Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tanezumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits nerve growth factor and is under investigation for chronic pain treatment. Tanezumab administered intravenously was effective and generally well tolerated in prior osteoarthritis (OA) studies. In patients (pts) with OA and moderate-severe pain taking oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID), we assessed the efficacy and general safety/tolerability of switching to subcutaneous (SC) tanezumab vs further treatment with oral NSAID. (Adjudicated joint safety events are reported in a separate abstract.)
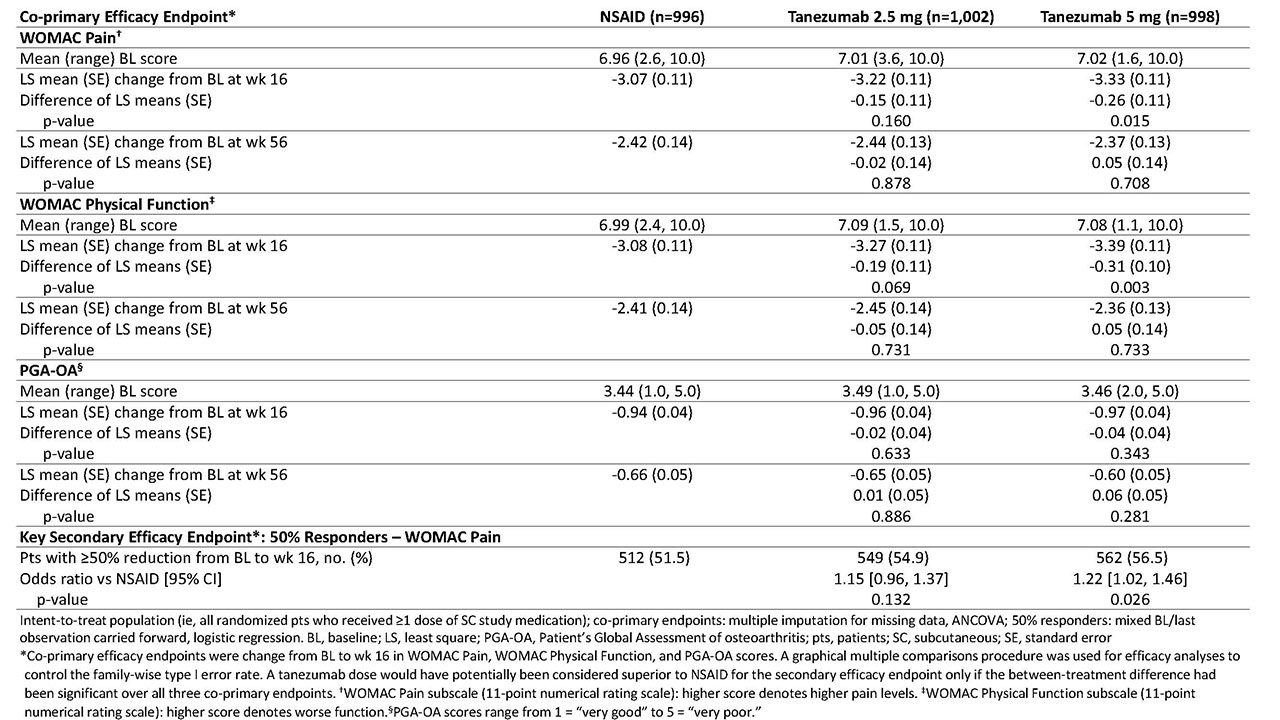
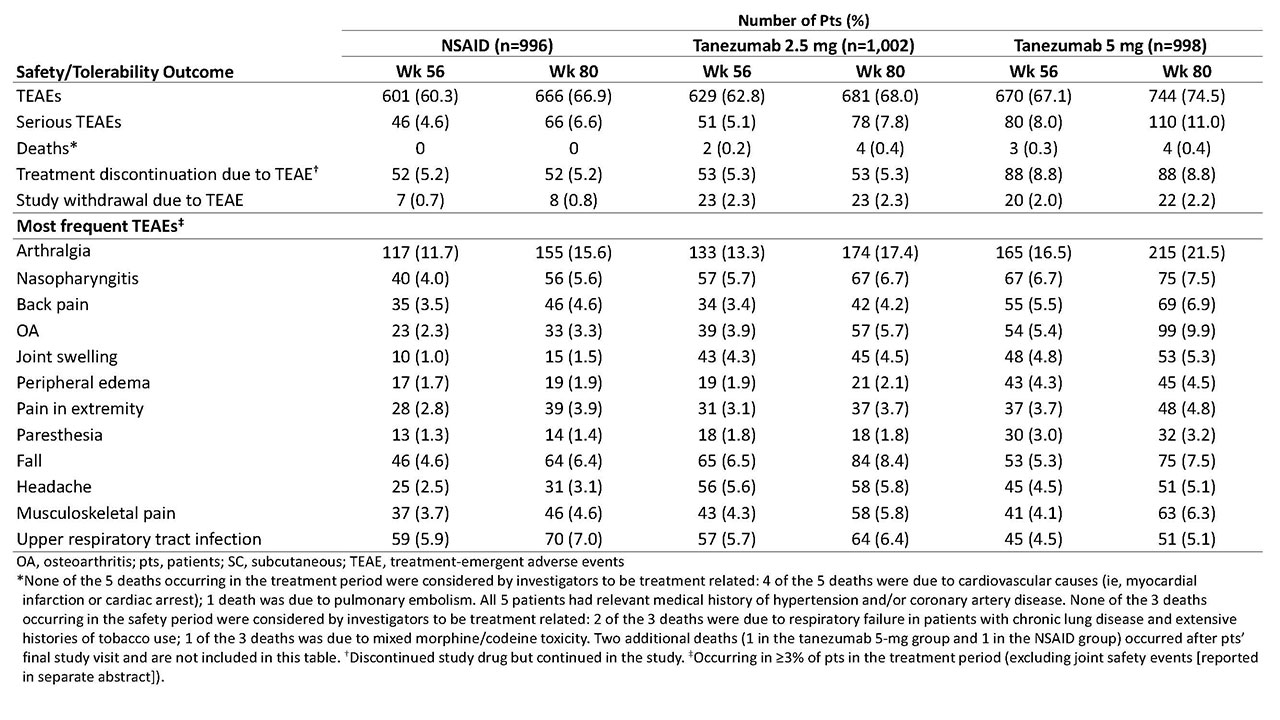
Methods: Eligible pts had hip or knee OA based on ACR criteria with x-ray confirmation; baseline (BL) WOMAC Pain and Physical Function subscale scores of ≥5 (11-pt numerical rating scale); BL Patient’s Global Assessment of OA (PGA-OA) of “fair,” “poor,” or “very poor”; history of inadequate pain relief with acetaminophen; inadequate pain relief with/intolerance to tramadol or an opioid; or unwillingness to take an opioid. Pts were on a stable dose of oral NSAID before study entry and during the 1-mo screening period. Pts were randomized to receive tanezumab (2.5 mg or 5 mg SC every 8 wk) or NSAID (naproxen 500 mg, celecoxib 100 mg, or diclofenac ER 75 mg orally bid) over the 56-wk treatment period. Co-primary efficacy endpoints were change from BL to wk 16 in WOMAC Pain, WOMAC Physical Function, and PGA-OA scores. The key secondary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of pts with ≥50% reduction in WOMAC Pain score at wk 16. Efficacy endpoints were also assessed at wk 56. Safety monitoring included treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) during the 56-wk treatment period and 24-wk safety period.
Results: Of 3,021 randomized pts, 2,996 were included in both the efficacy and safety analyses. A total of 1,312 completed the treatment period (NSAID, n=446 [45%]; tanezumab 2.5 mg, n=447 [45%]; and tanezumab 5 mg, n=419 [42%]) and 2,227 completed the safety period (n=757 [76%]; n=741 [74%]; and n=729 [73%], respectively). At BL, mean age was 60.3-61.2 y; OA duration, 8.5-9.1 y; 64-66% were female; and for 85-86%, the knee was the OA index joint. At wk 16, pts receiving tanezumab 5 mg had statistically significant improvement in WOMAC Pain and WOMAC Physical Function compared with pts receiving NSAID, but not in PGA-OA (Table 1). Improvement in co-primary endpoints with tanezumab 2.5 mg was not significantly different than that with NSAID at wk 16. At wk 56, neither tanezumab dose was significantly different than NSAID. The incidence of TEAEs overall and serious TEAEs was greatest with tanezumab 5 mg and similar between tanezumab 2.5 mg and NSAID (Table 2). Eight deaths occurred in tanezumab-treated pts and none in NSAID-treated pts; the investigators did not consider any deaths to be treatment-related.
Conclusion: In pts with hip or knee OA and moderate-severe pain despite NSAID therapy, pts who switched from NSAID to tanezumab 5 mg SC had greater improvement in OA pain and physical function, but not PGA-OA, at wk 16 than pts who continued NSAID therapy. Differences in efficacy endpoints between tanezumab 2.5 mg SC and NSAID did not reach statistical significance. The general safety/tolerability profile of tanezumab was consistent with that seen in prior tanezumab OA studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hochberg M, Carrino J, Schnitzer T, Guermazi A, Vignon E, Walsh D, White A, Nakajo S, Fountaine R, Hickman A, Pixton G, Viktrup L, Brown M, West C, Verburg K. Subcutaneous Tanezumab vs NSAID for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis: Efficacy and General Safety Results from a Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled, 80-Week, Phase-3 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-tanezumab-vs-nsaid-for-the-treatment-of-osteoarthritis-efficacy-and-general-safety-results-from-a-randomized-double-blind-active-controlled-80-week-phase-3-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-tanezumab-vs-nsaid-for-the-treatment-of-osteoarthritis-efficacy-and-general-safety-results-from-a-randomized-double-blind-active-controlled-80-week-phase-3-study/