Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose : Organ manifestation domain score improvement was assessed with subcutaneous (SC) belimumab (BEL) plus standard SLE care (SoC) in active, autoantibody-positive SLE.
Methods: BLISS-SC (BEL112341; NCT01484496) was a randomized, double-blind, multicenter (177 centers in 30 countries across North, Central and South America, Western and Eastern Europe and Asia) 2-week trial of weekly BEL 200 mg SC or placebo (PBO), plus SoC, in patients with SLE with a SELENA-SLEDAI ≥8 at screening (where randomization to PBO would be to maintain treatment with SoC). The primary endpoint was the SLE Responder Index 4 (SRI4; ≥4-point decrease in SELENA-SLEDAI, <0.3 increase in Physician’s Global Assessment, and no new BILAG A or ≤1 B organ domain scores, from baseline) at Week 52. Efficacy and safety data (including adverse events) have been published1; here, organ-specific responses by BILAG and SELENA-SLEDAI are reported. Analyses included improvements in patients with BILAG baseline A or B scores, measured at each visit (every 4 weeks) between baseline and Week 52 (improvement defined as a shift to B, C, or D; worsening defined as a shift from BILAG E, D, or C to B or A, or from B to A). An increase in total SELENA-SLEDAI domain scores between baseline and Week 52 defined worsening; a decrease defined improvement.
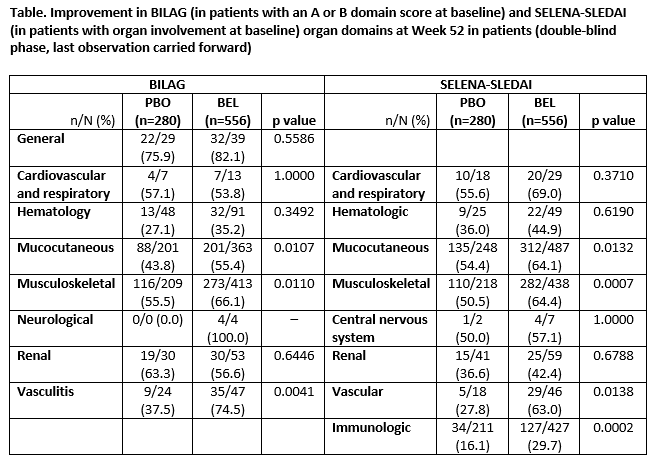
Results: 836 patients comprised the intent-to-treat population. BILAG (Grade A/B) and SELENA-SLEDAI organ system involvement at baseline were similar for both treatment groups, with mucocutaneous and musculoskeletal domains most prominent. The SELENA-SLEDAI immunologic domain was also prominent (not recorded by BILAG).
BEL demonstrated significant improvement versus PBO in the BILAG mucocutaneous, musculoskeletal and vasculitis domains at Week 52 (Table). No statistically significant differences were observed between BEL and PBO for worsening in any BILAG domain. Among patients with baseline SELENA-SLEDAI organ involvement, a statistically significant improvement was observed at Week 52 for BEL versus PBO for the immunologic, mucocutaneous, musculoskeletal, and vascular domains (Table). No statistically significant differences were observed between BEL and PBO for worsening in any SELENA-SLEDAI domain.
Conclusion: Weekly BEL 200 mg SC plus SoC improved organ manifestations in mucocutaneous, musculoskeletal, vascular, and immunologic domains after 52 weeks of therapy, compared with PBO (SoC).
1Stohl W, et al. Arthritis Rheum 2017;69:1016-27
Study funded/conducted by GSK. Medical writing assistance was provided by Louisa Pettinger, PhD, of Fishawack Indicia, funded by GSK.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Doria A, Pobiner B, Eastman W, Kurtinecz M, Hammer A, Groark J, Bass D. Subcutaneous Belimumab Plus Standard of Care Demonstrated Improvement in Multiple Organ Domains Versus Placebo Plus Standard of Care in Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017; 69 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-belimumab-plus-standard-of-care-demonstrated-improvement-in-multiple-organ-domains-versus-placebo-plus-standard-of-care-in-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/. Accessed .« Back to 2017 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/subcutaneous-belimumab-plus-standard-of-care-demonstrated-improvement-in-multiple-organ-domains-versus-placebo-plus-standard-of-care-in-patients-with-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/