Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is hampered by suboptimal accuracy of currently available serological biomarkers. Recent advancements in metabolomic profiling include dansylation liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS), resulting in 1000-fold increase in detection sensitivity of amine/phenol-containing metabolites, and universal metabolome-standard (UMS) methodology in conjunction with differential chemical isotope labeling (CIL LC−MS), to provide long-term analytical reproducibility and facilitate metabolome comparisons among different data sets. CIL LC-MS uses different labeling reagents to target chemical group-based submetabolomes to provide in-depth metabolomic analysis. We aimed to identify a metabolite signature with high accuracy for RA.
Methods: 12C-dansylation and acid labeling of individual serological samples and 13C-dansylation and acid labeling of pooled samples from 47 age/gender matched healthy control subjects, 52 age/gender matched RA patients, and 46 patients with seropositive myasthenia gravis was undertaken. A total of 7,458 amine/phenol and 9954 organic acid metabolites were combined into a single data set for analysis. Metabolite concentrations were natural-log transformed. Model accuracy estimation was performed using 5-fold cross-validation, and metabolites were selected using within-fold feature selection. Metabolites were ranked using Spearman correlation coefficient, and the top n were selected, with a varying n. Training of the predictive model was done using a linear Support Vector Machine (SVM). After cross-validation, the final model formula was calculated on the entire data set using the same methodology as was evaluated using cross-validation. Cross-validation accuracy was further analyzed using randomly selected metabolites. Data processing and analysis was performed entirely in R (version 3.2.3). SVM was trained using the e1071 package (version 1.6-7) and cross-validation was done using the caret package (version 6.0-64).
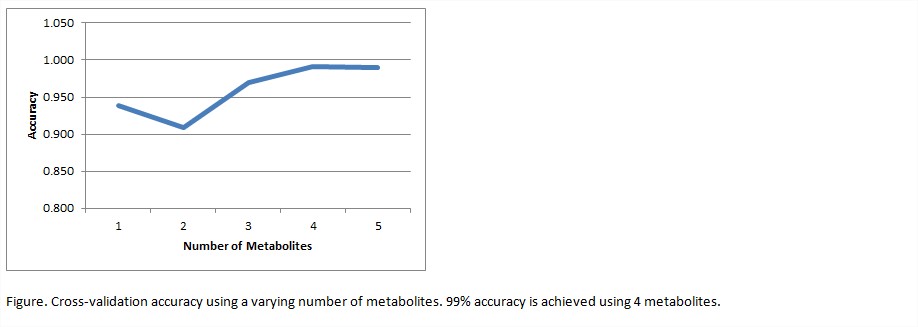
Results: A total of 5711 metabolites were identified in all samples with orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis showing a clear separation of the 3 groups (R2=0.98, Q2=0.80). 34 serum metabolites were identified as potential RA biomarkers with correlation coefficients ≥0.80. Cross-validation accuracy of top-ranked metabolites, according to Spearman’s correlation, and using a varying number of metabolites shows that 99.1% accuracy for RA versus controls is achieved using only 4 metabolites.
Conclusion: CIL LC-MS metabolomic profiling and UMS methodology reveals that serum metabolomes of RA patients differ considerably from healthy and autoimmune disease.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Maksymowych WP, Blackmore D, Eisner R, Li L, Siddiqi Z. Submetabolome Profiling with Differential Chemical Isotope Labeling Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry and a Universal Metabolome Standard Reveals a Metabolite Profile with 99% Accuracy for Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/submetabolome-profiling-with-differential-chemical-isotope-labeling-liquid-chromatography-mass-spectrometry-and-a-universal-metabolome-standard-reveals-a-metabolite-profile-with-99-accuracy-for-rheuma/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/submetabolome-profiling-with-differential-chemical-isotope-labeling-liquid-chromatography-mass-spectrometry-and-a-universal-metabolome-standard-reveals-a-metabolite-profile-with-99-accuracy-for-rheuma/