controls RoM: Range of Motion, RoK: Range of Kinematics, (tr): log-transformed
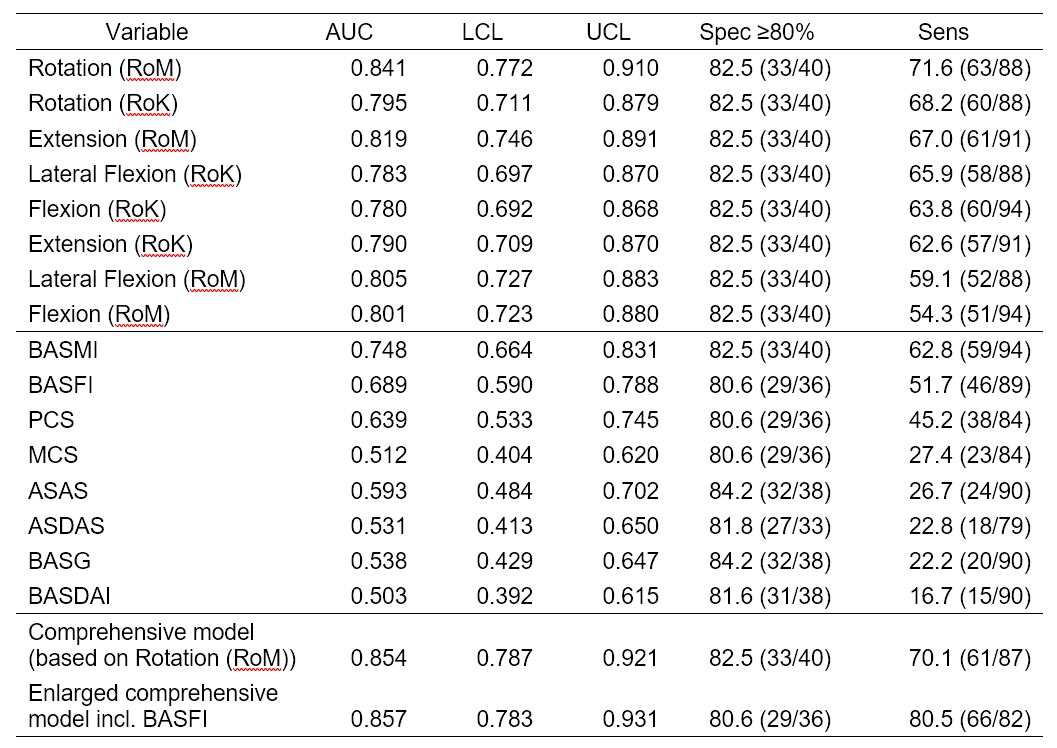 Table 2: Results of ROC curves for modeling r-axSpA of covariable-adjusted models of single derived ES variables, standardized questionnaires, the comprehensive model, and the enlarged comprehensive model incl. BASFI axSpA: axial spondyloarthritis, ES: Epionics SPINE, RoM: Range of Motion, RoK: Range of Kinematics, BASDAI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis (AS) disease activity score, BASFI: Bath AS functional index, BASMI, Bath AS metrology index, BAS-G: Bath patient global score, ASDAS: AS disease activity score, AS-HI: AS health index, PCS: physical component score of SF-12, MCS: mental component score of SF-12. AUC: area under the curve; LCL: lower confidence limit; UCL: upper confidence limit
Table 2: Results of ROC curves for modeling r-axSpA of covariable-adjusted models of single derived ES variables, standardized questionnaires, the comprehensive model, and the enlarged comprehensive model incl. BASFI axSpA: axial spondyloarthritis, ES: Epionics SPINE, RoM: Range of Motion, RoK: Range of Kinematics, BASDAI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis (AS) disease activity score, BASFI: Bath AS functional index, BASMI, Bath AS metrology index, BAS-G: Bath patient global score, ASDAS: AS disease activity score, AS-HI: AS health index, PCS: physical component score of SF-12, MCS: mental component score of SF-12. AUC: area under the curve; LCL: lower confidence limit; UCL: upper confidence limit
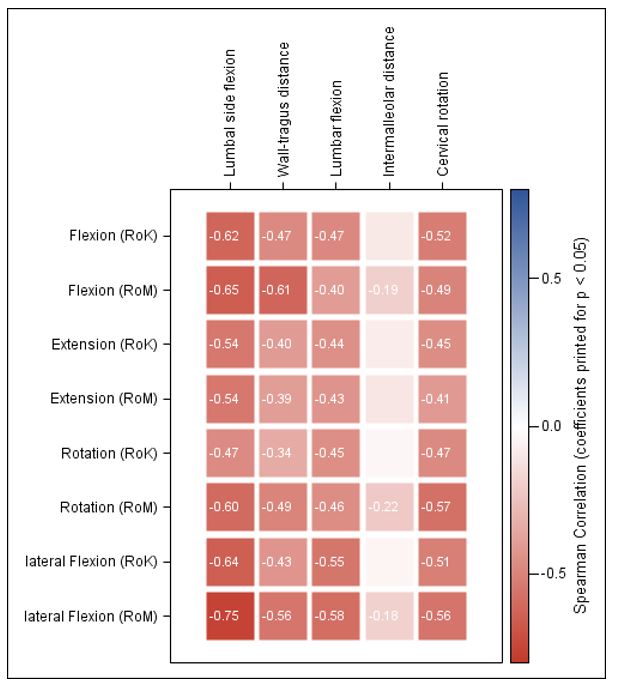 Figure 1: Heatmap of results of Spearman correlation analyses between Epionics SPINE variables and BASMI sub-scores for axSpA patients axSpA: axial spondyloarthritis, BASMI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis metrology index Correlation coefficient (r) values are only depicted in case of significance.
Figure 1: Heatmap of results of Spearman correlation analyses between Epionics SPINE variables and BASMI sub-scores for axSpA patients axSpA: axial spondyloarthritis, BASMI: Bath ankylosing spondylitis metrology index Correlation coefficient (r) values are only depicted in case of significance.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kiefer D, Baraliakos X, Adolf D, Chatzistefanidi V, Schwarze I, Lange U, Brandt-Jürgens J, Stemmler E, Sartingen S, Braun J. Successful Evaluation of Spinal Mobility Measurements with the Epionics SPINE Device in Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis Compared to Controls [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/successful-evaluation-of-spinal-mobility-measurements-with-the-epionics-spine-device-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-compared-to-controls/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/successful-evaluation-of-spinal-mobility-measurements-with-the-epionics-spine-device-in-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-compared-to-controls/
