Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a severe extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Abatacept (ABA) has demonstrated efficacy in RA-ILD. Clinical trials have shown equivalence in subcutaneous (SC) and intravenous (IV) administration of ABA for articular manifestations. However, it has not been studied in RA-ILD. Our objective was tocompare the effectiveness of ABA in RA-ILD patients according to the route of administration (IV-ABA vs SC-ABA).
Methods: National multicenter study of RA-ILD patients on treatment with ABA. They were divided into 2 groups according to the route of administration: a) IV, and b) SC. We analyzed from baseline the following outcomes in both groups: a) forced vital capacity (FVC), b) diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO), c) chest high resolution computed tomography (HRCT), d)dyspnea (assessed with the modified Medical Research Council scale), e) arthritis activity (assessed with DAS28-ESR or described in clinical records), and f) sparing corticosteroids effect.
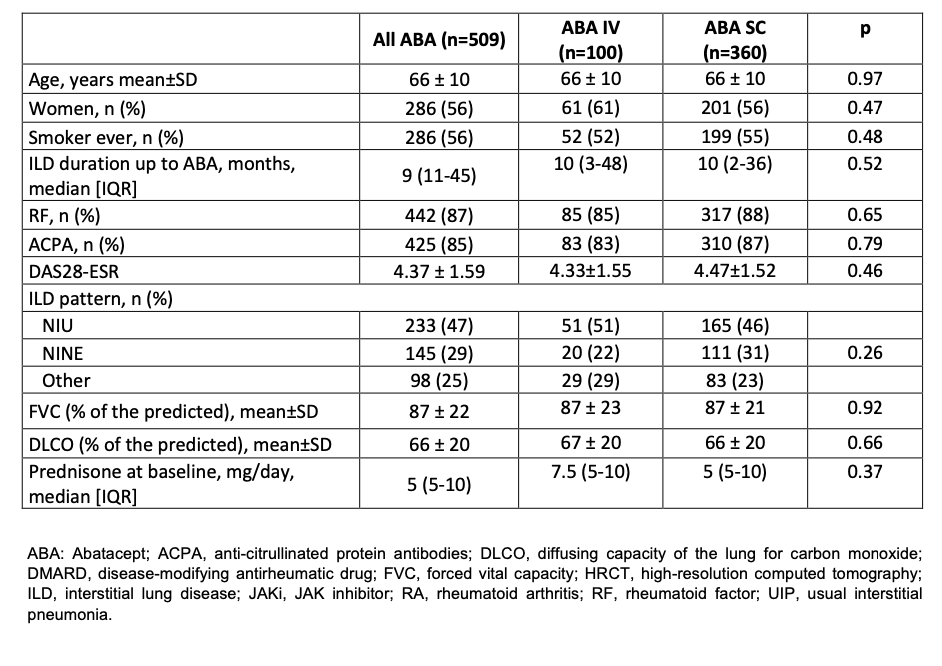
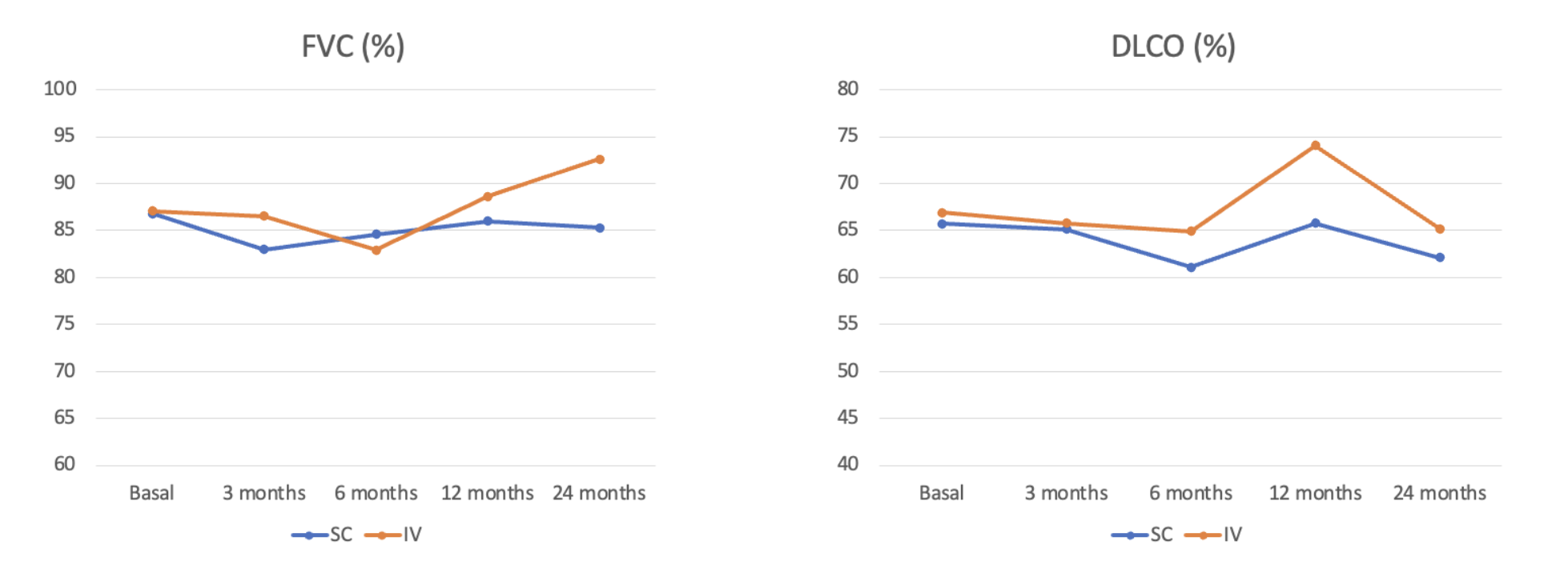
Results: We studied a total of 509 [SC-ABA/IV-AB; 360/100 (available data)] patients. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1.Patients were followed-up for a median [IQR] of 24 [7-48] months.FVC and DLCO remain stable during the first 24 months in both SC-ABA and IV-ABA [Figure 1]. Dyspnea stabilized or improved in 84% of patients (89% of IV-ABA; 82% of SC-ABA). ABA was withdrawn in 106 patients: 81(34%) in SC-ABA group and 25 (40%) in IV-ABA group. ILD worsening and articular inefficacy were the most common reasons of ABA discontinuation.
Conclusion: In RA-ILD, ABA seems equally effective and safe regardless of the route of administration IV or SC.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Serrano-Combarro A, Atienza-Mateo B, Ibarrola-Paino l, Casafont-Sole I, Melero-Gonzalez R, Perez Linaza A, Castañeda S, Ortega Castro R, Mena Vazquez N, Vegas Revenga N, Dominguez Casas L, Cañadillas-Sanchez E, Retuerto-Guerrero M, Perez-Albadalejo L, Lopez-Sanchez R, MANZANO CANABAL M, Brandy-Garcia A, Lopez-Viejo P, Bonilla G, Maiz-Alonso O, carrasco-Cubero C, Garijo Bufort M, Moreno M, Urruticoechea A, Ordonez-Palau S, Gonzalez-Montagut Gomez C, Garcia-Valle a, López M, Lozano F, Vazquez-Rodriguez T, Martin-Lopez M, Blanco-Madrigal J, Arciniega C, Brana Abascal I, Loarce-Martos J, Giner-Serret E, Ruiz-Esquide V, ventin-Rodriguez C, Rodriguez-lopez M, Andujar-Brazal P, Fernandez-Melon J, Lopez L, Juan Mas A, Fernandez-Diaz c, Loricera J, Ferrer D, Blanco R. Subcutaneus vs Intravenous Abatacept in Rheumatoid Arthritis-Interstitial Lung Disease. National Multicenter Study of 509 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneus-vs-intravenous-abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-national-multicenter-study-of-509-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneus-vs-intravenous-abatacept-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-national-multicenter-study-of-509-patients/